1 北京科技大学, 北京 100083
2 锡林郭勒盟博物馆, 内蒙古 锡林浩特 026099
3 中国人民大学, 北京 100872
考古发掘出土的遗物中, 有机残留物大部分是以附着在器物上, 或者是遗址表面而存在的, 由于没有固定形状, 或量少而难以发现, 且不易保存, 因此常常被忽视。 但是这类有机物作为古代人类生活生产资料, 包含重要的历史信息, 具有珍贵价值。 通过遗址中发现的器物或者有机残留物, 可以决定器物甚至是遗址的用途, 古代照明燃料就属于这类有机残留物。 中国古代多使用动物油、 植物油、 蜡等作为照明燃料, 对植物油和蜡都有一定研究, 但对于动物油种类的分析仅停留在区分反刍动物与非反刍动物。 引入热裂解气相色谱质谱技术(THM-Py-GC/MS)研究有机残留物, 使用600 ℃裂解温度经过12 s裂解时间, 可以将甘油三酯与老化过程中由于失去酰基逐步形成的双酰基甘油、 单酰基甘油等完全裂解成甘油与脂肪酸, 通过计算脂肪酸相对含量, 可以分析不同动物油具有的特征。 同时用高温裂解代替了传统酸化提纯样品的预处理方法, 能最大程度的保留样品中的各组分。 加入过量的四甲基氢氧化铵, 可将样品中脂肪酸与醇等量转化为对应的酯和醚, 在气相色谱初始50 ℃保持5 min, 然后以10 ℃·min-1升至280 ℃保持10 min的条件下, 将甲基化的样品组分分离, 质谱以1∶100的分流比进行测定。 对内蒙古伊和淖尔墓地出土铁灯内的残留物进行了分析, 结果显示, 灯内残留物样品中主要成分是C7—C22连续碳原子的脂肪酸, 含量较高的饱和脂肪酸有十四烷酸、 十五烷酸、 十六烷酸、 十七烷酸、 十八烷酸等。 对比老化前与老化后猪油、 牛油、 羊油等动物脂肪参考样品所含主要成分与相对含量, 老化后的羊油中的奇数碳饱和脂肪酸含量明显高于其他两种动物油, 并且这一特征也体现在考古样品中, 结合以往文献中动物油成分的研究结果, 可以判断出残留物中所含动物油的确切种类属羊油。 此外样品中包含的碳氢化合物与醇属于蜡的成分, 根据脂肪酸及醇的相对含量可以判断为蜂蜡。 热裂解气相色谱质谱技术(THM-Py-GC/MS), 为出土有机残留物, 特别是动物脂肪种类的的分析研究, 提供了更加高效、 便捷的方法。 并且, 对混合有机残留物种类的鉴别也做出了有益的尝试。
热裂解气相色谱质谱法 四甲基氢氧化铵 照明燃料 动物油 出土有机残留物 Py-GC/MS Tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide Illuminating fuel Animal tallow Unearthed residual organic materials 光谱学与光谱分析
2019, 39(12): 3868
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Solid State Physics, University of Latvia, Riga LV-1083, Latvia
An all-organic Mach-Zehnder waveguide device for volatile solvent sensing is presented. Optical waveguide devices offer a great potential for various applications in sensing and communications due to multiple advantageous properties such as immunity to electromagnetic interference, high efficiency, and low cost and size. One of the most promising areas for applications of photonic systems would be real-time monitoring of various hazardous organic vapor concentrations harmful to human being. The optical waveguide volatile solvent sensor presented here comprises a novel organic material applied as a cladding on an SU-8 waveguide core and can be used for sensing of different vapors such as isopropanol, acetone, and water. It is shown that the reason for the chemical sensing in device is the absorption of vapor into the waveguide cladding which in turn changes the waveguide effective refractive index. The presented waveguide device has small footprint and high sensitivity of the mentioned solvent vapor, particularly that of water. The preparation steps of the device as well as the sensing characteristics are presented and discussed.
