基于激光诱导击穿光谱定量检测土壤中营养元素的研究  下载: 989次
下载: 989次
Quantitative Detection of Nutrient Elements in Soil Based on Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
重庆邮电大学光电工程学院光电信息感测与传输技术重庆市重点实验室, 四川 重庆 400065
图 & 表
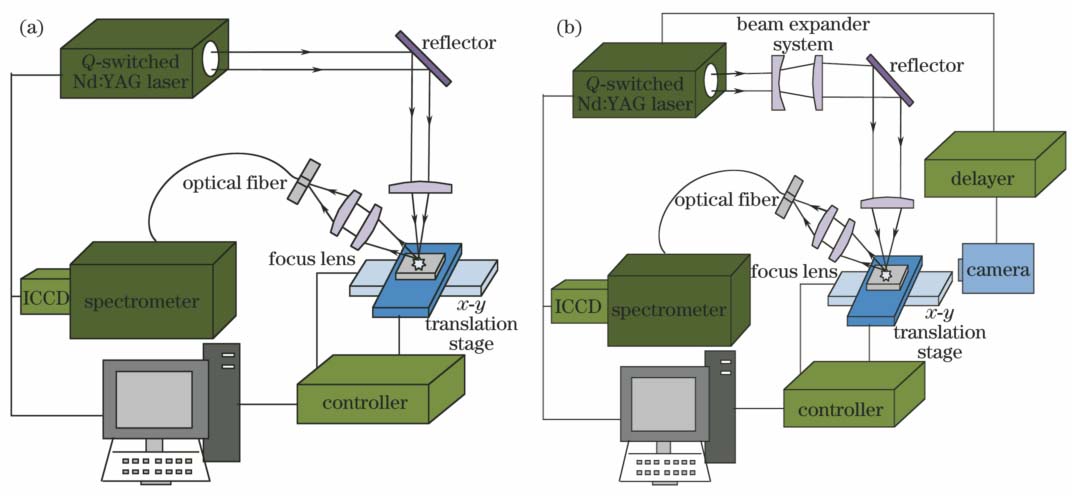
图 1. (a)传统LIBS系统与(b)笼式结构LIBS系统
Fig. 1. (a) Traditional LIBS system and (b) LIBS system with cage structure
下载图片 查看原文
图 2. 不同聚焦位置下Mg II 279.56 nm、Mg II 280.26 nm和Mg I 285.21 nm谱线信号强度的变化曲线
Fig. 2. Variation curves of signal intensity of Mg II 279.56 nm, Mg II 280.26 nm, and Mg I 285.21 nmspectral lines at different focusing positions
下载图片 查看原文
图 3. 不同聚焦位置下的等离子体图像
Fig. 3. Plasma images at different focusing positions
下载图片 查看原文
图 4. 传统LIBS系统下Mg II 279.56 nm、Mg II 280.26 nm和Mg I:285.21 nm谱线的稳定性
Fig. 4. Stability of Mg II 279.56 nm, Mg II 280.26 nm, and Mg I 285.21 nm spectral lines in traditional LIBS system
下载图片 查看原文
图 5. 笼式结构LIBS系统下Mg II:279.56 nm、Mg II:280.26 nm和Mg I:285.21 nm谱线的稳定性
Fig. 5. Stability of Mg II 279.56 nm, Mg II 280.26 nm, and Mg I 285.21 nm spectral lines in LIBS system with cage structure
下载图片 查看原文
图 6. 不同元素的定标曲线。(a) Cu元素;(b) Mn元素;(c) Mg元素;(d) K元素
Fig. 6. Calibration curves for different elements. (a) Copper element; (b) manganese element; (c) magnesium element; (d) potassium element
下载图片 查看原文
表 1土壤样品中Cu、Mn、Mg、K元素的质量分数
Table1. Mass fractions of Cu, Mn, Mg and K elements in soil samples10-6
| Number | Cu | Mn | Mg | K | Number | Cu | Mn | Mg | K |
|---|
| 1 | 24.6 | 677.0 | 15300.0 | 17600.0 | 9 | 44.2 | 863.0 | 16100.0 | 18933.3 | | 2 | 54.0 | 956.0 | 16500.0 | 19600.0 | 10 | 22.5 | 703.0 | 13140.0 | 19950.0 | | 3 | 18.3 | 755.0 | 8820.0 | 24650.0 | 11 | 20.4 | 729.0 | 10980.0 | 22300.0 | | 4 | 39.3 | 816.5 | 15900.0 | 18600.0 | 12 | 42.1 | 889.0 | 13940.0 | 21283.3 | | 5 | 21.5 | 716.0 | 12060.0 | 21125.0 | 13 | 34.4 | 770.0 | 15700.0 | 18266.7 | | 6 | 36.2 | 855.5 | 12660.0 | 22125.0 | 14 | 30.4 | 766.3 | 13980.0 | 19862.5 | | 7 | 32.3 | 796.0 | 13540.0 | 20616.7 | 15 | 37.7 | 836.0 | 14280.0 | 20362.5 | | 8 | 30.2 | 822.0 | 11380.0 | 22966.7 | 16 | 28.8 | 785.8 | 12360.0 | 21625.0 |
