1 上海理工大学上海市现代光学系统重点实验室,上海 200093
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所航天激光工程部,上海 201800
基于未来卫星间激光干涉任务的需求,介绍了一种基于迈克耳孙光纤干涉仪稳频的1064 nm激光稳频系统,该系统采用全光纤器件,结构紧凑、体积小、可靠性强。通过拍频测试,得到该系统的频率噪声在30 mHz~1 Hz范围内小于30 Hz/Hz1/2,频率稳定度在积分时间为1 s和1000 s时分别为1.2×10-14和3×10-13。该系统的性能满足LISA任务对稳频激光的需求,有望应用于未来的空间引力波探测任务。
激光光学 稳频 光纤干涉仪 频率噪声 光学学报
2023, 43(19): 1914001
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所航天激光工程部,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料科学与光电子技术学院,北京 100049
3 电子科技大学电子科学与工程学院,四川 成都 611731
4 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所量子光学重点实验室,上海 201800
射频蒸发冷却作为获取超冷原子简并量子气体的手段之一,对玻色-费米协同冷却的实现至关重要。为了在空间站上实现超冷量子简并气体,设计了一种特殊的射频天线。该天线被置于一个冷原子实验用真空腔内,与腔上集成的冷却、探测、光阱、磁阱、光晶格、Feshbach磁场等装置一同组成了通用型超冷原子物理实验系统,该实验系统满足载人航天工程在尺寸、重量、功耗、可靠性和电磁兼容性等方面的严格要求。利用有限元仿真方法对天线进行设计和评估,并在地面实验平台上对其各项性能指标进行测试和实验验证。结果表明,本设计除了能够降低90%的射频功率需求外,还能维持科学腔的超高真空水平,并具备良好的电磁兼容性,符合载人航天工程的要求。
量子光学 玻色-爱因斯坦凝聚体 射频诱导蒸发冷却 微波 Zeeman效应

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Space Laser Engineering, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
We demonstrate an ultrastable miniaturized transportable laser system at 1550 nm by locking it to an optical fiber delay line (FDL). To achieve optimized long-term frequency stability, the FDL was placed into a vacuum chamber with a five-layer thermal shield, and a delicate two-stage active temperature stabilization, an optical power stabilization, and an RF power stabilization were applied in the system. A fractional frequency stability of better than at 1 s averaging time and at 1000 s averaging time was achieved, which is the best long-term frequency stability of an all-fiber-based ultrastable laser observed to date.
fiber delay line frequency stability ultrastable laser Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(3): 031404

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
4 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Solid-State Laser and Application, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
We demonstrate an all-fiber-based photonic microwave generation with frequency instability. The system consists of an ultra-stable laser by optical fiber delay line, an all-fiber-based “figure-of-nine” optical frequency comb, a high signal-to-noise ratio photonic detection unit, and a microwave frequency synthesizer. The whole optical links are made from optical fiber and optical fiber components, which renders the whole system compactness, reliability, and robustness with respect to environmental influences. Frequency instabilities of at 100 s for 6.834 GHz signal and at 100 s for 9.192 GHz signal were achieved.
ultra-stable laser optical frequency comb photonic microwave generation Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(2): 021406

