2017, 15(10) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第15卷 第10期
In order to improve the frequency and precision of radiometric calibration, the automated vicarious calibration system (AVCS) is developed and deployed at the Dunhuang test site to perform vicarious calibration without the in situ manned measurements. The surface and atmospheric parameters are automatically collected by AVCS. An absolute radiometric calibration approach based on AVCS is proposed. Six successful calibrations of the Aqua Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) are conducted. The results are in good agreement with the on-board calibration system with all the relative differences less than 4%. It enables us to monitor the change of a sensor over long time scales.
010.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors 120.0280 Remote sensing and sensors We demonstrate an ultralow-noise single-photon detection system based on a sensitive photomultiplier tube (PMT) with precise temperature control, which can capture fast single photons with intervals around 10 ns. By improvement of the electromagnetic shielding and introduction of the self-differencing method, the dark counts (DCs) are cut down to ~ 1 % 20 ° C
030.5260 Photon counting In this Letter, a method based on the effects of imperfect oscillators in lasers is proposed to distinguish targets in continuous wave tracking lidar. This technique is based on the fact that each lidar signal source has a specific influence on the phase noise that makes real targets from the false ones. A simulated signal is produced by complex circuits, modulators, memory, and signal oscillators. For example, a deception laser beam has an unequal and variable phase noise from a real target. Thus, the phase noise of transmitted and received signals does not have the same power levels and patterns. To consider the performance of the suggested method, the probability of detection (P D
030.5630 Radiometry 050.5080 Phase shift 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing Series resistance influence on performance of waveguide-type germanium photodetectors on silicon Download:734次
Download:734次
 Download:734次
Download:734次We investigate influences of series resistances on the performance of 1.55 μm waveguide-type germanium photodetectors (Ge-PDs) on a silicon-on-insulator substrate. The current–voltage characteristics, responsivities, saturation photo-current characteristics, electrical reflection coefficients, and photodetection frequency responses of Ge-PDs, having different series resistances, are measured, and their equivalent circuit models are established. By analyzing the resulting circuit model parameters, we determine how much Ge-PD series resistances influence Ge-PD saturation photo-currents and photodetection bandwidth. These results should be of great use for optimization of Ge-PD fabrication processes and device parameters for target applications.
040.5160 Photodetectors 040.6040 Silicon 060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications This research proposes a simple and practical method to make low-stray-light gratings, where the substrate shifts about a 1 mm distance in the direction parallel or perpendicular to the exposure interference fringes. When the substrate shifts, a reference grating next to the substrate is used to adjust in real time the phase of the exposure interference fringes relative to the substrate. Shifting eliminates the exposure defects and therefore decreases the stray light of gratings. Several gratings are successfully made by using this method, which have straighter grooves, smoother surfaces, and lower stray light than gratings made in conventional interference lithography.
050.1950 Diffraction gratings 050.2770 Gratings 290.2648 Stray light A tunable single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA)-based fiber laser based on a dispersion-shifted fiber (DSF) is proposed and successfully demonstrated. SLM operation is obtained due to the spectral narrowing effect resulting from inverse four-wave mixing in a DSF. A tunable optical filter performs wavelength selection function. By inserting a length of DSF in the laser cavity, SLM lasing can possibly be obtained when laser oscillation is stably established after traveling through the DSF many roundtrips. Stable tunable SLM oscillation with a signal-to-noise ratio as high as 65 dB over a wavelength range of about 35 nm is achieved experimentally, and each spectral linewidth is less than 6.5 kHz.
