Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
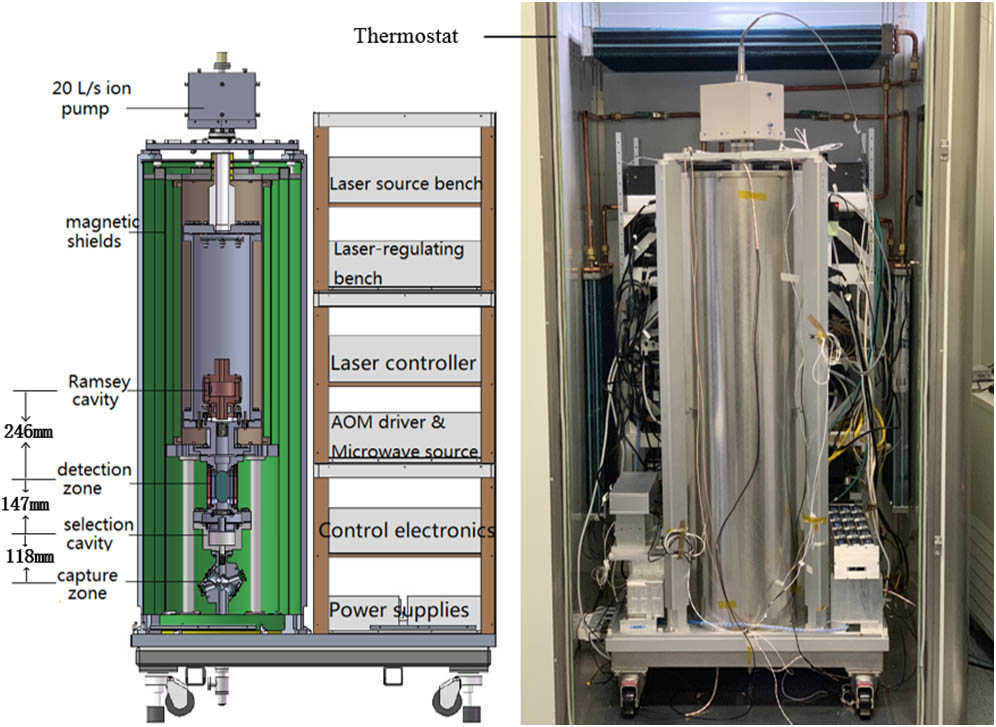
A high-performance transportable fountain clock is attractive for use in laboratories with high-precision time-frequency measurement requirements. This Letter reports the improvement of the stability of a transportable rubidium-87 fountain clock because of an optimization of temperature characteristics. This clock integrates its physical packaging, optical benches, microwave frequency synthesizers, and electronic controls onto an easily movable wheeled plate. Two optical benches with a high-vibration resistance are realized in this work. No additional adjustment is required after moving them several times. The Allan deviation of the fountain clock frequency was measured by comparing it with that of the hydrogen maser. The fountain clock got a short-term stability of at 1 s and long-term stability on the order of 10 16 at 100,000 s.
020.3320 Laser cooling 120.3940 Metrology 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise 270.5570 Quantum detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 080201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Optics, Department of Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 Center for Optics and Optoelectronics Research, College of Science, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, China
For most atom interferometers, the vibration isolation unit is applied to reduce vibration noise. In our experiment, instead of isolation, the vibration signals are monitored, and combining with the sensitive function, the compensation phase shift for the atom interferometer is obtained. We focus on the correction over a wide spectrum rather than on “monochromatic” frequencies. The sensitivity of the atom gravimeter can be upgraded by a factor of more than two. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the atom interferometer can still produce a good measurement result without passive vibration isolation in extremely noisy environments by using vibration compensation.
