Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Photonic Devices and Sensing Systems for Internet of Things, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Guangdong and Hong Kong Joint Research Centre for Optical Fibre Sensors, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
Fiber Bragg grating has been successfully fabricated in the silica microfiber by the use of femtosecond laser point-by-point inscription. Temporal thermal response of the fabricated silica microfiber Bragg grating has been measured by the use of the CO2 laser thermal excitation method, and the result shows that the time constant of the microfiber Bragg grating is reduced by an order of magnitude compared with the traditional single-mode fiber Bragg grating and the measured time constant is ~ 21 ms.
Fiber optics sensors fiber optics and optical communications fiber optics components Photonic Sensors
2021, 11(4): 387

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Optical Information Technology, Ministry of Education, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
We propose and demonstrate a novel scheme of semi-open-loop polarization control (SOL-PC), which controls the state of polarization (SOP) with high accuracy and uniform high speed. For any desired SOP, we first adjust the initial SOP using open-loop control (OLC) based on the matrix model of a three-unit piezoelectric polarization controller, and quickly move it close to the objective one. Then closed-loop control (CLC) is performed to reduce the error and reach precisely the desired SOP. The response time is three orders faster than that of the present closed-loop polarization control, while the average deviation is on par with it. Finally, the SOL-PC system is successfully applied to realize the suppression of the polarization mode dispersion (PMD) effect and reduce the first-order PMD to near zero. Due to its perfect performance, the SOL-PC energizes the present polarization control to pursue an ideal product that can meet the future requirements in ultrafast optical transmission and quantum communication.
polarization control polarization mode dispersion fiber optics components coherent communications Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(5): 050601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Laser Polarization and Information Technology, Department of Physics, School of Physics and Engineering, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, China
2 College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, China
3 College of Precision Instrument & Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
4 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronics Information and Technical Science, Ministry of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
The polarization of a D-shaped fiber is modulated after immersing it in magnetic fluid (MF) and applying a magnetic field. Theoretical analysis predicts that magneto-optical dichroism of MF plays a key role in light polarization modulation. During light polarization modulation, the evanescent wave polarized parallel to the magnetic field has greater loss than its orthogonal component. Light polarization of a D-shaped fiber with a wide polished surface can be modulated easily. High concentration MF and a large magnetic field all have great ability to modulate light polarization.
fiber optics components polarization-selective devices magneto-optic systems magneto-optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(1): 010601

