2016, 4(1) Column
Photonics Research 第4卷 第1期
Resolution enhancement of optical scanning holography with a spiral modulated point spread function Download:1035次
Download:1035次
 Download:1035次
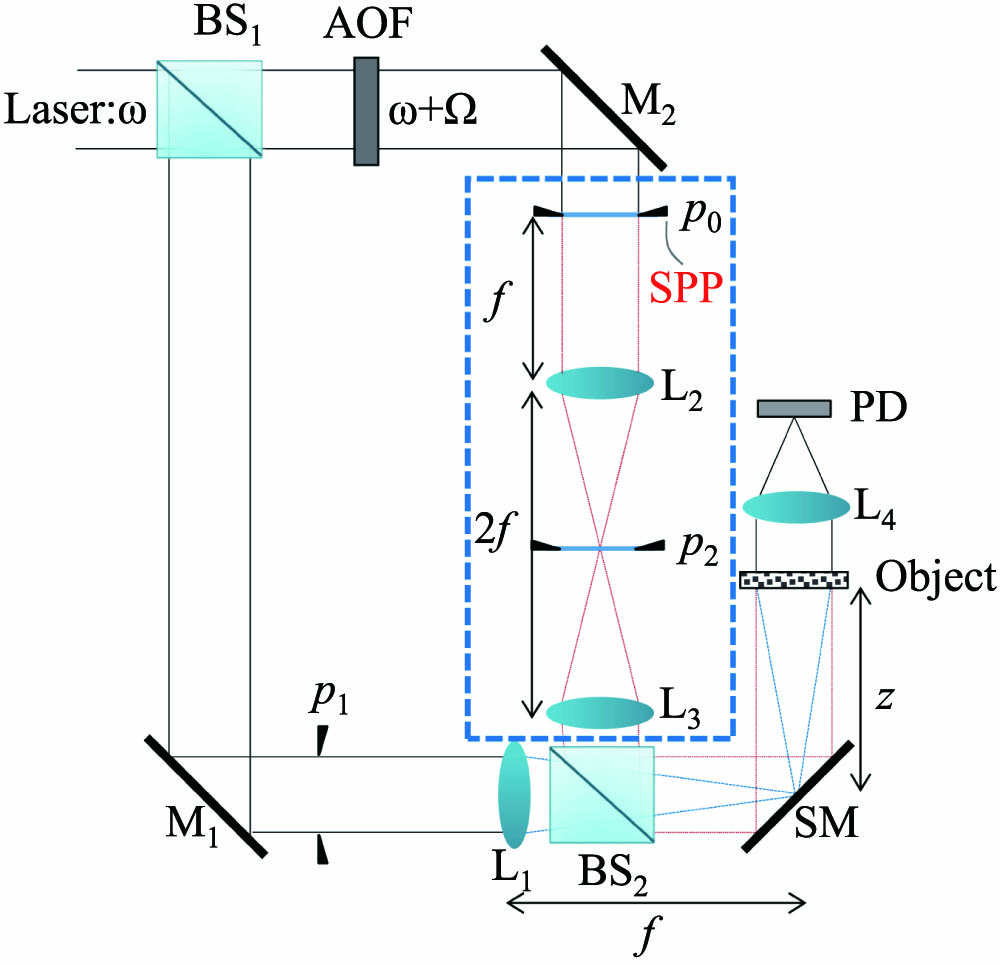
Download:1035次In optical scanning holography, one pupil produces a spherical wave and another produces a plane wave. They interfere with each other and result in a fringe pattern for scanning a three-dimensional object. The resolution of the hologram reconstruction is affected by the point spread function (PSF) of the optical system. In this paper, we modulate the PSF by a spiral phase plate, which significantly enhances the lateral and depth resolution. We explain the theory for such resolution enhancement and show simulation results to verify the efficacy of the approach.