020.3320 Laser cooling 000.2780 Gravity 270.5570 Quantum detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 070201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Opto-Electronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
The continuous-time quantum walk (CTQW) is the quantum analogue of the continuous-time classical walk and is widely used in universal quantum computations. Here, taking the advantages of the waveguide arrays, we implement large-scale CTQWs on chips. We couple the single-photon source into the middle port of the waveguide arrays and measure the emergent photon number distributions by utilizing the fiber coupling platform. Subsequently, we simulate the photon number distributions of the waveguide arrays by considering the boundary conditions. The boundary conditions are quite necessary in solving the problems of quantum mazes.
270.5570 Quantum detectors 270.0270 Quantum optics Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 052701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Semiconductor Materials Science, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing Key Laboratory of Low Dimensional Semiconductor Materials and Devices, Beijing 100083, China
2 College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
We report on a quantum dot quantum cascade detector (QD-QCD), whose structure is derived from a QD cascade laser. In this structure, more ordered InAs QD layers formed in the Stranski–Krastanow growth mode on a thin GaAs buffer layer are incorporated into the active region. This QD-QCD can operate up to room temperature with a peak detection wavelength of 5.8 μm. A responsivity of 3.1 mA/W at 160 K and a detectivity of 3.6 × 108 Jones at 77 K are obtained. The initial performance of the detector is promising, and, by further optimizing the growth of InAs QDs, integrated QD-quantum cascade laser/QCD applications are expected.
230.5590 Quantum-well, -wire and -dot devices 040.3060 Infrared 040.5570 Quantum detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(10): 102301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Quantum Information and Quantum Optoelectronic Devices of Shaanxi Province, School of Science, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
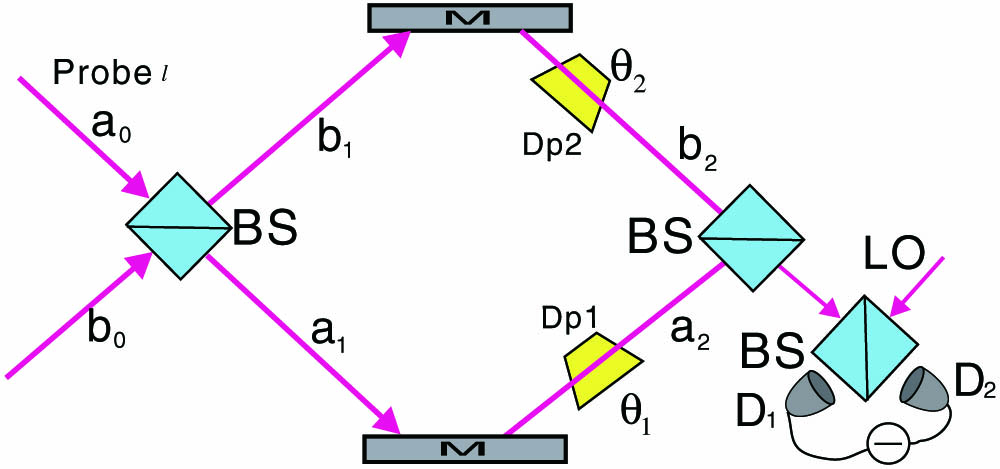
We investigate the sensitivity of the angular rotation measurement with the method of homodyne detection in SU(2) and SU(1,1) interferometers by employing orbital angular momentum (OAM). By combining a coherent beam with a vacuum beam in an SU(2) interferometer, we get the sensitivity of the angular rotation measurement as 12Nl. We can surpass the limit of the angular rotation measurement in an SU(1,1) interferometer by combining a coherent beam with a vacuum beam or a squeezed vacuum beam when the probe beam has OAM. Without injection, the sensitivity can reach 12Nl. In addition, by employing another construction of an SU(1,1) interferometer where the pump beam has OAM, with the same injection of an SU(1,1) interferometer, the sensitivity of the angular rotation measurement can be improved by a factor of 2, reaching 14Nl. The results confirm the potential of this technology for precision measurements in angular rotation measurements.
