1 新疆师范大学物理与电子工程学院新疆发光矿物与光功能材料研究重点实验室,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830054
2 新疆师范大学物理与电子工程学院新疆矿物发光材料及其微结构实验室,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830054
3 新疆师范大学化学化工学院,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830054
采用高温固相法,通过阳离子替代的实验策略,制备出系列窄带发射且颜色可由深黄色调至绿色的K2-xNaxZn0.94SiO4∶0.06Mn2+ (0≤x≤2)荧光粉。用X射线粉末衍射仪对样品的物相进行表征,通过扫描电子显微镜和能量色散谱测试对样品的形貌和元素分布进行分析。结果表明,成功地合成了纯相且元素分布均匀的K2-xNaxZn0.94SiO4∶0.06Mn2+ (0≤x≤2)荧光粉。在蓝光激发下,随着Na+离子逐渐代替K+离子,K2-xNaxZn0.94SiO4∶0.06Mn2+ (0≤x≤2)荧光粉的发光强度逐渐增强,原荧光粉的发光强度得到有效提高的同时发光颜色由深黄色调至绿色。在427 nm激光的激发下:当x=0.8时,K1.2Na0.8Zn0.94SiO4∶0.06Mn2+荧光粉发光最强;当x=2.0时,即K+完全被Na+替代,Na2Zn0.94SiO4∶0.06Mn2+荧光粉发射出中心波长为517 nm、半峰全宽为32 nm的绿光,相较于商用β-SiAlON∶Eu2+绿色荧光粉,其半峰全宽更窄。
材料 过渡金属掺杂材料 K2-xNaxZn0.94SiO4∶Mn2+(0≤x≤2) 窄带绿光发射 颜色调控 液晶显示背光源 光学学报
2023, 43(11): 1116001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Tunable Laser Technology, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Optoelectronic Information System, Shenzhen Graduate School, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
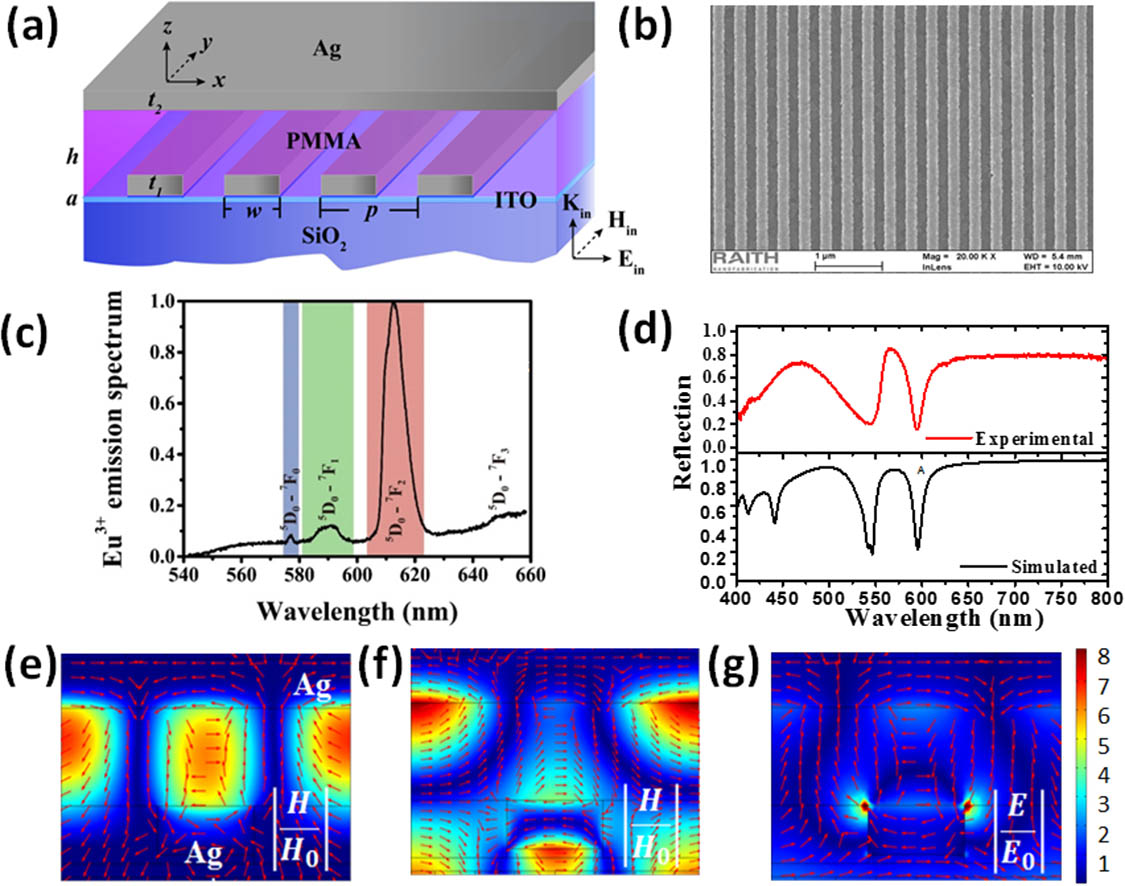
Magnetic dipole (MD) transitions are important for a range of technologies from quantum light sources and displays to lasers and bio-probes. However, the typical MD transitions are much weaker than their electric counterparts and are usually neglected in practical applications. Herein, we experimentally demonstrate that the MD transitions can be significantly enhanced by the well-developed magnetic metamaterials in the visible optical range. The magnetic metamaterials consist of silver nanostrips and a thick silver film, which are separated with an Eu3+:polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) film. By controlling the thickness of the Eu3+:PMMA film, the magnetic resonance has been tuned to match the emission wavelength of MDs. Consequently, the intensity of MD emission has been significantly increased by around 30 times at the magnetic resonance wavelength, whereas the intensity of electric dipole emission is well-preserved. The corresponding numerical calculations reveal that the enhancement is directly generated by the magnetic resonance, which strongly increases the magnetic local density of states around the MD emitter and can efficiently radiate the MD emission into the far field. This is the first demonstration, to the best of our knowledge, that MD transitions can be improved by an additional degree of magnetic freedom, and we believe this research shall pave a new route towards bright magnetic emitters and their potential applications.
