Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
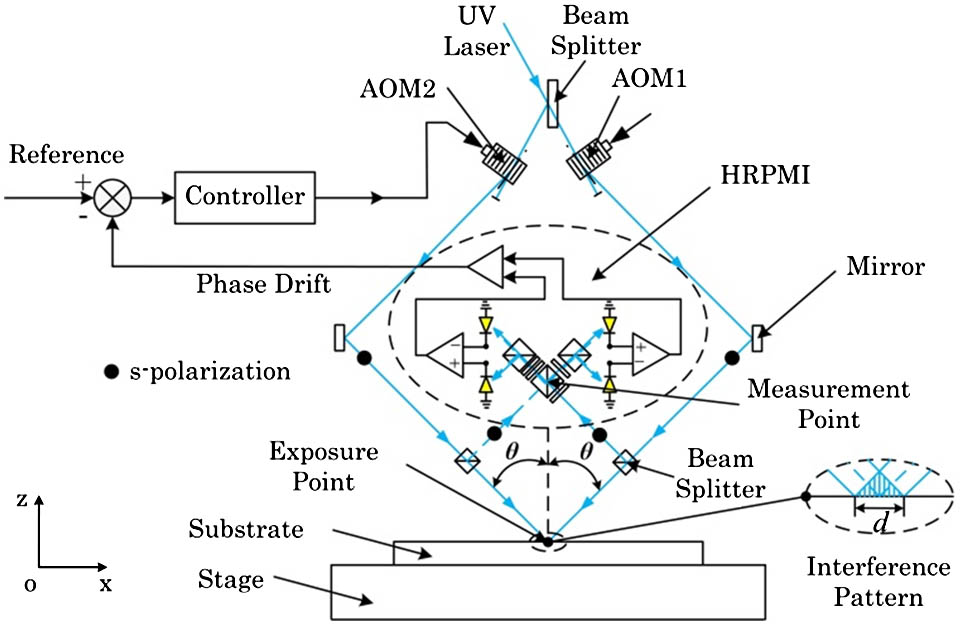
We present a novel homodyne frequency-shifting interference pattern locking system to enhance the exposure contrast of interference lithography and scanning beam interference lithography (SBIL). The novel interference pattern locking system employs a special homodyne redundant phase measurement interferometer (HRPMI) as the sensor and an acousto-opto modulator (AOM) as the actuator. The HRPMI offers the highly accurate value as well as the direction recognition of the interference pattern drift from four quadrature interference signals. The AOM provides a very fine resolution with a high speed for phase modulation. A compact and concise system with a short optical path can be achieved with this new scheme and a small power laser head in tens of microwatts is sufficient for exposure and phase locking, which results in a relatively low-cost system compared with the heterodyne system. More importantly, the accuracy of the system is at a high level as well as having robustness to environmental fluctuation. The experiment results show that the short-time (4 s) accuracy of the system is ±0.0481 rad(3σ) at present. Moreover, the phase of the interference pattern can also be set arbitrarily to any value with a high accuracy in a relatively large range, which indicates that the system can also be extended to the SBIL application.
000.2170 Equipment and techniques 050.1950 Diffraction gratings 120.3180 Interferometry 220.3740 Lithography Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(6): 061201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
A novel large-stage atomic force microscope (AFM) for nondestructive characterization of optical thin films is built. An open sample stage and a probe unit are employed to measure samples with large size and weight. Three optical thin films with large areas are imaged using this AFM without needing to cut the pieces apart. Experimental results show that the maximum scanning range for one single image can reach 20×20 (μm) while keeping a high resolution laterally and vertically. The maximum possible size of a sample is 600×1000 (mm). The new AFM is capable of performing wide-range and high-resolution characterizations of large samples such as large-area optical thin films.
大面积 光学薄膜 原子力显微镜 大扫描范围 无损表征 180.5810 Scanning microscopy 120.6650 Surface measurements, figure 000.2170 Equipment and techniques Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(s1): 111
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 2300312
2 Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049
A new polarization lidar has been developed for detecting depolarization characteristics of aerosol and cirrus over Hefei (31.90N, 117.16E), China. The fundamental principle of polarization lidar is briefly introduced. Overall structure and specifications of the polarization lidar, as well as measurement method, are described. The observational results of depolarization ratio for cirrus over Hefei from February to May in 2005-2007 are presented and discussed. The exploring temperatures by radiosonde during the spring of 2005 are also presented and analyzed. The results show that the cirrus generally presents in the altitude from 7 to 12 km, and the depolarization ratio varies from 0.2 to 0.5. At the meanwhile, depolarization ratio appears a climbing tendency with the increasing height and the decreasing temperature.
大气光学 偏振激光雷达 卷云 退偏振比 000.2170 Equipment and techniques 010.1290 Atmospheric optics 280.3640 Lidar Chinese Optics Letters
2008, 6(4): 235
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute for Applied Optics, 2-5-5-1 Tomioka, Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-0047, Japan
2 Department of Physics, School of Science, Tokai University, 1117 Kitakaname, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa 259-1292, Japan
We demonstrated the measurements of attenuation constant of a multi-mode fiber with 300-micron core diameter and 1-km length at 1070 nm. The observed attenuation constant was below 0.7 dB/km, the laser power of 5 kW was coupled into the 1-km fiber at 1070 nm, and the overall transmittance was 85%, and the first Raman Stokes signal was observed in the transmitted laser spectrum. We demonstrated concrete cutting with a 4-kW fiber laser at 1070 nm. The slab thickness was 100 mm. This technique can be extended to thick concrete slabs more than 1 m without increasing laser power.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 000.2170 Equipment and techniques Chinese Optics Letters
2007, 5(s1): 39
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Semiconductor Materials Science, Institute of Semiconductor, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100083
The principle of step-scan Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is introduced. Double modulation step-scan FTIR technique is used to obtain the quantum cascade laser's stacked emission spectra in the time domain. Optical property and thermal accumulation of devices due to large drive current are analyzed.
000.2170 equipment and techniques 060.4080 modulation 230.3990 microstructure devices 300.6360 spectroscopy laser Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(10): 10603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laboratory for Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Center for Cold Atom Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800
A new method of frequency-shifting for a diode laser is realized. Using a sample-and-hold circuit, the error signal can be held by the circuit during frequency shifting. It can avoid the restraint of locking or even lock-losing caused by the servo circuit when we input a step-up voltage into piezoelectric transition (PZT) to achieve laser frequency-shifting.
000.2170 equipment and techniques 140.0140 lasers and laser optics 300.6260 spectroscopy diode lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(9): 09524
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices, Institute of Opto-Electronics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006
Using lock-in amplifer and proportional, integral, and derivative (PID) electric circuit, the frequency of diode laser is stabilized on a highly mechanical stable Fabry-Perot (FP) cavity transmission peak. When the frequency locking system is on, the frequency tunable range of the laser is about 4 GHz around the D1 transition of Rb. The laser frequency tuning is implemented by scanning the FP cavity length. The fluctuation of frequency of the output laser is less than 1 MHz, and the drift of the center frequency is less than 1.5 MHz in 1.5 min. This system has great potential of the application in the experimental investigation of the interaction between light and atoms, especially, for the case of far off the atomic resonance.
000.2170 equipment and techniques 140.5960 semiconductor lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2004, 2(12): 12710





