
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Peking University, School of Electronics, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Beijing, China
2 University of California, Santa Barbara, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Santa Barbara, California, United States
3 Peking University, School of Physics, State Key Laboratory for Artificial Microstructure and Mesoscopic Physics, Beijing, China
4 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen, China
5 Peking University, Frontiers Science Center for Nano-Optoelectronics, Beijing, China
Microcombs are revolutionizing optoelectronics by providing parallel, mutually coherent wavelength channels for time-frequency metrology and information processing. To implement this essential function in integrated photonic systems, it is desirable to drive microcombs directly with an on-chip laser in a simple and flexible way. However, two major difficulties have prevented this goal: (1) generating mode-locked comb states usually requires a significant amount of pump power and (2) the requirement to align laser and resonator frequency significantly complicates operation and limits the tunability of the comb lines. Here, we address these problems by using microresonators on an AlGaAs on-insulator platform to generate dark-pulse microcombs. This highly nonlinear platform dramatically relaxes fabrication requirements and leads to a record-low pump power of <1 mW for coherent comb generation. Dark-pulse microcombs facilitated by thermally controlled avoided mode crossings are accessed by direct distributed feedback laser pumping. Without any feedback or control circuitries, the comb shows good coherence and stability. With around 150 mW on-chip power, this approach also leads to an unprecedentedly wide tuning range of over one free spectral range (97.5 GHz). Our work provides a route to realize power-efficient, simple, and reconfigurable microcombs that can be seamlessly integrated with a wide range of photonic systems.
dark-pulse microcomb direct pumping scheme widely tunable source Advanced Photonics
2023, 5(3): 036007
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 GoLP/Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, 1049-001 Lisboa, Portugal
2 Central Laser Facility, Science and Technology Facilities Council, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot OX11 0QX, UK
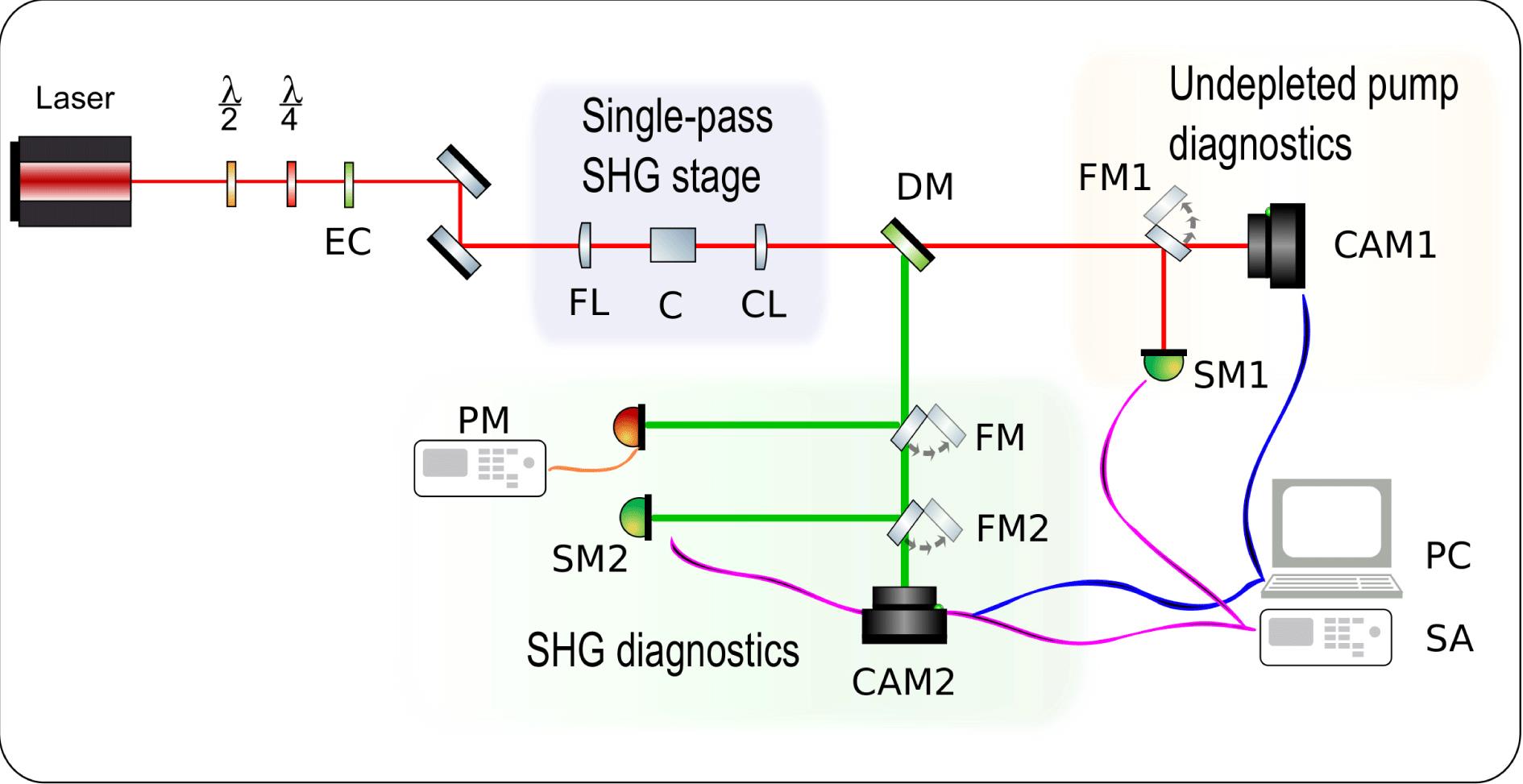
