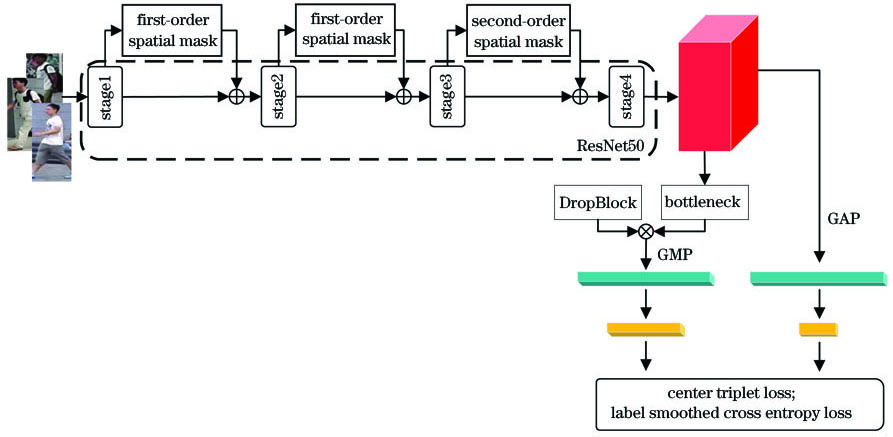
结合一阶和二阶空间信息的行人重识别  下载: 1014次
下载: 1014次
刘莎, 党建武, 王松, 王阳萍. 结合一阶和二阶空间信息的行人重识别[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(2): 0215005.
Sha Liu, Jianwu Dang, Song Wang, Yangping Wang. Person Re-Identification Based on First-Order and Second-Order Spatial Information[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(2): 0215005.
[1] 杨锋, 许玉, 尹梦晓, 等. 基于深度学习的行人重识别综述[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(5): 1243-1252.
[2] Liao SC, HuY, Zhu XY, et al. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning[C]∥2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 7-12, 2015, Boston, MA, USA. New York: IEEE, 2015: 2197- 2206.
[3] Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7): 971-987.
[4] 朱小波, 车进. 基于特征融合与子空间学习的行人重识别算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(2): 021503.
[5] ZhaoR, Ouyang WL, Wang XG. Unsupervised salience learning for person re-identification[C]∥2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 23-28, 2013, Portland, OR, USA. New York: IEEE, 2013: 3586- 3593.
[6] XiongF, Gou MR, CampsO, et al. Person re-identification using kernel-based metric learning methods[M] ∥Fleet D, Pajdla T, Schiele B, et al. Computer Vision-ECCV 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer, 2014, 8695: 1- 16.
[7] LiW, ZhaoR, XiaoT, et al. DeepReID: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification[C]∥2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 23-28, 2014, Columbus, OH, USA. New York: IEEE, 2014: 152- 159.
[8] Zhao HY, Tian MQ, Sun SY, et al. Spindle net: person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion[C]∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), July 21-26, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA. New York: IEEE, 2017: 907- 915.
[9] 毕晓君, 汪灏. 基于视角信息嵌入的行人重识别[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(6): 0615007.
[10] ChengD, Gong YH, Zhou SP, et al. Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function[C]∥2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 27-30, 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA. New York: IEEE, 2016: 1335- 1344.
[11] Sun YF, ZhengL, YangY, et al. Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline)[EB/OL]. [2020-05-23].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/1711. 09349.
[12] 徐龙壮, 彭力. 基于多尺度卷积特征融合的行人重识别[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(14): 141504.
[13] Liu H, Feng J S, Qi M B, et al. End-to-end comparative attention networks for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3492-3506.
[14] LiW, Zhu XT, Gong SG. Harmonious attention network for person re-identification[C]∥2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 18-23, 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA. New York: IEEE, 2018: 2285- 2294.
[15] BryanB, GongY, Zhang YZ, et al. Second-order non-local attention networks for person re-identification[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), October 27-November 2, 2019, Seoul, Korea (South). New York: IEEE, 2019: 3759- 3768.
[16] He KM, Zhang XY, Ren SQ, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 27-30, 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA. New York: IEEE, 2016: 770- 778.
[17] Dai ZZ, Chen MQ, Zhu SY, et al. Batch feature erasing for person re-identification and beyond[EB/OL]. [2020-05-21].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/1811. 07130.
[18] YuF, KoltunV, FunkhouserT. Dilated residual networks[C]∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), July 21-26, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA. New York: IEEE, 2017: 636- 644.
[19] GhiasiG, Lin TY, Le QV. Dropblock: a regularization method for convolutional networks[EB/OL]. [2020-05-24].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1810. 12890.
[20] SzegedyC, VanhouckeV, IoffeS, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]∥2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 27-30, 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA. New York: IEEE, 2016: 2818- 2826.
[21] HeT, ZhangZ, ZhangH, et al. Bag of tricks for image classification with convolutional neural networks[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 15-20, 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA. New York: IEEE, 2019: 558- 567.
[22] HermansA, BeyerL, LeibeB. In defense of the triplet loss for personre-identification[EB/OL]. [2020-05-24].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/1703. 07737.
[23] ZhengL, Shen LY, TianL, et al. Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark[C]∥2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), December 7-13, 2015, Santiago, Chile. New York: IEEE, 2015: 1116- 1124.
[24] RistaniE, SoleraF, ZouR, et al. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking[EB/OL]. [2020-05-20].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/1609. 01775.
[25] DengJ, DongW, SocherR, et al. ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database[C]∥ 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 20-25, 2009, Miami, FL, USA. New York: IEEE, 2009: 248- 255.
[26] Zheng ZD, ZhengL, YangY. Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro[C]∥2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), October 22-29, 2017, Venice, Italy. New York: IEEE, 2017: 3774- 3782.
[27] Sun YF, ZhengL, Deng WJ, et al. SVDNet for pedestrian retrieval[C]∥2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), October 22-29, 2017, Venice, Italy. New York: IEEE, 2017: 3820- 3828.
[28] XuJ, ZhaoR, ZhuF, et al. Attention-aware compositional network for personre-identification[C]∥2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 18-23, 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA. New York: IEEE, 2018: 2119- 2128.
[30] Wang GS, Yuan YF, ChenX, et al. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification[EB/OL]. [2020-05-21].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1804.01438.pdf.
[31] ZhengF, DengC, SunX, et al. Pyramidal person re-identification via multi-loss dynamic training[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 15-20, 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA. New York: IEEE, 2019: 8506- 8514.
刘莎, 党建武, 王松, 王阳萍. 结合一阶和二阶空间信息的行人重识别[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(2): 0215005. Sha Liu, Jianwu Dang, Song Wang, Yangping Wang. Person Re-Identification Based on First-Order and Second-Order Spatial Information[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(2): 0215005.