
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Instituto de Bioingeniería, Universidad Miguel Hernández, Elche 03202, Spain
2 Departamento de Física Aplicada, Universidad Miguel Hernández, Elche 03202, Spain
3 Departamento de Ciencia de Materiales, Óptica y Tec. Electrónica, Universidad Miguel Hernández, Elche 03202, Spain
In this work, we compare different methods for implementing a triplicator, a phase grating that generates three equi-intense diffraction orders. The design with optimal efficiency features a continuous phase profile, which cannot be easily reproduced, and is typically affected by quantization. We compare its performance with binary and sinusoidal phase profiles. We also analyze the effect of quantizing the phase levels. Finally, a random approach is adopted to eliminate the additional harmonic orders. In all cases, a liquid-crystal-on-silicon spatial light modulator is employed to experimentally verify and compare the different approaches.
diffraction gratings phase modulation triplicator spatial light modulators Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(2): 020501

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 School of Physics, University of the Witwatersrand, Wits, South Africa
Spatial light modulators, as dynamic flat-panel optical devices, have witnessed rapid development over the past two decades, concomitant with the advancements in micro- and opto-electronic integration technology. In particular, liquid-crystal spatial light modulator (LC-SLM) technologies have been regarded as versatile tools for generating arbitrary optical fields and tailoring all degrees of freedom beyond just phase and amplitude. These devices have gained significant interest in the nascent field of structured light in space and time, facilitated by their ease of use and real-time light manipulation, fueling both fundamental research and practical applications. Here we provide an overview of the key working principles of LC-SLMs and review the significant progress made to date in their deployment for various applications, covering topics as diverse as beam shaping and steering, holography, optical trapping and tweezers, measurement, wavefront coding, optical vortex, and quantum optics. Finally, we conclude with an outlook on the potential opportunities and technical challenges in this rapidly developing field.
liquid crystal spatial light modulators liquid crystal devices structured light holography applications Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(8): 230026
光子学报
2021, 50(11): 1123001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Biomedical Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong, N.T., Hong Kong, China
There is an ongoing technological revolution in the field of biomedical instruments. Consequently, high performance healthcare devices have led to remarkable economic developments in the medical hardware industry. Until now, nearly all optical bio-imaging systems are based on the 2-dimensional imaging chip architecture. In fact, recent developments in digital micromirror devices (DMDs) are gradually making their way from conventional optical projection displays into biomedical instruments. As an ultrahigh-speed spatial light modulator, the DMD may offer a range of new applications including real-time biomedical sensing or imaging, as well as orientation tracking and targeted screening. Given its short history, the use of DMD in biomedical and healthcare instruments has emerged only within the past decade. In this paper, we first provide an overview by summarizing all reported cases found in the literature. We then critically analyze the general pros and cons of using DMD, specifically in terms of response speed, stability, accuracy, repeatability, robustness, and degree of automation, in relation to the performance outcome of the designated instrument. Particularly, we shall focus our discussion on the use of Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS)-based devices in a set of representative instruments including the surface plasmon resonance biosensor, optical microscopes, Raman spectrometers, ophthalmoscopes, and the micro stereolithographic system. Finally, the prospects of using the DMD approach in biomedical or healthcare systems and possible next generation DMD-based biomedical devices are presented.
DMD MEMS micromirrors spatial light modulators biomedical instruments Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2020, 13(6): 2030011
华中科技大学 材料科学与工程学院 连接与电子封装中心, 武汉 430074
提出了一种扫描白光干涉法, 用于获取LCOS芯片的相位调制特性曲线并对其进行相位校准, 而且实现了对LCOS芯片建立的相位光栅的像素级相位分析.将补偿玻璃平板紧贴于参考镜处, 克服了白光短相干长度的限制, 提高了干涉条纹间的对比度.利用Morlet小波变换法求取白光干涉信号包络曲线的峰值点进行相位值重构, 实现了0.01π的相位测量精度, 同时保证了横向分辨率为0.79 μm.利用Logistics函数对相位调制幅度为2π的二元光栅相位轮廓进行拟合, 得到其相位回程区宽度为11.49 μm.小像素LCOS芯片构建的闪耀光栅存在相位线性增长区和相位回程区.周期为40 μm的闪耀光栅相位回程区宽度为8.81 μm, 其衍射效率为71.9%.对不同周期的闪耀光栅的相位轮廓进行分析, 结果表明:闪耀光栅的周期越小, 相位回程区相对宽度越大, 衍射效率降低.
空间光调制器 相位调制 衍射光栅 干涉仪 条纹分析 Spatial light modulators Phase modulation Diffraction gratings Interferometry Fringe analysis

