1 上海理工大学光电信息与计算机工程学院,上海 200093
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所微纳光电子功能材料实验室,上海 201800
相变材料具备良好的光热稳定性和可擦写特征,其在相变前后存在光学参数的明显变化,通过施加不同参数的激光激励能够实现对相变材料晶化状态的精确调控。由此,在相变材料不同晶化状态呈现不同光学参数的基础上,提出一种多阶折射率调制的薄膜平板透镜。以典型相变材料Ge2Sb2Te5作为光调制介质,对介质薄膜的晶化状态开展多阶和多区域的离散控制以满足理论上聚焦透镜所需的相位约束。完成具有多种数值孔径的平板透镜的设计,并通过有限差分时域方法和Zemax分别分析透镜聚焦的参数指标,检验了平板透镜的成像性能。
材料 光存储材料 衍射透镜 折射率 相位 光学学报
2022, 42(19): 1916002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory for Micro/Nano Optoelectronic Devices of Ministry of Education & Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Structural Physics and Devices, School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
In this Letter, a photonic crystal (PC) flat lens with a scatterer-size gradient is proposed, which simultaneously achieves imaging of the point source and sub-wavelength focusing of the plane wave in the first, second, and fifth bands. The imaging of the point source breaks through the diffraction limit in the second and fifth bands. The PC flat lens with the scatterer-size gradient is expected to be used in a new multifunctional optical imaging and focusing device, which improves the application potential of a PC flat lens.
050.1965 Diffractive lenses 050.5298 Photonic crystals 050.6624 Subwavelength structures Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 080501
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
设计出不同相移步长的多焦点光子筛阵列,利用相移数字全息术对USAF1951分辨率板进行成像,在光学波段验证了光子筛阵列的相移功能。实验结果表明,多焦点光子筛阵列在不同相移步长下均可消除零级像和共轭像,系统分辨率均与理论预期结果一致。作为一种振幅型衍射透镜,多焦点光子筛阵列在X射线全息术和生物细胞显微等领域有着广阔的应用前景。
全息 数字全息 相移 衍射透镜 X射线成像

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
The full aperture complex amplitude transmittance function of a multi-level diffraction lens with mask-alignment errors was derived based on scalar diffraction theory. The point spread function (PSF) was calculated by the Kirchhoff diffraction integral. It is found that the radius of the Airy disk increases with the increase of the error in the direction of misalignment, and the image center shifts along the direction of misalignment. A four-level diffractive lens with a diameter of 80 mm was fabricated, and its PSF and diffraction efficiency of +1st order were calculated and measured. The distribution of PSF is consistent with the calculated results, and the tested diffraction efficiency is slightly smaller than the calculated value; the relative error is 5.71%.
050.1380 Binary optics 050.1965 Diffractive lenses 110.3000 Image quality assessment Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(9): 090501
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, China
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
3 School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
We propose axial line-focused spiral zone plates (ALFSZPs) for generating tightly focused X-ray vortex beams with ultra-long depth of focus (DOF) along the propagation direction. In this typical design, compared with the conventional spiral zone plates (SZPs) under the same numerical aperture (NA), the DOF of ALFSZPs has been extended to an ultra-length by optimizing the corresponding parameters. Besides, it also exhibits lower side lobes and smaller dark cores in the whole focus volume. The diameters of dark cores increase as the topological charge value increases.
050.1220 Apertures 050.1940 Diffraction 050.1965 Diffractive lenses Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(8): 080501

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing Engineering Research Center for Mixed Reality and Advanced Display, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Beijing Key Laboratory for Metamaterials and Devices, Key Laboratory of Terahertz Optoelectronics, Ministry of Education, and Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Imaging Technology, Department of Physics, Capital Normal University, Beijing 100048, China
3 Micro and Nanotechnology Research Center, School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
4 e-mail: yzhang@mail.cnu.edu.cn
Metasurfaces have become a new photonic structure for providing potential applications to develop integrated devices with small thickness, because they can introduce an abrupt phase change by arrays of scatterers. To be applied more widely, active metasurface devices are highly desired. Here, a tunable terahertz meta-lens whose focal length is able to be electrically tuned by ~4.45λ is demonstrated experimentally. The lens consists of a metallic metasurface and a monolayer graphene. Due to the dependence of the abrupt phase change of the metasurface on the graphene chemical potential, which can be modulated using an applied gate voltage, the focal length is changed from 10.46 to 12.24 mm when the gate voltage increases from 0 to 2.0 V. Experimental results are in good agreement with the theoretical hypothesis. This type of electrically controlled meta-lens could widen the application of terahertz technology.
Terahertz imaging Phase modulation Metamaterials Modulators Diffractive lenses Photonics Research
2018, 6(7): 07000703