060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Femtoseconds soliton mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser based on nickel oxide nanoparticle saturable absorber Download:1104次
Download:1104次
 Download:1104次
Download:1104次We demonstrate a femtosecond mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) using a nickel oxide (NiO) as a saturable absorber (SA). NiO nanoparticles are hosted into polyethylene oxide film and attached to fiber ferrule in the laser cavity. The NiO-SA shows a 39% modulation depth with a 0.04 MW / cm 2
060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Photonic generation of radio-frequency (RF) arbitrary microwave waveform with ultra-wide frequency tunable range based on a dispersion compensated optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. Dispersion compensation scheme and specially designed fiber Bragg grating (FBG)-based Fabry–Perot (F-P) filters are employed in the OEO loop to realize a frequency tunable range of 3.5–45.4 GHz. An optimization process provided by the combination of an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) and FBG is employed to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of final RF signals. The generation of linear-frequency and phase-coded microwave waveforms, with a tunable carrier frequency ranging from 4 to 45 GHz and tuned chirping bandwidths or code rates, is experimentally demonstrated.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 350.4010 Microwaves We demonstrate an indoor 5 m free-space optical wireless coherent communication in mid L-band (1606.7 nm) by employing a tunable self-seeded InAs/InGaAlAs/InP quantum-dash (Qdash) laser as a subcarrier generator for 128 Gb/s dual-polarization quadrature phase shift keying (DP-QPSK) modulation signal. The bare Qdash laser diode displays ~ 6 nm ~ 30 dB ~ 10 dBm ~ 10 10 × 128 Gb / s
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 250.5590 Quantum-well, -wire and -dot devices 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers A simple and effective approach is proposed to minimize the effect of unmodulated light and uneven intensity caused by the pixelated structure of the spatial light modulator in a holographic display. A more uniform image is produced by purposely shifting the holographic images of multiple reconstructed lights with different incident angles from the zero-diffraction-order and overlapping those selected different orders. The simulation and optical experimental results show that the influence of the zero-diffraction-order can be reduced, while keeping the good uniformity of the target images by this new approach.
090.1995 Digital holography 070.7345 Wave propagation Simple and effective method to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of compressive imaging Download:929次
Download:929次
 Download:929次
Download:929次This Letter presents a simple and effective method to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of compressing imaging. The main principles of the proposed method are the correlation of the image signals and the randomness of the noise. Multiple low SNR images are reconstructed firstly by the compressed sensing reconstruction algorithm, and then two-dimensional time delay integration technology is adopted to improve the SNR. Results show that the proposed method can improve the SNR performance efficiently and it is easy to apply the algorithm to the real project.
110.1758 Computational imaging 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques Compressed sensing in synthetic aperture photoacoustic tomography based on a linear-array ultrasound transducer Download:1053次
Download:1053次
 Download:1053次
Download:1053次Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) has the unique capability of visualizing optical absorption inside several centimeters-deep biological tissue with a high spatial resolution. However, single linear-array transducer-based PAT suffers from the limited-view challenge, and thus the synthetic aperture configuration is designed that still requires multichannel data acquisition hardware. Herein, a feasible synthetic aperture PAT based on compressed sensing reconstruction is proposed. Both the simulation and experimental results tested the theoretical model and validated that this approach can improve the image resolution and address the limited-view problem while preserving the target information with a fewer number of measurements.
110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Large-range displacement measurement using sinusoidal phase-modulating laser diode interferometer Download:858次
Download:858次
 Download:858次
Download:858次A signal processing method of realizing a large-range displacement measurement in a sinusoidal phase-modulating laser diode interferometer is proposed. The method of obtaining the dynamic value of the effective sinusoidal phase-modulating depth is detailed, and the residual amplitude modulation is also taken into account. Numerical simulations and experiments are carried out to compare this method with the traditional one. We prove that, with this method, the sinusoidal phase-modulating laser diode interferometer can realize a centimeter-level displacement measurement range with high precision, which is much better than the traditional method.
120.3180 Interferometry 070.6020 Continuous optical signal processing Using single wavelength light to improve the synchronization accuracy of the White Rabbit system Download:788次
Download:788次
 Download:788次
Download:788次We demonstrate a new synchronization method for the White Rabbit system. Signals are transmitted in a single mode fiber in both directions with the same light wavelength. Without the complex calibration process of the fiber asymmetry parameter, the new method reduces the effect of chromatic dispersion and improves the synchronization accuracy. The experiment achieves timing synchronization accuracy below 200 ps over 50 km fiber constructed by different companies’ fiber spools. The proposed method would make White Rabbit technology immune to the chromatic dispersion of fiber links and can be applied to long distance synchronization.
120.3930 Metrological instrumentation 120.3940 Metrology 060.4265 Networks, wavelength routing Design of a grating by a joint optimization method for a phase-shifting point diffraction interferometer Download:892次
Download:892次
 Download:892次
Download:892次A grating is an important element of a phase-shifting point diffraction interferometer, and the grating constant and duty cycle have a great impact on the interferometer, so the design of a grating becomes significant. In order to measure the projection objective with a numerical aperture of 0.2, we present a joint optimization method of a pinhole and grating based on scalar diffraction and the finite difference time domain method. The grating constant and the film thickness are selected, and the duty cycle of the grating is optimized. The results show that in the grating processing the material chromium is adopted, the thickness is 200 nm, and the grating constant is 15 μm. When the duty cycle is 55%, the interference fringe contrast is the greatest. The feasibility of the design result is further verified by experiment.