160.3918 Metamaterials 160.6990 Transition-metal-doped materials 350.5400 Plasmas 310.6628 Subwavelength structures,nanostructures 300.6550 Spectroscopy, visible Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050008
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Applied Physics, Chongqing University, Chongqing 401331, China
2 Chongqing Key Laboratory on Optoelectronic Functional Materials, Chongqing Normal University, Chongqing 401331, China
The electronic and optical properties, including band structure, density of states (DOS), absorption rate, refractive index, and dielectric function, of anatase TiO2 codoped with N and first transition elements are investigated using the plane wave pseudopotential method based on the density functional theory. The calculation results show that TiO2 codoping with N and first transition elements (Sc, V, Cr, Mn, and Fe) lead to significant reduction of conduction band relative to the Fermi level, reduction of band gap width, formation of new donor, and acceptor impurity levels below the conduction band and above the valence band, and cause some redshifts of optical absorption band edge with the amount of redshift decrease in the following order: N–Fe > N–Cr > N–Mn. Further, the synergistic effect of shallow donor and acceptor levels enhances light excitation for effective separation of electron–hole pairs and enhancement of light absorption ability, thereby increasing the TiO2 photocatalytic properties. This study reveals that the visible-light absorption ability of the codoped anatase TiO2 decreases in the order of N–Fe > N–Cr > N–Mn > N–Sc > N–V > N, and does not monotonically follow the dopant atomic number. Especially, in N–Cr codoped TiO2, the 4s atomic orbit of Cr is not completely filled, which hybridized with the p electronic orbit most probably acts as photo-generated electron trap centers resulting in higher photocatalytic activity than that of N–Mn codoped TiO2.
160.6990 Transition-metal-doped materials 160.4760 Optical properties Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(9): 091602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The Eu2+/Tb3+/Sm3+ co-doped oxyfluoride glass ceramics containing Ba2LaF7 nanocrystals are prepared in the reducing atmosphere. The X-ray diffraction results show that Eu2+, Tb3+ and Sm3+ ions are enriched into the precipitated Ba2LaF7 nanophase after the annealing process. It deduces efficient energy transfers from Eu2+ to Tb3+ and Sm3+ and intenses warm white luminescence of the glass ceramics. Comparing with the glass, the luminescence quantum yield of the glass ceramics is also enlarged by about 3 times. This demonstrates the potential white light-emitting diode application of the glass ceramics produced in this letter.
160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 160.6990 Transition-metal-doped materials Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(3): 031602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Material Science and Technology for High Power Lasers, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
The growth of a Mn-doped LiAlO2 single crystal by the Czochralski (CZ) method and the characterization of its spectroscopy and thermoluminescence (TL) are presented. The X-ray rocking curve and chemical etching analysis show that the as-grown crystal has good crystallinity. The full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the LiAlO2 (200) \omega rocking curve is 23.2 arcsec and the etching pits density of the (100) plane is (1.6–4.0)×104 cm-2. The transmission spectrum indicates that the crystal is highly transparent in the 200–1500-nm wavelength range. The emission spectrum of the crystal consists of a peak around 579 nm when excited with 428-nm light. The TL spectra show that the LiAlO2:Mn crystal has glow peaks at 150 and 172 ℃. The change of TL characteristics of the crystal before and after thermal annealing in the air is discussed, and the effect of annealing and irradiation on the evolution of defect types is analyzed.
LiAlO2:Mn晶体 提拉法 结晶质量 光谱 热释光 160.2220 Defect-center materials 160.6990 Transition-metal-doped materials 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 300.6550 Spectroscopy, visible Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(4): 414
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800
The optical loss coefficient at 1053-nm wavelength, influenced by Fe ions in N31-type Nd-doped phosphate laser glass, was determined precisely and analyzed in detail. It is found that the optical loss coefficient per unit of Fe concentration (cm^(-1)/ppmw) increases with Fe concentration in the range of 0---300 ppmw, but it approaches a constant as the Fe concentration is larger than 300 ppmw. Such a concentration effect is due to a shift in the redox equilibrium between Fe3+ and Fe2+ ions in the glass. The effect of oxygen pressure, temperature, and variable valence states of other metal ions in glass samples on the optical loss is also discussed.
160.2750 glass and other amorphous materials 160.6990 transition metal-doped materials 300.1030 absorption 140.3530 lasers neodymium Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(12): 12701





