1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所 高功率激光单元技术实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
采用高温熔融法制备百分比为(100-x)(23.6Al2O3-53CaO-7.7BaO-2.1Na2O-10.3Ga2O3-3.1B2O-0.2Er2O3)-xYb2O3(x=0,0.9,1.9,2.8,3.6,4.5)的铝酸盐玻璃。应用差示扫描量热法、吸收光谱、荧光光谱、红外光谱以及拉曼光谱等检测手段, 系统研究了不同Yb3+离子引入量对玻璃的物性、热稳定性、Er3+离子光谱性质和结构的影响。结果表明,Yb2O3含量越高, 玻璃的密度和折射率越大, 抗析晶能力有所增强。随着Yb2O3的增加, 玻璃在976 nm吸收系数增大, 对应于Er3+离子的2H11/2→4I15/2、4S3/2→4I15/2以及4F9/2→4I15/2跃迁的527, 549, 666 nm的上转换发光、红光与绿光发光强度比以及对应于4I13/2→4I15/2的1.53 μm近红外荧光强度明显增加。当Yb2O3浓度为3.6%时, 铝酸盐玻璃样品在近红外1.53 μm荧光最强, 此时Yb3+→Er3+正向能量传递效率η1最大, 约为82.9 %。该系列铝酸盐玻璃中Er3+离子1.53 μm最大发射截面为0.77×10-20 cm2, 荧光半高宽最大值为39.4 nm, 荧光寿命最大值为4.46 ms。
铝酸盐玻璃 Yb3+/Er3+共掺杂 上转换发光 1.53 μm发光 aluminate glass Yb3+/Er3+ co-doping up-conversion emission 1.53 μm emission
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Laser Fusion Research Center, Chinese Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, Sichuan 621900, China
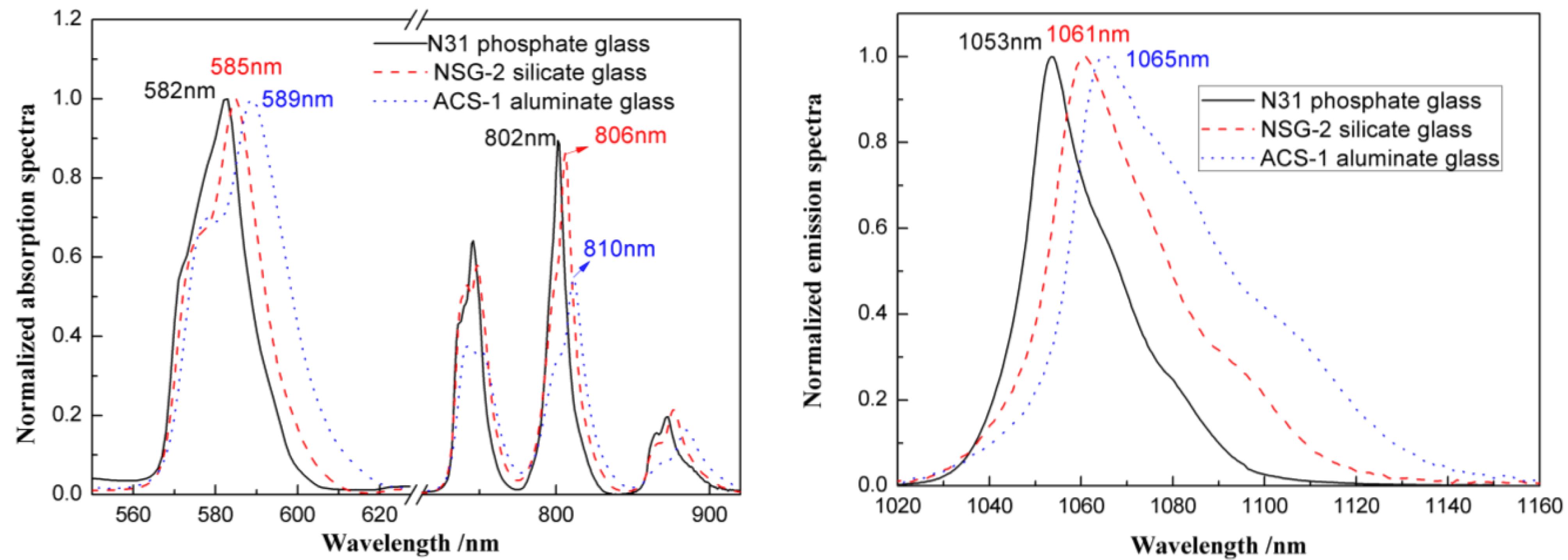
This work presents a brief introduction on three kinds of newly developed $\text{Nd}^{3+}$-doped laser glasses in Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM), China. Two $\text{Nd}^{3+}$-doped phosphate glasses with lower thermal expansion coefficient and thermal shock resistance 4 times higher than that of N31 glass are developed for laser processing. Nd:Silicate and Nd:Aluminate glasses with peak emission wavelength at 1061 and 1065 nm, effective emission bandwidth of 34 and 50 nm, respectively, are developed for Exawatt-class laser system application. Fluorophosphate glasses with low nonlinear refractive index ($n_{2}=0.6{-}0.86$) and long fluorescence lifetime ($430{-}510~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{s}$) are investigated for the purpose of decreasing B integral in high-power laser system. The properties of all these glasses are presented and compared with those of commercial neodymium laser glasses.
aluminate glass fluorophosphate glass high-power laser neodymium laser glass phosphate glass silicate glass High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2017, 5(1): 010000e1





