
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Systems, College of Optics and Electronic Information Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Institute of Modern Optics, Key Laboratory of Optical Information Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
3 Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201210, China
4 e-mail: py@usst.edu.cn
5 e-mail: ymzhu@usst.edu.cn
In this work, it has been demonstrated that in order to fully understand the terahertz (THz) pulse generation process during femtosecond laser filamentation, the interaction between THz wave and air plasma has to be taken into account. This interaction is mainly associated with the spatial confinement of the THz pulse by the plasma column, which could be described by the one-dimensional negative dielectric (1DND) waveguide model. By combining the 1DND model with the conventional four-wave mixing (4WM) and photocurrent (PC) models, the variation of THz spectral amplitude and width obtained in experiments could be better understood. Finally, a three-step procedure, with 1DND bridging 4WM and PC processes, has been established for the first time to describe the underlying mechanism of THz radiation from plasma sources.
Ultrafast nonlinear optics Femtosecond phenomena Plasmas Propagation Spectroscopy, terahertz Photonics Research
2018, 6(4): 04000296

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, N.T., Hong Kong, China
2 School of Science, Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, Hangzhou 310023, China
3 Department of Electronic Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon, N.T., Hong Kong, China
4 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Warwick University, Coventry, UK
In this work, we show how fiber-based terahertz systems can be robustly configured for accurate terahertz ellipsometry. To this end, we explain how our algorithms can be successfully applied to achieve accurate spectroscopic ellipsometry with a high tolerance on the imperfect polarizer extinction ratio and pulse shift errors. Highly accurate characterization of transparent, absorptive, and conductive samples comprehensively demonstrates the versatility of our algorithms. The improved accuracy we achieve is a fundamental breakthrough for reflection-based measurements and overcomes the hurdle of phase uncertainty.
Ellipsometry and polarimetry Spectroscopy, terahertz Photonics Research
2018, 6(8): 08000768
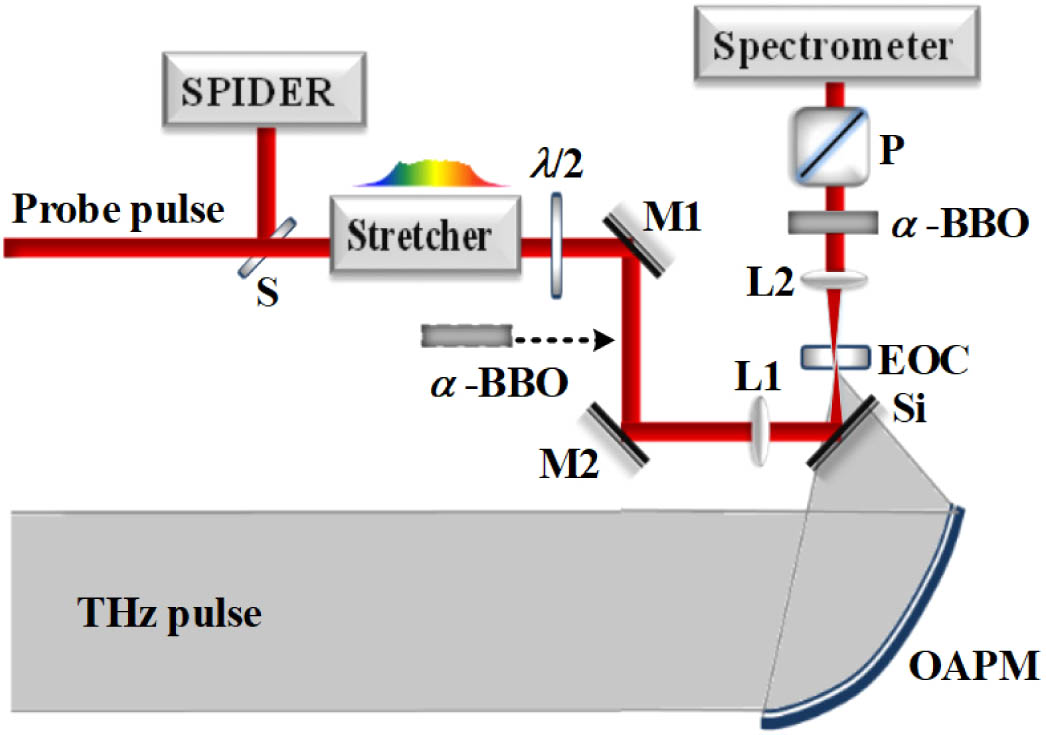
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Photonic Information Technology, College of Electronic Science and Technology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 SZU-NUS Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Science & Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
To seek high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is critical but challenging for single-shot intense terahertz (THz) coherent detection. This paper presents an improved common-path spectral interferometer for single-shot THz detection with a single chirped pulse as the probe for THz electro-optic (EO) sampling. Here, the spectral interference occurs between the two orthogonal polarization components with a required relative time delay generated with only a birefringent plate after the EO sensor. Our experiments show that this interferometer can effectively suppress the noise usually suffered in a non-common-path interferometer. The measured single-shot SNR is up to 88.85, and the measured THz waveforms are independent of the orientation of the used ZnTe EO sensor, so it is easy to operate and the results are more reliable. These features mean that the interferometer is quite qualified for applications where strong THz pulses, usually with single-shot or low repetition rate, are indispensable.
Far infrared or terahertz Ultrafast measurements Electro-optical devices Spectroscopy, terahertz Interferometry Photonics Research
2018, 6(3): 03000177
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Electronic Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
2 e-mail: emma@ee.cuhk.edu.hk
3 Department of Chemistry, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8107, USA
4 e-mail: charles.schmuttenmaer@yale.edu
We give an introduction to the feature issue comprised of six articles on terahertz photonics techniques and applications.
Far infrared or terahertz Terahertz imaging Spectroscopy, terahertz Photonics Research
2016, 4(3): 03000TP1