Optical sensor waveguide organic materials Mach-Zehnder interference Photonic Sensors
2019, 9(4): 356

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Green Energy & Semiconductor Engineering, Hoseo University, Asan 31499, Korea
2 R&D Center, A-PRO Co. Ltd., Gunpo 15830, Korea
3 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong 070, China
4 Department of Engineering Physcis, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario L8S 4L7, Canada
In order to realize single emissive white phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices (PHOLEDs) with three color phosphorescent dopants (red, green, and blue), the energy transfer between the host material and the three dopants, as well as the among the three dopants themselves, should be considered and optimized. To explore the effect of red phosphorescent dopant on the color rendering index (CRI), the authors investigate the wavelength position of the maximum emission peak from three phosphorescent dopants. The CRI and luminous efficiency of white PHOLED in which Ir(pq)2(acac) acts as the red phosphorescent dopant are found to be greater than those of devices prepared using Ir(piq)3 and Ir(btp)2(acac) as the emission spectrum has a relatively high intensity near the human perception of blue, red, and green wavelengths. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the performance of the three dopants is related to the absorption characteristics of the red phosphorescent dopant. With a maximum emission peak at 600 nm, Ir(pq)2(acac) has a higher intensity in the concave section between 550 and 600 nm seen for red and blue dopants. In addition, the long metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) absorption tail of Ir(pq)2(acac) overlaps with the emission spectra of the green dopant, enhancing emission. Such energy transfer mechanisms are confirmed to optimize white emission in the single emissive white PHOLEDs.
160.4890 Organic materials 300.1030 Absorption 260.2160 Energy transfer Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(5): 051602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Bialystok University of Technology, Bialystok 15-351, Poland
2 AGH University of Science and Technology, Krakow 30-059, Poland
Lanthanide-doped polymers are very attractive, since they can be used for luminescent optical fiber fabrications. This Letter presents the terbium-ions-doped poly(methyl methacrylate) fiber fabrication and spectroscopic characterization. The measured excited state (D45) lifetime of 0.741 ms confirms that a used organometallic can be used to obtain an intense luminescence in a polymeric fiber. The luminescence spectrum shape modification versus the fiber length is also investigated.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 160.4890 Organic materials 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(7): 070602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of High Performance and Complex Manufacturing, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
The optical constants, photoluminescence properties, and resistivity of Al-Alq3 thin films prepared by the thermal co-evaporation method on a silicon substrate are studied with various Al fractions. A variable angle spectroscopic ellipsometry is employed to determine the optical constants in the wavelength from 300 to 1200 nm at incidence angles of 65°, 70°, and 75°, respectively. Both the refractive indices and extinction coefficient apparently increase with increasing Al fractions. The intensity of photoluminescence spectra gradually increases with decreasing Al fractions due to intrinsic energy level transition of Alq3 organic semiconductor in the ultraviolet wave band. The resistivity decreases from 42.1 to 3.36 Ω·cm with increasing Al fraction from 40% to 70%, resulting in a larger emission intensity in photoluminescence spectra for the 40% Al fraction sample.
