1 北京交通大学电子信息工程学院通信与信息系统北京市重点实验室,北京 100044
2 武汉长盈通光电技术股份有限公司,湖北 武汉 430074
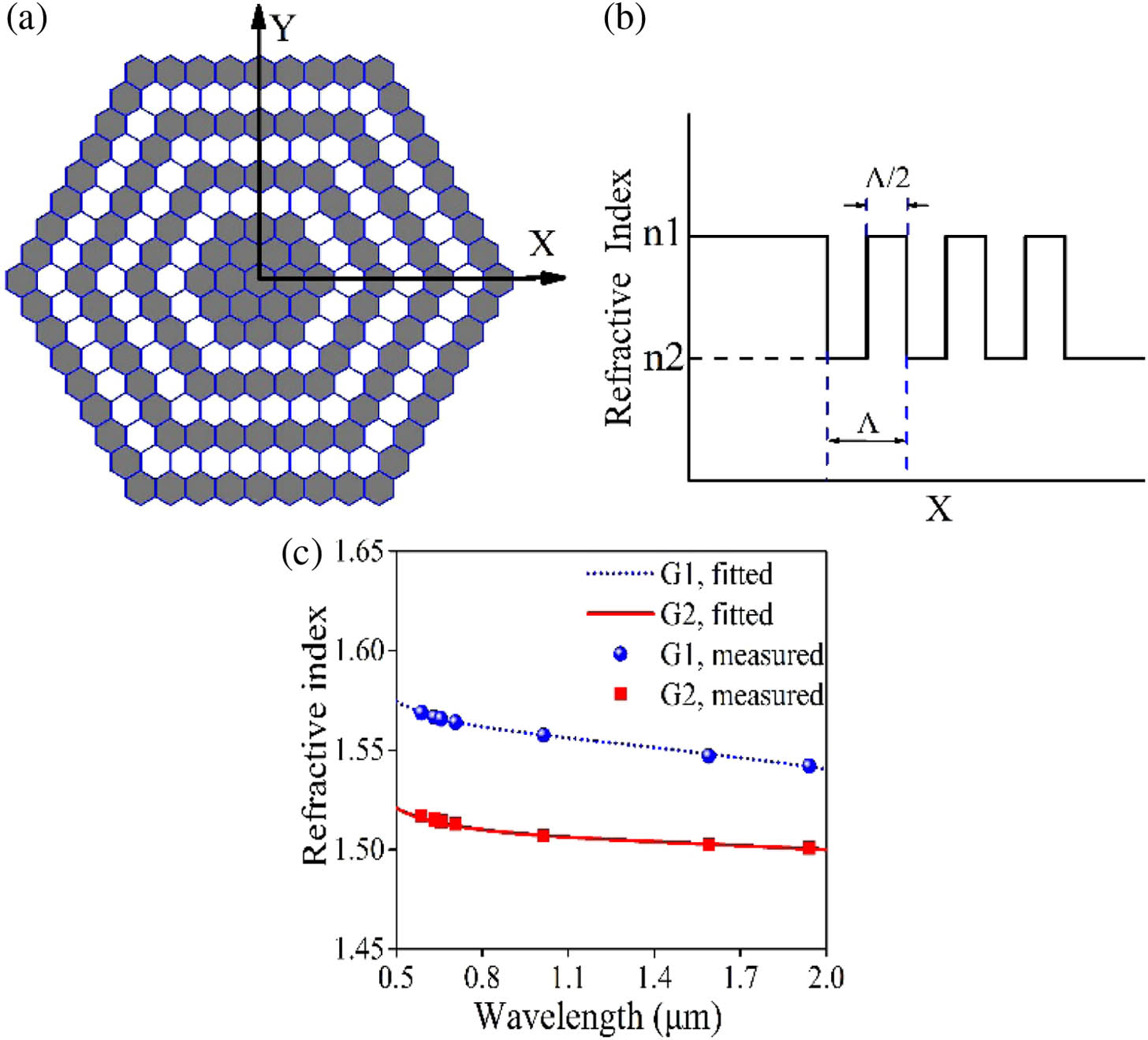
空芯微结构光纤的弯曲损耗是决定其能否真正应用到光纤陀螺中的一个核心指标。设计并成功拉制出一款具有超低弯曲损耗的19芯空芯光子带隙光纤,通过与拉制的具有相近纤芯直径的空芯反谐振光纤进行对比,详细探究了空芯微结构光纤弯曲损耗的产生机理,证明了空芯光子带隙光纤具有更优异的抗弯曲特性。使用对称缠绕法,在0.25 cm的极限弯曲半径下,实验测量得到的空芯光子带隙光纤的弯曲损耗为每圈3.63×10-3 dB @1624 nm,这是目前实验报道的空芯微结构光纤在最小弯曲半径下的最低弯曲损耗。面向光纤陀螺的应用需求,首次实验研究了在不同张力下空芯光子带隙光纤敏感环的插入损耗的变化情况。研究结果显示,随着绕制张力的增加,环体插入损耗显著增加,因此宜在小张力条件下进行空芯光子带隙光纤敏感环的绕制。研究成果对空芯微结构光纤在光纤陀螺领域的实用化进程有着重要的推进作用。
光纤光学 光纤设计与制作 光纤测量 光纤传感 光纤陀螺
1 华中科技大学武汉国家光电研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
2 武汉长进激光技术有限公司,湖北 武汉 430206
为了提升铒镱共掺光纤的抗辐照性能,以适用于远距离太空通信应用,采用改进的化学气相沉积(MCVD)方法制备了抗辐照铒镱共掺光纤。在常温下使用Co60辐射源对自研铒镱共掺光纤进行剂量为300 Gy和1000 Gy、平均剂量率为0.2 Gy/s的辐照。在940 nm和1550 nm处,该光纤在300 Gy辐照剂量下的辐致吸收(RIA)分别为0.10 dB/m和0.19 dB/m,在1000 Gy辐照剂量下的RIA分别为0.46 dB/m和0.37 dB/m。搭建了铒镱共掺光纤放大器(EYDFA)进行增益测试,采用输入功率为40 mW的1550 nm信号与940 nm的泵浦源,泵浦功率为7.3 W时其辐致增益变化(RIGV)分别为0.2 dB(300 Gy)和0.7 dB(1000 Gy)。
光纤光学 铒镱共掺光纤设计与制备 抗辐照性能 光纤通信 铒镱共掺光纤放大器 中国激光