120.3180 Interferometry 120.4640 Optical instruments 260.1960 Diffraction theory Switchable single and double Brillouin multiwavelength and pulsed laser is successfully demonstrated. Brillouin spacing can be switched from single (0.08 nm) to double spacing (0.16 nm) or vice versa by swapping the ports of the coupler in the proposed configuration. The proposed configuration can also be used to produce pulsed laser by inserting a home-made carbon nanotubes saturable absorber into the laser cavity. The proposed system is very versatile and flexible as it can be used as a multiwavelength laser or pulsed laser to cater for different types of applications.
140.3500 Lasers, erbium 290.5900 Scattering, stimulated Brillouin Graphene oxide-COOH as a new saturable absorber for both Q-switching and mode-locking fiber lasers Download:978次
Download:978次
 Download:978次
Download:978次Graphene oxide carboxylic acid (COOH), a novel two-dimensional (2D) layered material with its unique optical and electronic properties, is discovered to exhibit the saturation of optical absorption under laser illumination. Applying the liquid-phase exfoliation method, we prepare graphene oxide-COOH dispersions with deionized water and fabricate graphene oxide-COOH polyvinyl alcohol polymer composite film. We further obtain stable Q-switching pulse and mode-locked laser operation with a 22.7 MHz repetition rate and a 1.5 ps pulse duration by incorporating the graphene oxide-COOH-based saturable absorbers into the all-fiber erbium-doped fiber laser cavity. The experimental results show that the proposed graphene oxide-COOH material can act as an effective absorber for pulsed fiber lasers, which demonstrate potential applications in the area of ultrafast optics.
140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Polarization-independent two-dimensional beam steering using liquid crystal optical phased arrays Download:1198次
Download:1198次
 Download:1198次
Download:1198次A polarization-independent nonmechanical laser beam steering scheme is proposed to realize continuous two-dimensional (2D) scanning with high efficiency, where the core components are two polarization-dependent devices, which are called liquid crystal optical phased arrays (LC-OPAs). These two one-dimensional (1D) devices are orthogonally cascaded to work on the state of azimuthal and elevation steering, respectively. Properties of polarization independence as well as 2D beam steering are mathematically and experimentally verified with a good agreement. Based on the experimental setup, linearly polarized beams with different polarization angles are steered with high accuracy. The measured angular deviations are less than 5 μrad, which is on the same order of the accuracy of the measurement system. This polarization-independent 2D laser beam steering scheme has potential application for nonmechanical laser communication, lidar, and other LC-based systems.
160.3710 Liquid crystals 120.4820 Optical systems 230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices We report on a quantum dot quantum cascade detector (QD-QCD), whose structure is derived from a QD cascade laser. In this structure, more ordered InAs QD layers formed in the Stranski–Krastanow growth mode on a thin GaAs buffer layer are incorporated into the active region. This QD-QCD can operate up to room temperature with a peak detection wavelength of 5.8 μm. A responsivity of 3.1 mA/W at 160 K and a detectivity of 3.6 × 10 8
230.5590 Quantum-well, -wire and -dot devices 040.3060 Infrared 040.5570 Quantum detectors Imaging process and signal-to-noise ratio improvement of enhanced self-heterodyne synthetic aperture imaging ladar Download:816次
Download:816次
 Download:816次
Download:816次This Letter gives the general construction of an enhanced self-heterodyne synthetic aperture imaging ladar (SAIL) system, and proposes the principle of image processing. A point target is reconstructed in the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL as well as in down-looking SAIL experiments, and the achieved imaging resolution of the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL is analyzed. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the point target final image in the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL is higher than that in the down-looking SAIL. The enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL can improve the SNR of the target image in far-distance imaging, with practicality.