|
查看原文
表 220次激光脉冲的实际能量
Table2. Actual laser pulse energy for 20 timesmJ
| Number | Energy | Number | Energy | Number | Energy | Number | Energy | Number | Energy |
|---|
| 1 | 50.5 | 5 | 51.9 | 9 | 51.1 | 13 | 50.6 | 17 | 49.6 | | 2 | 50.8 | 6 | 48.9 | 10 | 50.6 | 14 | 51.5 | 18 | 50.5 | | 3 | 51.6 | 7 | 49.6 | 11 | 51.0 | 15 | 50.0 | 19 | 48.9 | | 4 | 49.6 | 8 | 51.3 | 12 | 52.0 | 16 | 50.2 | 20 | 49.6 |
|
查看原文
表 3利用笼式结构LIBS系统和传统LIBS系统得出的Cu、Mn、Mg、K元素的检出限(质量分数)
Table3. Detection limits of Cu, Mn, Mg and K elements obtained by LIBS system with cage structure and traditional LIBS system(mass fraction)10-6
| Element | Cu | Mn | Mg | K |
|---|
| LIBS system with cage structure | 0.42 | 13.2 | 38.5 | 62 | | Traditional LIBS system | 10.58 | 145.25 | 56.2 | 80.56 |
|
查看原文
表 4土壤样品中Cu、Mn、Mg、K元素含量的预测值及相对误差
Table4. Predicted mass fractions and relative errors of Cu, Mn, Mg, K elements in soil samples
| Number | Predicted mass fraction /10-6 | Relative error /% |
|---|
| Cu | Mn | Mg | K | Cu | Mn | Mg | K |
|---|
| 9 | 48.1 | 1021.3 | 17363.5 | 17170.8 | 8.1 | 15.5 | 7.3 | 10.3 | | 10 | 22.9 | 623.7 | 14219.0 | 21741.6 | 1.6 | 12.7 | 7.6 | 8.2 | | 11 | 21.5 | 737.2 | 12265.4 | 25488.5 | 5.2 | 1.1 | 10.5 | 12.5 | | 12 | 48.0 | 1005.2 | 15681.0 | 23653.9 | 12.3 | 11.6 | 11.1 | 10.0 | | 13 | 39.2 | 891.1 | 16531.0 | 20979.2 | 12.3 | 13.6 | 5.0 | 12.9 | | 14 | 33.6 | 694.0 | 15385.9 | 21978.3 | 9.7 | 10.4 | 9.1 | 9.6 | | 15 | 42.0 | 838.0 | 15934.7 | 22784.5 | 10.2 | 0.2 | 10.4 | 10.6 | | 16 | 33.5 | 705. | 13246.5 | 24883.0 | 13.9 | 11.4 | 6.7 | 13.1 |
|
查看原文
王金梅, 颜海英, 郑培超, 谭癸宁. 基于激光诱导击穿光谱定量检测土壤中营养元素的研究[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(11): 1111002. Wang Jinmei, Yan Haiying, Zheng Peichao, Tan Guining. Quantitative Detection of Nutrient Elements in Soil Based on Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(11): 1111002.
 下载: 989次
下载: 989次