2022, 49(22): 2215001
1 山东富通光导科技有限公司,山东 济南 250119
2 成都富通光通信技术有限公司,四川 成都 611731
3 上海大学特种光纤与光接入网省部共建国家重点实验室培育基地/特种光纤与先进通信国际合作联合实验室,上海 200444
采用一种具有中心凹陷的三角芯+环型的折射率剖面设计,利用外部气相沉积(OVD)工艺制备了新型非零色散位移G.655.D光纤。实验结果表明:在1550 nm和1625 nm波长处,光纤的衰减值分别为0.195 dB/km和0.203 dB/km,截止波长为1200 nm;将光纤绕在半径为25 mm的圆柱体上100圈,此时其在1550 nm和1625 nm波长处的宏弯损耗值分别低于0.027 dB和0.045 dB;该光纤在1530~1625 nm波段的色散为1.6~9.5 ps/(nm·km),尤其是在1550 nm波长处,其有效面积达到72 μm2,比常规G.653光纤大1.4倍。通过这种设计和方法制备的光纤可以实现零色散波长的平移,获得良好的纵向色散均匀性、较低的弯曲损耗以及较大的有效面积,适用于1530~1625 nm波段的密集波分复用应用,在长距离光纤通信中对四波混频(FWM)、交叉相位调制(XPM)等非线性效应具有较好的抑制作用,可以减少色散管理成本,具有非常重要的应用价值。
光纤光学 外部气相沉积工艺 G.655.D光纤 大有效面积 非零色散位移 密集波分复用 光纤设计与制造 中国激光
2022, 49(23): 2306004
山东大学 信息科学与工程学院 山东省激光技术与应用重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266200
晶体光纤是一种新型的高性能光纤材料,具有稀土离子掺杂浓度高、传光性好、耐高温、耐腐蚀等优点.晶体光纤在激光及传感方面具有巨大的应用潜力,然而至今还没有成功制备出真正意义上的同时具有晶体纤芯和晶体包层的小芯径晶体光纤.与传统的玻璃光纤相比,晶体光纤的制备工艺更加复杂,如何对晶体光纤制备工艺进行完善和创新是当前需要解决的重要问题.为了探索提高晶体光纤质量的途径,本文以晶体光纤的四种制备技术为主线,回顾了晶体光纤及其制备方法的发展历程,讨论了每种制备方法的局限性,对晶体光纤目前的应用状况进行了总结,并对其未来发展趋势进行了展望.