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Physics Department, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai 200237, China
2 ECE Department, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong 999077, China
3 College of Information Science and Technology, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
4 E-mail: amwtam@ust.hk
A liquid crystal Pancharatnam–Berry (PB) axilens is proposed and fabricated via a digital micro-mirror-device-based photo-patterning system. The polarization-dependent device behaves as an axilens for a left-handed circularly polarized incident beam, for which an optical ring is focused with a long focal depth in the transverse direction at the output, and an anti-axilens for a right-handed circularly polarized incident beam, for which an optical ring gradually expands at the output. The modification of the size and the sharpness of the diffracted ring beam is demonstrated by encoding a positive (negative) PB lens term into the director expression of a PB (anti-)axicon.
230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices 160.3710 Liquid crystals 050.1965 Diffractive lenses 230.3120 Integrated optics devices Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(6): 062301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, China
2 Hefei Meiya Optoelectronic Technology Inc., Hefei 230088, China
We design a new kind of phase zone plates (PZPs) to improve the diffraction efficiency of soft x ray zone plates (ZPs). The design replaces blank parts of PZPs with metals of negative phase shift at the working energy, which is called as the positive and negative PZPs (PNPZPs). According to the calculation, PNPZPs have a higher maximum efficiency than conventional ZPs with the same zone width. With the help of a negative phase coefficient, it is much easier to achieve a π phase shift in one period, resulting in a smaller zone height. This design can help fabricate finer PZPs to achieve a better image resolution.
050.1965 Diffractive lenses 050.1970 Diffractive optics Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 020501
在飞秒激光随机扫描双光子显微成像系统中使用宽带二维声光偏转器扫描飞秒激光, 可以增大扫描角度至74 mrad, 增大双光子显微成像范围。但宽带二维声光偏转器在大角度扫描时引入的色散较大, 造成成像范围边缘的光斑严重畸变, 边缘光斑直径达2.3 μm, 影响边缘视场的成像质量。为了提高成像质量, 设计了一种新的色散补偿方法, 基于衍射透镜组成的开普勒望远系统, 可以同时补偿不同扫描角度的不同色散。经过色散补偿后成像边缘的光斑直径小于1 μm, 使系统获得大范围扫描成像的同时, 所有扫描角度的色散都能够得到很好的补偿, 在整个视场范围内光斑直径小于1 μm, 实现更均匀的荧光激发, 均匀成像。
双光子荧光显微成像 声光偏转器 色散补偿 随机扫描 衍射透镜 two-photon fluorescence microscopy acousto-optic deflector dispersion compensation random-access laser scanning diffractive lenses Zemax Zemax
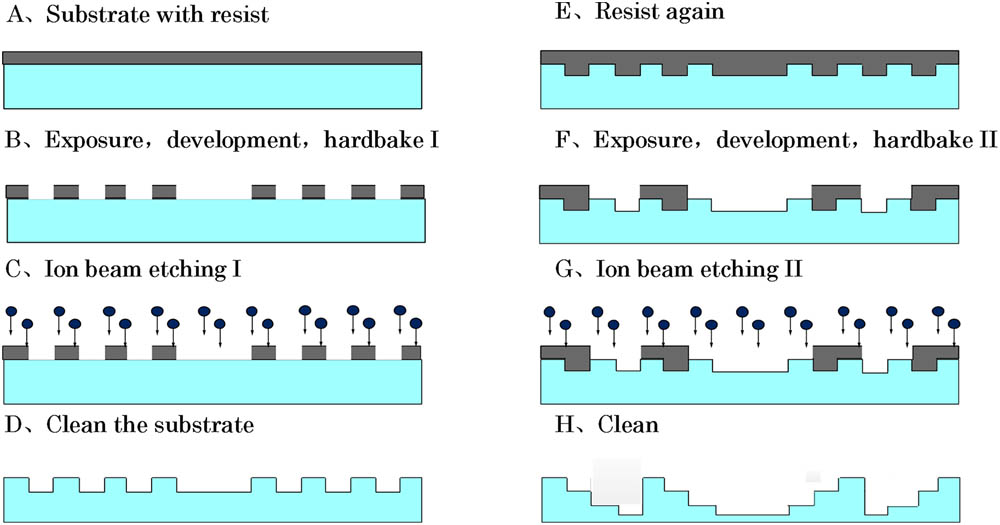
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optical System Advanced Manufacturing Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
The demand for space-borne telescopes with an aperture of 20 m is forcing the development of large diameter diffractive Fresnel zone lenses (FZLs) on membranes. However, due to the fabrication errors of multi-level microstructures, the real diffraction efficiency is always significantly smaller than the theoretical value. In this Letter, the effects of a set of fabrication errors on the diffraction efficiency for a diffractive membrane are studied. In order to verify the proposed models, a 4-level membrane FZL with a diameter of 320 mm is fabricated. The fabrication errors of the membrane FZL are measured, and its diffraction efficiency in the +1 order is also tested. The results show that the tested diffraction efficiency is very close to the calculated value based on the proposed models. It is expected that the present work could play a theoretical guiding role in the future development of space-borne diffractive telescopes.
050.1965 Diffractive lenses 160.5470 Polymers 120.4610 Optical fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 120501