160.4890 Organic materials 120.2130 Ellipsometry and polarimetry Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(11): 111602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Bialystok University of Technology, Wiejska 45D Street, Bialystok 15-351, Poland
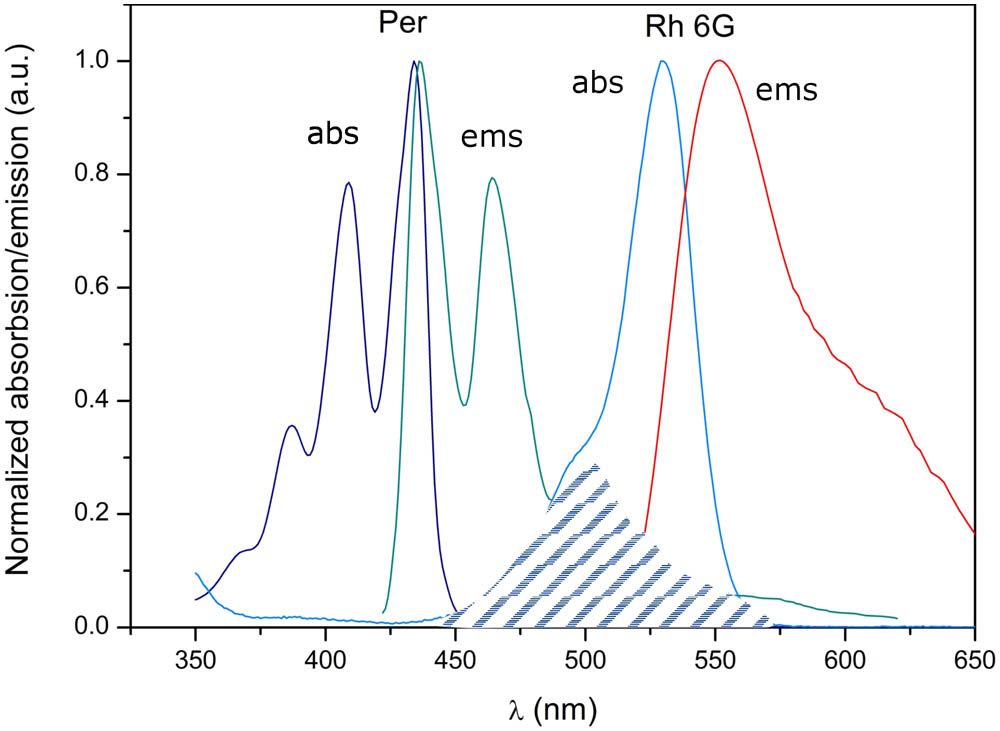
This Letter presents the fabrication and characterization of a perylene (Per) and Rhodamine 6 G (Rh 6 G) co-doped polymeric fiber. The spectroscopic properties (luminescence spectra, attenuation, energy transfer) of the co-doped polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) fiber are presented. Two different concentrations of Rh 6 G (2.2×10 4 and 4.1×10 4 mol/L) and a constant Per concentration (6.2×10 4 mol/L) are used in the experiments. The luminescence spectrum changes versus the fiber length are discussed. Additionally, the ratio of the maximum fluorescence peaks of the used dyes is calculated versus the fiber length. The obtained results show the energy transfer from Per (donor) to Rh 6 G (acceptor). The proposed co-doped fiber can be used in applications in lighting and sensor technology.
160.4890 Organic materials 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.5470 Polymers Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 121602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Science, Chang’an University, Xi’an 710064, China
Two kinds of novel blue-emitting materials, anthracene-based derivatives, are synthesized by the Suzuki coupling reaction. It is worth noting that the maximum emission wavelengths of the two materials are 441 and 444 nm in tetrahydrofuran and 456 and 454 nm in film states, which are the typical blue fluorescence and the fluorescence quantum yields of them are 0.87 and 1.12 by using 9,10-diphenylanthracene (Φf=0.90) as a calibration standard. The full width at half maximum of them are 56, 55 nm in solution, respectively, presenting good color purity. Both of them display superior thermal properties and electrochemical properties. Scanning electronic microscope results show that the films of two compounds are continuous, compact, and smooth after 100°C for 3 h. These data indicate their potential to be prepared for high efficiency and long operation lifetime organic light-emitting diodes devices.
230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.4890 Organic materials Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 042301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Institute of Spacecraft Electrical Technology, Yantai 264670, China
2 Laser Fusion Research Center, China Academic of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
In this Letter, temporal self-modifying behavior of amplitude modulation pulse propagation characteristics in multiphoton absorbers is presented by solving the underlying theoretical model coupling the propagation equation with the rate equations. The characteristics of the output temporal shapes are of primary concern and are discussed in detail. Amplitude modulation suppressing effects of multiphoton absorbers are numerically demonstrated; they have not been reported previously, to our knowledge. By taking a time resolved absorption coefficients, the corresponding physical mechanism is explicitly interpreted.
190.4710 Optical nonlinearities in organic materials 140.3300 Laser beam shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(7): 070009