光纤材料 晶体光纤 光纤设计与制造 激光加热基座法 微下拉法 无粘合剂键合法 熔融芯法 Fiber materials Crystal fiber Fiber design and fabrication Laser heated pedestal growth Micro-pulling-down Adhesive-free bonding Molten core 光子学报
2019, 48(11): 1148003
1 武汉长盈通光电技术有限公司, 湖北 武汉 430205
2 北京交通大学电子信息工程学院, 北京 100044
光纤作为光信息和光能量的传输元器件已成为基础建设不可或缺的组成部分。针对功能光纤进行概括性介绍。着重介绍了微结构光纤的导光机理以及制备方案。微结构光纤由于其实现了灵活的预制棒制备方式、空芯传输以及理论上的超低衰耗,广泛地应用于光电传感和激光器应用。未来光纤发展的趋势将是光、电功能集成于一根光纤中,详细介绍了纳米机械光纤的制备和潜在应用,为全光器件和光集成技术发展提供重要的研究方向。
光纤光学 光纤设计与制造 微结构光纤 光子晶体光纤 光微机电器件 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(17): 170615
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A large-mode-area neodymium-doped silicate photonic bandgap fiber was theoretically designed and experimentally demonstrated. The relative index step between the high-index rods and the background glass was ~0.5%, which is the lowest cladding index difference reported on rare-earth-doped all-solid photonic bandgap fibers to our knowledge. An output power of 3.6 W with a slope efficiency of 31% was obtained for a 100-cm-long fiber.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.3510 Lasers, fiber 060.5295 Photonic crystal fibers Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(8): 080601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
4 School of Electronic Science & Applied Physics, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
High flatness, wide bandwidth, and high-coherence properties of supercontinuum (SC) generation in fibers are crucial in many applications. It is challenging to achieve SC spectra in a combination of the properties, since special dispersion profiles are required, especially when pump pulses with duration over 100 fs are employed. We propose an all-solid microstructured fiber composed only of hexagonal glass elements. The optimized fiber possesses an ultraflat all-normal dispersion profile, covering a wide wavelength interval of approximately 1.55 μm. An SC spectrum spanning from approximately 1030 to 2030 nm (corresponding to nearly one octave) with flatness <3 dB is numerically generated in the fiber with 200 fs pump pulses at 1.55 μm. The results indicate that the broadband ultraflat SC sources can be all-fiber and miniaturized due to commercially achievable 200-fs fiber lasers. Moreover, the SC pulses feature high coherence and a single pulse in the time domain, which can be compressed to 13.9-fs pulses with high quality even for simple linear chirp compensation. The Fourier-limited pulse duration of the spectrum is 3.19 fs, corresponding to only 0.62 optical cycles.
Fiber design and fabrication Photonic crystal fibers Nonlinear optics, fibers Pulse compression Femtosecond phenomena Supercontinuum generation Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Next Generation Internet Access National Engineering Laboratory (NGIA), School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1037 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Institute of Physics and Applied Physics, Yonsei University, Seoul 120-749, South Korea
3 School of EEE, Nanyang Technological University, 50 Nanyang Avenue, Singapore 639798, Singapore
We propose a novel waveguide design of a polarization-maintaining few mode fiber (PM-FMF) supporting ≥10 non-degenerate modes, utilizing a central circular air hole and a circumjacent elliptical-ring core. The structure endows a new degree of freedom to adjust the birefringence of all the guided modes, including the fundamental polarization mode. Numerical simulations demonstrate that, by optimizing the air hole and elliptical-ring core, a PM-FMF supporting 10 distinctive polarization modes has been achieved, and the effective index difference Δneff between the adjacent guided modes could be kept larger than 1.32×10 4 over the whole C+L band. The proposed fiber structure can be flexibly tailored to support an even larger number of modes in PM-FMF (14-mode PM-FMF has been demonstrated as an example), which can be readily applicable to a scalable mode division multiplexing system.