Xin Tian 1,2,3Hao Li 1,2,3Le Liu 1,2,3Meng Wang 1,2,3[ ... ]Zefeng Wang 1,2,3,*
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Pulsed Power Laser Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of High Energy Laser Technology, Changsha 410073, China
We report here an ultra-broadband linearly polarized (LP) LP01 LP11 mode converter operating at 1 μm based on a long period fiber grating (LPFG) fabricated in a conventional two-mode fiber (TMF) by a line-focused CO2 laser. The measured 3 dB bandwidth is about 240 nm, which is the broadest bandwidth for such fiber mode converters. The maximum conversion efficiency between the LP01 and LP11 modes is >99% over the range of 1000 nm to 1085 nm, almost covering the whole emission band of Yb3+, which is useful for further power scaling of high-power fiber lasers operating at the 1 μm band.
060.2340 Fiber optics components 060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(12): 120602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MIIT Key Laboratory of Advanced Solid Laser, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
2 School of Electronic Engineering and Optoelectronic Technology, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
Suppression of stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) by means of chirped and tilted fiber Bragg gratings (CTFBGs) has become a key topic. However, research on high-power systems is still lacking due to two problems. Firstly, after the inscription, there are a large number of hydroxyl compounds and hydrogen molecules in CTFBGs that cause significant heating due to their strong infrared absorption. Secondly, CTFBGs can couple Stokes light from the core to the cladding and the coating, which causes serious heating in the coating of the CTFBG. Aimed at overcoming these bottlenecks, a process that combines constant-low-temperature and variable-high-temperature annealing is used to reduce the thermal slope of the CTFBG. Also, a segmented-corrosion cladding power stripping technology is used on the CTFBG to remove the Stokes light which is coupled to the cladding, which solves the problem of overheating in the coating of the CTFBG. Thereby, a CTFBG with both a kilowatt-level power-carrying load and the ability to suppress SRS in a fiber laser has been developed. Further, we establish a kW-level CW oscillator to test the CTFBG. Experimental results demonstrate that the power-carrying load of the CTFBG is close to 1 kW, the thermal slope is lower than $0.015\,^{\circ }\text{C}/\text{W}$, and the SRS suppression ratio is nearly 23 dB.
chirped and tilted fiber Bragg gratings fiber optics components high-power fiber laser stimulated Raman scattering High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2019, 7(2): 02000e31
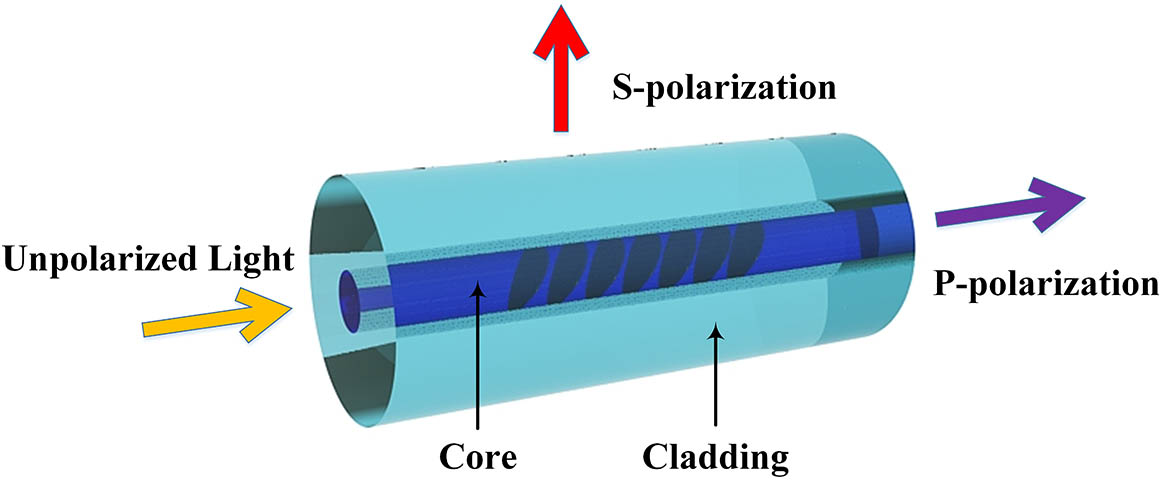
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Optical and Electronic Information, National Engineering Laboratory for Next Generation Internet Access System, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Aston Institute of Photonic Technologies, Aston University, Birmingham B4 7ET, UK
We have investigated the whole polarization-extinction-ratio (PER) spectrum and annealing properties of 45°-tilted fiber gratings (45°-TFGs). Experimental results show the PER spectrum of 45°-TFGs is a Gaussian-like profile and covers a 540 nm bandwidth from 1260 to 1800 nm, in which the bandwidth with PER greater than 10 dB is over 250 nm. The output polarization distribution of 45°-TFGs was analyzed by employing a bulk linear polarizer, and the results show a perfect figure “8”, which indicates that the 45°-TFG is a type of linear polarizer. Moreover, the annealing property of 45°-TFGs was measured up to 700°C, in which the PER of the grating started to decrease at 300°C and reached the minimum at 700°C. Based on these results, the 45°-TFGs can be used as an ultra-wide bandwidth in-fiber polarizing device.
060.2340 Fiber optics components 230.5440 Polarization-selective devices 230.1150 All-optical devices 050.2770 Gratings Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 050601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
2 Key Laboratory of Weak Light Nonlinear Photonics, Ministry of Education, Nankai University, Tianjin 300457, China
A mode field adapter (MFA) fabricated by the thermal expanded core (TEC) technique is investigated. Firstly, the mode field characteristics of the TEC large mode area fiber (LMAF) are analyzed. Compared with the single-mode fiber (SMF), the mode field diameter of the LMAF enlarged slower than that of the SMF. Secondly, the mode field characteristics of the different fibers with TEC treatment are discussed. Thirdly, the transmission efficiency of the MFA fabricated by the SMF and LMAF is also investigated. Finally, we used the 6/125 μm SMF and 15/130 μm LMAF to fabricate an MFA with transmission efficiency of 92% and the handling power as high as 100 W.
060.2340 Fiber optics components 060.2310 Fiber optics 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(3): 030602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Instrument Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 International Research Institute for Multidisciplinary Science, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
A novel slotted optical microdisk resonator, which significantly enhances light–matter interaction and provides a promising approach for increasing the sensitivity of sensors, is theoretically and numerically investigated. In this slotted resonator, the mode splitting is generated due to reflection of the slot. Remarkably, effects of the slot width and angular position on the mode splitting are mainly studied. The results reveal that the mode splitting is a second function of the slot width, and the maximum mode splitting induced by the slot deformation is achieved with 2.7853×109 Hz/nm. Therefore, the slotted resonator is an excellent candidate for pressure and force sensing. Besides, the influence of the slot angular position on the mode splitting is a cosine curve with the highest sensitivity of 1.23×1011 Hz/deg ; thus, the optical characteristic demonstrates that the slotted resonator can be used for inertial measurements.
Resonators Optical devices Fiber optics components Fiber optics Fiber optics and optical communications Photonics Research
2017, 5(3): 03000194

Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Seoul, 163 Seoulsiripdae-ro, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 02504, South Korea
An all-fiber acousto-optic modulator (AOM), which features a compact structure and a low-driving voltage, is experimentally demonstrated for the active mode-locking of a fiber laser. The proposed AOM is based on the short length of the cladding-etched fiber, the ends of which are fixed on a slide glass. On top of the cladding-etched fiber, a piezoelectric transducer was overlaid. A chemical wet-etching technique, which is based on a mixed solution of NH4F and (NH4)2SO4, is used to reduce the fiber diameter down to ~25 μm, and the length of the etched section is only 0.5 cm. The fabricated device exhibited a modulation depth of 73.10% at an acoustic frequency of 918.9 kHz and a peak-to-peak electrical voltage of 10 V, while a laser beam was coupled at 1560 nm. By using the prepared AOM within an erbium-doped-fiber ring cavity, the mode-locked pulses with a temporal width of 2.66 ps were readily obtained at a repetition rate of 1.838 MHz.
(060.2340) Fiber optics components (140.4050) Mode-locked lasers (230.1040) Acousto-optical devices. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000391