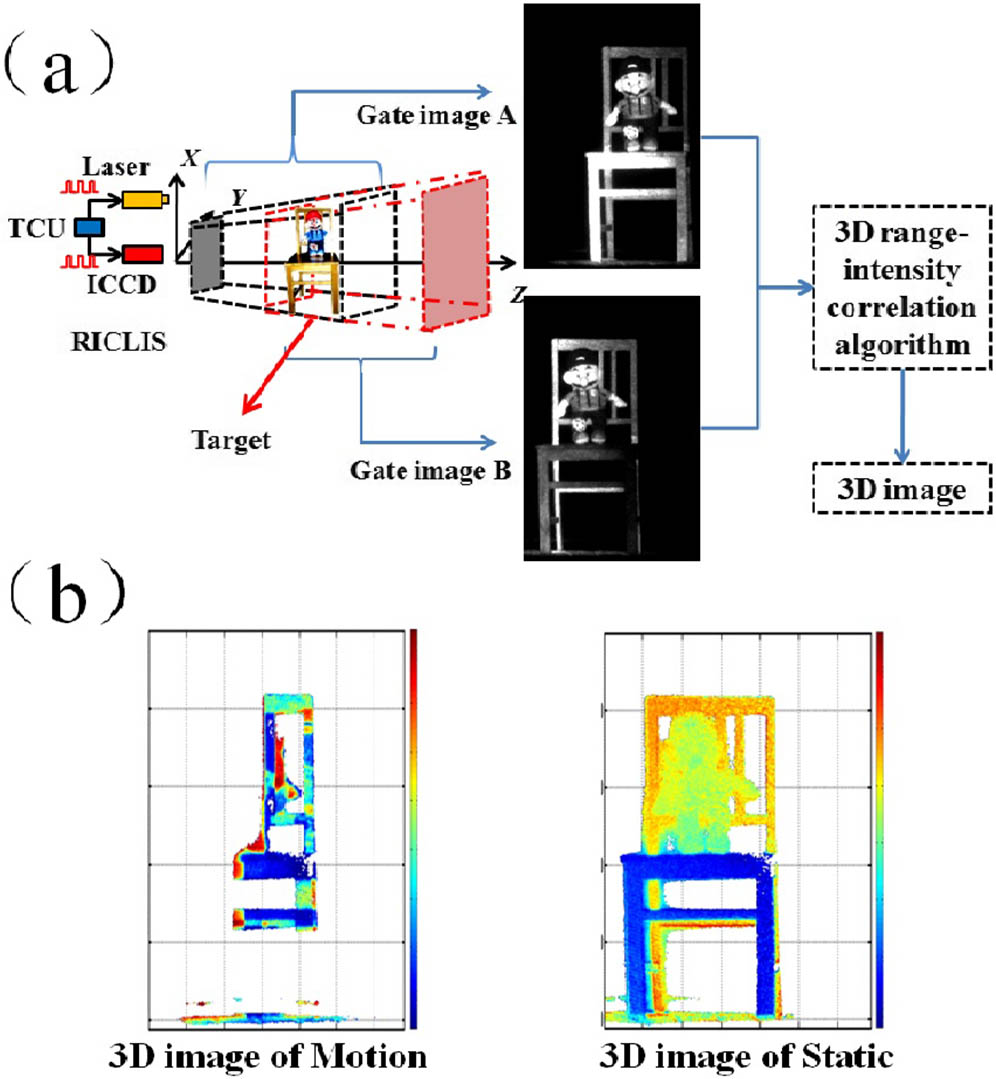
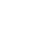
280.3640 Lidar 280.6730 Synthetic aperture radar 100.2000 Digital image processing 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques This Letter proposes a coordinate difference homogenization matching method to solve motion influence in three-dimensional (3D) range-intensity correlation laser imaging. Firstly, features and feature pairs of gate images are obtained by speeded-up robust figures and bi-directional feature matching methods. The original mean value of the feature-pair coordinate differences is calculated. Comparing the coordinate differences with the original mean value, the wrong feature pairs are removed, and then an optimized mean value is updated. The final feature-pair coordinates are re-registered based on the updated mean value. Thus, an accurate transformation is established to rectify motion gate images for 3D reconstruction. In the experiment, a 3D image of a tower at 780 m is successfully captured by our laser gated imaging system on a pan–tilt device.
280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors Aiming to overcome the low converging rate and susceptibility to the environment in focusing the coherent light through the turbid medium, four-element division algorithm (FEDA) optimization is proposed. Full levels of comparisons with the currently employed element-based algorithms, stepwise sequential algorithm (SSA), and continuous sequential algorithm (CSA) show that FEDA only takes one third of the measurement time to find the optimized solution, which means that FEDA is promising in practical applications, such as for deep tissue imaging.
290.0290 Scattering 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