We demonstrate high efficiency second harmonic generation (SHG) of near infrared femtosecond pulses using a $\text{BiB}_{3}\text{O}_{6}$ crystal in a single-pass tight focusing geometry setup. A frequency doubling efficiency of $63\%$ is achieved, which is, to the best of our knowledge, the highest value ever reported in the femtosecond regime for such low energy (nJ-level) pumping pulses. Theoretical analyses of the pumping scheme focusing waist and the SHG efficiency are performed, by numerically solving the three wave mixing coupled equations in the plane-wave scenario and by running simulations with a commercial full 3D code. Simulations show a good agreement with the experimental data regarding both the efficiency and the pulse spectral profile. The simulated SHG pulse temporal profile presents the characteristic features of the group velocity mismatch broadening in a ‘thick’ crystal.
nonlinear process second harmonic generation pumping scheme parametric amplification/oscillators high power laser High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2019, 7(1): 01000e11
1 中国科学院物理研究所光物理实验室, 北京 100190
2 北京理工大学光电学院, 北京 100081
如何有效地减少抽运过程和激光发射过程中激光介质内产生的热量, 是全固态高功率激光研究过程中所面临的主要难题之一。与传统波长的抽运方式相比, 采用长波长的直接抽运技术不但可使激光介质中产生的热量减少30%~50%, 而且还可显著改善激光的输出特性。以最常用的Nd3+激光器的研究作为切入点, 简述了直接抽运技术的研究发展, 介绍了直接抽运技术相对于传统抽运技术的优缺点以及目前的研究现状, 最后对未来的发展前景作了初步分析和展望。
全固态激光技术 直接抽运 四能级激光运转 准三能级激光运转
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
2 烽火通信科技股份有限公司, 武汉 430079
采用两个中心波长约976 nm准直输出的高功率半导体激光模块为抽运源,通过空间滤波和非球面透镜耦合技术,双端抽运长度为21 m的大模场面积国产掺镱双包层光纤,获得了714.5 W的高功率连续激光输出。采用反向抽运,当入纤抽运功率为760 W时,激光输出功率达到501 W;采用双端抽运,当入纤抽运功率为1137 W时,获得了714.5 W的高功率连续输出,光光转换效率为62.8%,斜率效率为67%。
激光器 光纤激光器 国产双包层光纤 双端抽运
1 中国工程物理研究院研究生部,北京,100088
2 北京应用物理与计算数学研究所,北京,100088
类氖离子的X光激光理论研究可以为类镍X光激光提供有益启示.设计了一系列瞬态电子碰撞激发类氖锗19.6 nm X光激光的实验,采用2ω1ω泵浦方式,即预脉冲采用倍频钕玻璃激光,主脉冲采用基频,用新开发的瞬态电子碰撞激发类氖锗的系列程序进行了模拟,并与1ω1ω驱动的情况进行了比较.模拟表明,2ω1ω泵浦方案使类氖锗19.6 nm X光激光的小信号增益系数增大为1ω1ω方案的1.6倍,增益区也转移到了更高的电子密度区,是获得更短波长X光激光的一种有效方法.
瞬态电子碰撞激发 X光激光 类氖锗 2ω1ω泵浦方案 Transient collisional excitation X-ray laser Ne-like Ge 2ω1ω pumping scheme
中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所,上海,201800
利用数值模拟对在空间不同三点设立抽运点的几种典型抽运条件下包含放大自发发射的掺Yb光纤高功率激光器特性进行了分析。结果表明,即使不考虑抽运光的腔镜反射,对于不同的三点抽运情形,也存在不同的激光分配及功率分布特点。
光纤激光器 放大自发发射 三点抽运 数值模拟
中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
研究了类氢、类氦、类锂和类钠离子等四种实现复合机制X射线激光的方案,对可能实现水窗波段X射线激光的几种方案比较,分析了其各自的优缺点,并讨论了可能的具体实验方法。
水窗波段X射线激光 复合泵浦机制





