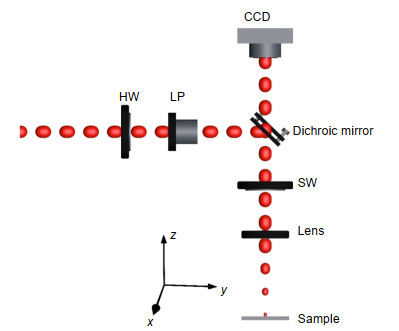
Omnidirectional iridescence via cylindrically-polarized femtosecond laser processing
Nikolaos Livakas, Evangelos Skoulas, Emmanuel Stratakis. Omnidirectional iridescence via cylindrically-polarized femtosecond laser processing[J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2020, 3(5): 05190035.
[2] C S S R Kumar. Biomimetic and Bioinspired Nanomaterials. Wiley, Weinheim, 2010.
[4] E G Loewen, E Popov. Diffraction Gratings and Applications. M. Dekker, New York, 1997.
[6] N P Mahalik. Micromanufacturing and nanotechnology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2006.
[44] Hecht E.
[45] Palmer C.
Nikolaos Livakas, Evangelos Skoulas, Emmanuel Stratakis. Omnidirectional iridescence via cylindrically-polarized femtosecond laser processing[J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2020, 3(5): 05190035.