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
2 Institute of Systems Engineering, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621000, China
The phase modulation characteristics of a reflective liquid crystal (LC) spatial light modulator (SLM) under oblique incidence are studied by using our proposed self-interference method. The experimental setup of the method is very simple and has good robustness to mechanical vibrations. By changing the gray value of the combined grayscale loaded on the LC-SLM, different sheared fringe patterns, generated by the interference between the constant phase-modulated beam and the +1-order diffracted beam of the blazed grating, can be obtained. The amount of phase modulation of the LC-SLM is obtained by subtracting the phase of the two side lobes in the frequency domain. By turning the turntable where the SLM is mounted, the phase modulation characteristics at different incident angles can be measured. The experimental results show that the phase modulation curves do not change significantly with the small angle. When the angle is large (i.e. larger than 10°), the phase modulation curves become different, especially for the high gray levels. With the increase of the incident angle, the phase modulation depth is reduced. The results indicate that the incident angle plays an important role in the performance of the phase modulation of an LC-SLM.
070.6120 Spatial light modulators 120.5060 Phase modulation 120.5050 Phase measurement Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(9): 090701
1 深圳大学电子科学与技术学院, 广东 深圳 518060
2 深圳大学微纳光电子技术研究所, 广东 深圳 518060
为进一步缩小光学相关器体积,设计了一种折反式2f系统光学相关器,光路采用折叠反射式结构,用数字微透镜取代传统相关器中的实体透镜,缩减了结构体积,提升了系统集成度。利用等效光路法对其进行理论分析,给出了折反式2f相关器的结构设计条件及结构参数。针对该相关器,设计了与之匹配的综合鉴别函数滤波器,利用自编程序进行模拟仿真分析。结果显示,当待识别目标发生缩放与旋转畸变时, 该相关器仍具有较好的畸变不变识别性能。
信号处理 相关器 集成光学器件 空间滤波 空间光调制器
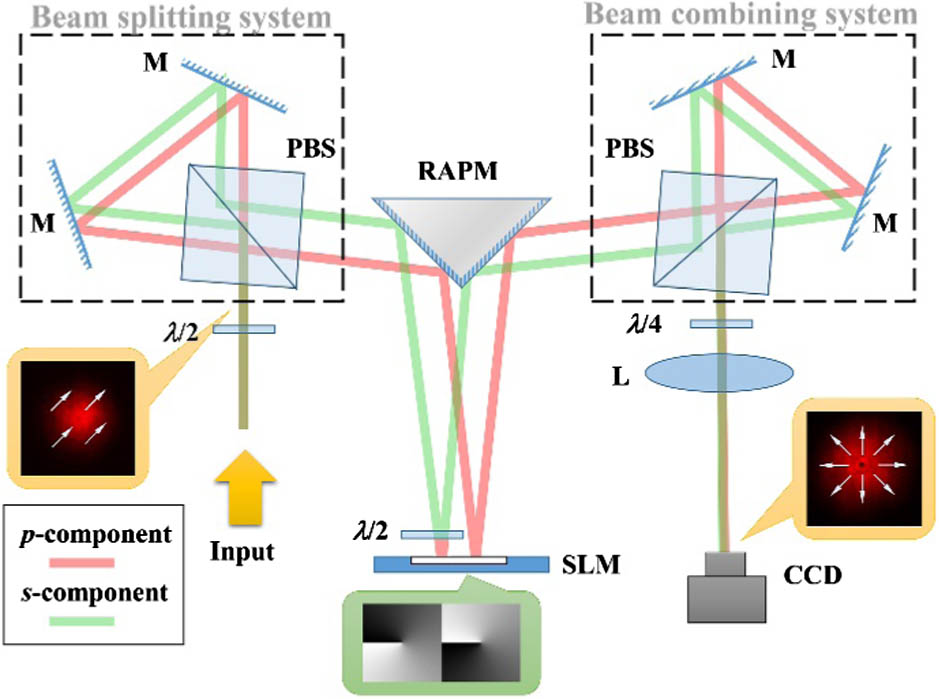
Author Affiliations
Abstract
MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, School of Science, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710129, China
We propose an efficient and robust method to generate tunable vector beams by employing a single phase-type spatial light modulator (SLM). With this method, a linearly polarized Gaussian beam can be converted into a vector beam with arbitrarily controllable polarization state, phase, and amplitude. The energy loss during the conversion is greatly reduced and depends mainly on the reflectivity of the SLM. We experimentally demonstrate that conversion efficiency of about 47% is achieved by using an SLM with reflectivity of 62%. Several typical vector beams, including cylindrical vector beams, vector beams on higher order Poincaré spheres, and arbitrary vector beams attached with phases and with tunable amplitude, are generated and verified experimentally. This method is also expected to create high-power vector beams and play important roles in optical fabrication and light trapping.
Polarization Singular optics Spatial light modulators Photonics Research
2018, 6(4): 04000228

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, College of Physics Science and Technology, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
In the process of high-harmonic generation with a Laguerre-Gaussian (LG) mode, it was well established that the topological charge could be of an N-fold increase due to angular momentum conservation. Here, by mimicking the effect of high-harmonic generation, we devise a simple algorithm to generate optical vortex arrays carrying arbitrary topological charges with a single phase-only spatial light modulator. By initially preparing a coaxial superposition of suitable low-order LG modes, we demonstrate experimentally that the topological charges of the embedded vortices can be multiplied and transformed into arbitrarily high orders on demand, while the array structure remains unchanged. Our algorithm offers a concise way to efficiently manipulate the structured light beams and holds promise in optical micromanipulation and remote sensing.
050.4865 Optical vortices 070.6120 Spatial light modulators 140.3300 Laser beam shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(3): 030501