Digital holography Digital holography Computational imaging Computational imaging Optical transfer functions Optical transfer functions We report the observation of electric field induced random lasing in a dye doped liquid crystal system. This was achieved by using a liquid crystal host with negative dielectric anisotropy doped with laser dye PM 597 in a 75 μm cell with a homeotropic alignment layer. In the absence of an applied field, only amplified spontaneous emission was observed since the liquid crystal orientation was uniform. However, application of a field resulted in a fieldinduced planar-like configuration with local nonuniformity in liquid crystal orientation. This led to random lasing in the energized state (voltage greater than a transition threshold). The onset of lasing occurs by application of either a spatially homogenous or a spatially inhomogeneous electric field across the liquid crystal. The characteristics of the emission spectra as a function of different (i) dye concentration and (ii) applied voltage were investigated using nanosecond pulsed laser excitation at 532 nm. The effects of using an inhomogeneous field were compared to the use of a homogenous field and reported. It is shown that the spatial configuration can be used to alter the emission spectra of the system. The work is used to suggest a new configuration, referred to here as “reverse mode,” for liquid crystal-based random lasers. This new configuration may provide additional avenues for their use in commercial devices.
Laser materials Laser materials Liquid crystals Liquid crystals High-precision group-delay dispersion measurements of optical fibers via fingerprint-spectral wavelength-to-time mapping Download:1039次
Download:1039次
 Download:1039次
Download:1039次The group-delay dispersion of an optical fiber was measured with the time-of-flight method, using fingerprint-like characteristic spectra from a mode-locked fiber laser source. To determine the group-delay dispersion up to the fourth order, least-squares fitting was applied to the overall time waveform mapped on the time axis for the fingerprint- spectral broadband pulses through a long optical fiber. The analysis of all 4003 data points reduced statistical uncertainty, and provided second-, third-, and fourth-order dispersion with uncertainties of 0.02%, 0.4%, and 4%, respectively.
Fiber characterization Fiber characterization Dispersion Dispersion Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Probability theory Probability theory stochastic processes stochastic processes and statistics and statistics White-light emission from InGaN/GaN quantum well microrings grown by selective area epitaxy Download:691次
Download:691次
 Download:691次
Download:691次Monolithic white-light-emitting diodes (white LEDs) without phosphors are demonstrated using InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells (MQWs) grown on GaN microrings formed by selective area epitaxy on SiO2 mask patterns. The microring structure is composed of {1-101} semi-polar facets and a (0001) c-plane, attributed to favorable surface polarity and surface energy. The white light is realized by combining short and long wavelengths of electroluminescence emissions from InGaN/GaN MQWs on the {1-101} semi-polar facets and the (0001) c-plane, respectively. The change in the emission wavelengths from each microfacet is due to the In composition variations of the MQWs. These results suggest that white emission can possibly be obtained without using phosphors by combining emission light from microstructures.
Light-emitting diodes Light-emitting diodes Quantum-well Quantum-well -wire and -dot devices -wire and -dot devices We experimentally demonstrate a 4 × 4 nonblocking silicon thermo-optic (TO) switch fabric consisting of three stages of tunable generalized Mach–Zehnder interferometers. All 24 routing states for nonblocking switching are characterized. The device’s footprint is 4.6 mm × 1.0 mm. Measurements show that the worst cross talk of all switching states is ?7.2 dB. The on-chip insertion loss is in the range of 3.7–13.1 dB. The average TO switching power consumption is 104.8 mW.
Integrated optics Integrated optics Integrated optics devices Integrated optics devices Optical switching devices Optical switching devices We report on a compact passive mode-locked Er:fiber ring laser operated at the fundamental repetition rate of 517 MHz, which we believe is the highest fundamental repetition rate ever reported in a ring cavity fiber laser. The key technique is the employment of two innovative high-power wavelength domain multiplexer collimators with all gain fiber cavity suited for the high power (up to 2 W) pumping. The laser is featured with a direct chirpfree output pulse, which is 97 fs without extracavity compression at an average output power of 90 mW.
Ultrafast lasers Ultrafast lasers Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Photonics Research Editor-in-Chief Zhiping (James) Zhou and Deputy Editor Michael Fiddy report on the status of the journal as the fourth volume begins.
Announcements Announcements awards awards news news and organizational activities and organizational activities Physics literature and publications Physics literature and publications 公告
动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-25
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 2): 封面|超紧凑片上偏振控制器动态信息 丨 2024-04-11
PR Highlight (Vol. 11, Iss. 12): 亮点 | 十亿像素级、高通量的无透镜偏振编码叠层成像技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 3): 封面 | 基于时空编码神经网络的像差感知超分辨成像动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 1) 光涡旋与手性器件微纳3D打印动态信息 丨 2024-03-14
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 1): 同步双脉冲激光烧蚀中的气泡相互作用效应激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