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
In this article, taking advantage of the special magnetic shieldings and the optimal coil design of a transportable Rb atomic fountain clock, the intensity distribution in space and the fluctuations with time of the quantization magnetic field in the Ramsey region were measured using the atomic magneton-sensitive transition method. In an approximately 310 mm long Ramsey region, a peak-to-peak magnetic field intensity of a 0.74 nT deviation in space and a 0.06 nT fluctuation with time were obtained. These results correspond to a second-order Zeeman frequency shift of approximately . This is an essential step in advancing the total frequency uncertainty of the fountain clock to the order of .
Zeeman effect hyperfine structure atomic clock magnetic-sensitive method Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(12): 120201
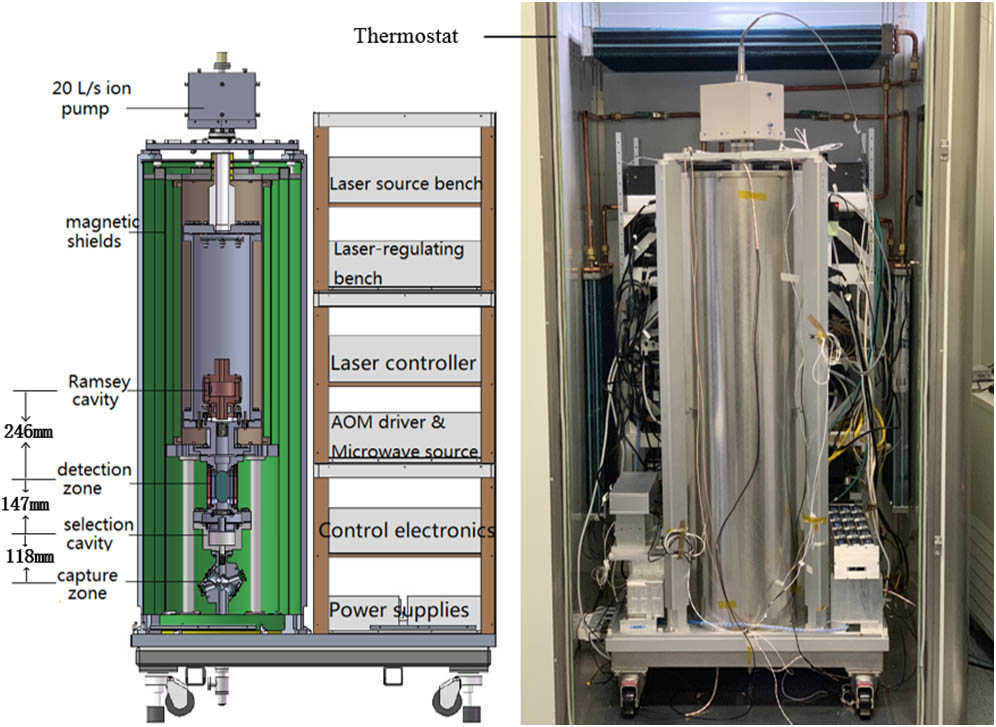
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A high-performance transportable fountain clock is attractive for use in laboratories with high-precision time-frequency measurement requirements. This Letter reports the improvement of the stability of a transportable rubidium-87 fountain clock because of an optimization of temperature characteristics. This clock integrates its physical packaging, optical benches, microwave frequency synthesizers, and electronic controls onto an easily movable wheeled plate. Two optical benches with a high-vibration resistance are realized in this work. No additional adjustment is required after moving them several times. The Allan deviation of the fountain clock frequency was measured by comparing it with that of the hydrogen maser. The fountain clock got a short-term stability of at 1 s and long-term stability on the order of 10 16 at 100,000 s.
020.3320 Laser cooling 120.3940 Metrology 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise 270.5570 Quantum detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 080201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Excess frequency noise induced by mechanical vibration is the dominant noise source at low Fourier frequencies in fiber-delay-line stabilized lasers. To resolve this problem, a double-winding fiber spool is designed and implemented that has ultralow acceleration sensitivity in all spatial directions. By carefully choosing the optimal geometry parameters of the fiber spool, we achieve acceleration sensitivity of 8 × 10 11/g and 3 × 10 11/g (g denotes the gravitational acceleration) in axial and radial directions, respectively.
140.3425 Laser stabilization 120.7280 Vibration analysis 060.2310 Fiber optics Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081403
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
We demonstrate the frequency stabilization of a 1.55 μm erbium-doped fiber laser by locking it to a 5-km-long optical fiber delay line (FDL). The stabilized laser is characterized via comparison with a second identical laser system. We obtain a fractional frequency stability of better than 3 × 10 15 over time scales of 1–10 s and a laser linewidth of 0.2 Hz, which is the narrowest linewidth of an FDL-stabilized laser observed to date.
140.3425 Laser stabilization 060.2310 Fiber optics 060.2840 Heterodyne Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 071407
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所量子光学重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
对780 nm声光调制器(AOM)的温度响应进行了详细的理论计算,发现AOM衍射光偏振角的温度响应系数远大于衍射效率和衍射角的温度响应系数。针对AOM衍射光偏振角的温度响应,在地面实验室环境下对其进行了实验验证。在空间微重力环境下,AOM的温度响应可能会成为制约空间项目光学平台工作温度范围和性能指标提高的主要因素之一。基于AOM在实际空间应用中的脉冲工作模式,通过仿真建模给出了AOM声光晶体温度随环境温度的变化曲线,并给出了优化措施。
测量 声光调制器 温度响应 空间应用 激光冷却
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所量子光学重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
在使用铷原子饱和吸收谱线作为激光频率参考进行稳频的激光稳频系统中,环路带宽是影响激光输出频率噪声的重要因素之一。对激光稳频系统中限制环路带宽的主要因素进行分析,使用射频调制信号直接调制商用外腔半导体激光器的高速电流调制端来对激光稳频系统的环路带宽进行拓展。根据对稳频环路的分析,合理设置反馈电路,实现激光稳频。使用低频谱分析仪对稳频后的鉴频信号进行分析,发现带宽拓展后,在傅里叶频率为5 kHz处对频率噪声的抑制度达到了20 dB以上。通过将该稳频激光器输出的激光与锁定在极稳恒温晶振上的飞秒光学频率梳进行拍频,测量了该稳频激光相对光梳的频率噪声,测量结果与直接分析鉴频信号的结果吻合。经过测量,通过拓展带宽抑制频率噪声,稳频激光器的短期频率稳定度得到改善。最后,测量了稳频激光相对于锁定在恒温晶振上的飞秒光学频率梳的频率稳定度,Allan方差在平均时间1 s时达到4.52×10-12,在平均时间20 s时达到1.65×10-12。
激光器 激光稳频 饱和吸收光谱 射频调制 频率噪声