Fibers, polarization-maintaining Fiber properties Fiber design and fabrication Fiber optics communications Photonics Research
2017, 5(3): 03000261
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light, Staudtstr. 2, D-91058 Erlangen, Germany
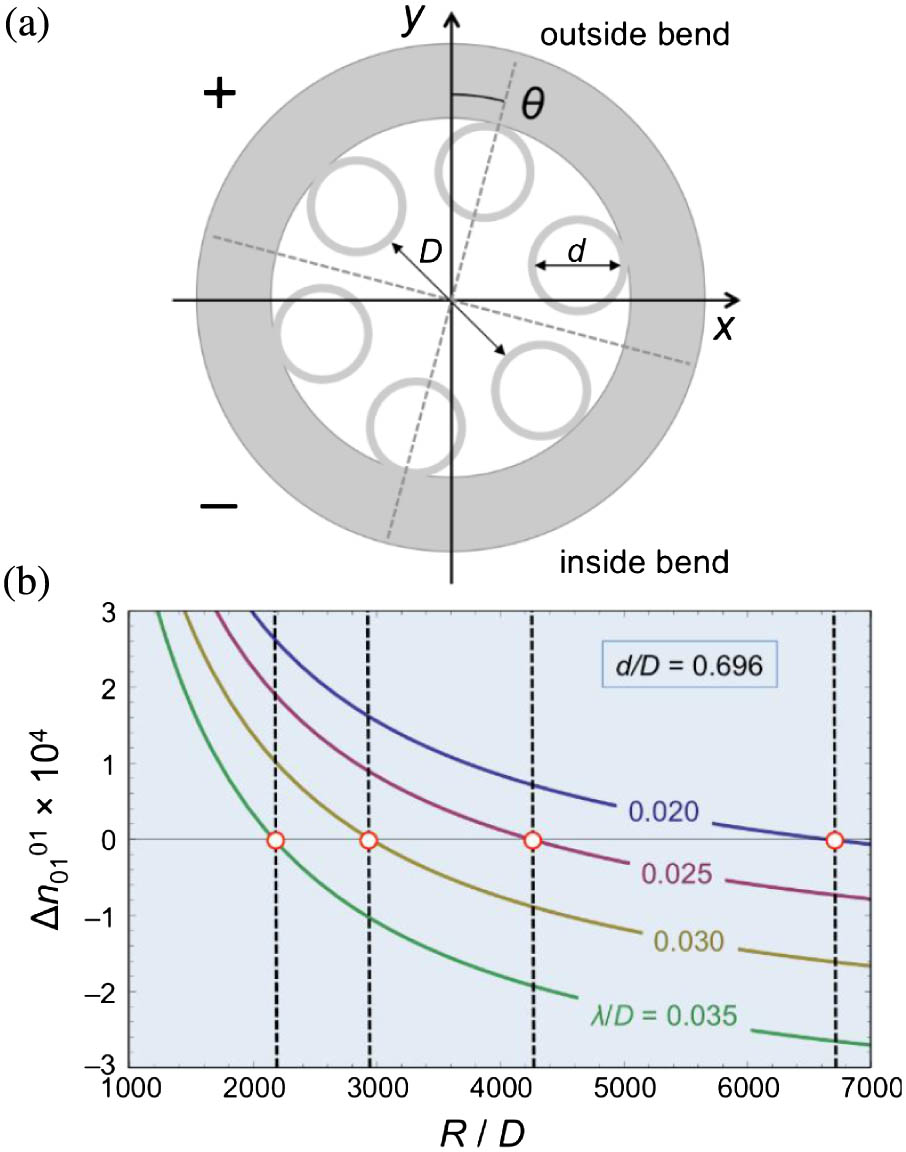
Understanding bend loss in single-ring hollow-core photonic crystal fibers (PCFs) is becoming of increasing importance as the fibers enter practical applications. While purely numerical approaches are useful, there is a need for a simpler analytical formalism that provides physical insight and can be directly used in the design of PCFs with low bend loss. We show theoretically and experimentally that a wavelength-dependent critical bend radius exists below which the bend loss reaches a maximum, and that this can be calculated from the structural parameters of a fiber using a simple analytical formula. This allows straightforward design of single-ring PCFs that are bend-insensitive for specified ranges of bend radius and wavelength. It also can be used to derive an expression for the bend radius that yields optimal higher-order mode suppression for a given fiber structure.
Fiber design and fabrication Fiber optics Microstructured fibers Photonic crystal fibers Photonics Research
2017, 5(2): 02000088

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Vibration and Noise Control Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
3 School of Optoelectronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
We propose a temperature-insensitive refractive index (RI) fiber sensor based on a Mach–Zehnder interferometer. The sensor with high sensitivity and a robust structure is fabricated by splicing a short photonic crystal fiber (PCF) between two single-mode fibers, where two microcavities are formed at both junctions because of the collapse of the PCF air holes. The microcavity with a larger equatorial dimension can excite higher-order cladding modes, so the sensor presents a high RI sensitivity, which can reach 244.16 nm/RIU in the RI range of 1.333–1.3778. Meanwhile it has a low temperature sensitivity of 0.005 nm/°C in the range of 33°C–360°C.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 020603