(040.5570) Quantum detectors (350.5730) Resolution (120.3180) Interferometry. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000617

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Space Object Measurements, Beijing Institute of Tracking and Telecommunications Technology, Beijing 100094, China
2 Research Institute of Superconductor Electronics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
3 Yunnan Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming 650011, China
4 Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
We demonstrate laser-ranging results for non-cooperative targets at ranges of 237 m and 19 km using superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors (SSPD). We upgrade the kilohertz rate laser-ranging system with a newly developed SSPD module, and the equivalent detection diameter is enlarged to 50 μm with a fiber and micro-lenses. Both retroreflectors and non-cooperative surfaces of aluminum foil, a solar panel, and a concrete panel at distances of 237 m and 19 km, whose echoes are of single-photon level, are ranged with sub-centimeter precision. Experimental signal-to-noise ratio curves with the product of quantum efficiency and system transmittance are obtained, which indicates that our system, with an average laser power of 0.8 W and a receiving aperture of 1.2 m, may be capable for space debris ranging at a distance of 800 km. This work suggests that SSPDs have the potential to be used for space debris surveillance.
280.3400 Laser range finder 120.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 040.5570 Quantum detectors 120.1880 Detection Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(7): 071201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices, Institute of Opto-Electronics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
A low-noise photodetector is a basic tool for the research of quantum information processing. We present a specially designed low-noise photoelectric detector with a bandwidth of 130 MHz, using a transimpedance amplification circuit. Based on the detailed calculation of the dependence on each parameter of the detector, a useful method of how to design a low-noise and broadband photodetector is provided. When the optical power is between 1.0 and 16 mW, the photodetector has a good linear response to the injected light. Its electronics noise power is below 77 dBm, which is within the whole bandwidth. When the incident light power is 2 mW, the output noise powers are 10.0, 8.0, and 6.0 dB higher than the corresponding electronics noise within the bandwidth of 1–50, 50–90, and 90–130 MHz, respectively, which is in good agreement with the theoretical prediction. Thus, this photoelectric detector could have good application prospects in quantum communication and an optical cavity locking system.
270.5570 Quantum detectors 270.5585 Quantum information and processing 040.5570 Quantum detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 122701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics and Center for Cold Atom Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Lab of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 e-mail: yshzhang@ustc.edu.cn
4 e-mail: yzgui@siom.ac.cn
Quantum beats can be produced in fourth-order interference such as in a Hong–Ou–Mandel (HOM) interferometer by using photons with different frequencies. Here we present theoretically the appearance of interference of quantum beats when the HOM interferometer is combined with a Franson-type interferometer. This combination can make the interference effect of photons with different colors take place not only within the coherence time of downconverted fields but also in the region beyond that. We expect that it can provide a new method in quantum metrology, as it can realize the measurement of time intervals in three scales.
Coherent optical effects Photon statistics Quantum detectors Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000082
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
The even-order dispersion cancellation effect based on the frequency anti-correlated photon pairs has attracted much attention in the research of quantum dispersion cancellation in two-photon systems. In this letter, we demonstrate a four-photon quantum interferometry in which we can not only observe the even-order dispersion cancellation effect but also the odd-order cancellation. Importantly, the four-photon scheme can get a much better resolution than the two-photon case and help us get a better understanding of the -interference phenomenon in a four-photon interferometry.
270.1670 Coherent optical effects 270.5290 Photon statistics 270.5570 Quantum detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(11): 112701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 Lab of Photonic Information Technology, School for Information and Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
We examine the saturation of relative current gain of In0.53Ga0.47As/InP single photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) operated in Geiger mode. The punch-through voltage and breakdown voltage of the SPADs can be measured using a simple and accurate method. The analysis method is temperature-independent and can be applied to most SPADs.
单光子雪崩二极管 盖革模式 雪崩击穿电压 040.1345 Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) 040.3060 Infrared 040.5160 Photodetectors 040.5570 Quantum detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(1): 010402





