
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic Engineering and Intelligentization, Dongguan University of Technology, Dongguan 523808, China
2 Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies, CNRS, Université Paris-Saclay, C2N, 91120 Palaiseau, France
A multi-direction bending sensor based on spot pattern demodulation of a dual-hole fiber (DHF) is proposed. By using the interference and scattering in a DHF, the related multidirectional variations can be captured by the optical field. Furthermore, the multi-directional bending characteristics of the fiber are quantitatively described by the pattern of the output light spot, achieving multidirectional bending sensing. In addition, considering the subtle changes in the deformation patterns over time, a convolutional neural network (CNN) model based on deep learning is introduced for accurate recognition and prediction of the bending angle. The experimental results show that the sensor can perceive different bending angles in four directions. These outstanding results indicate that the multi-directional bending sensor based on dual-hole interference pattern decoding has potential applications in multi-directional quantitative sensing and artificial intelligence perception.
microstructured optical fiber fiber device bending sensor Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(12): 122201
东北大学信息科学与工程学院流程工业综合自动化国家重点实验室, 辽宁 沈阳 110004
为满足空分复用和模分复用系统对大容量、多通道通信光纤的需求,提出了一种新型的沟槽-“十字形”空气孔辅助型多芯少模微结构光纤。利用有限元法(FEM)计算并优化光纤结构参数。结果表明:在工作波长1550 nm处,该光纤实现了LP01、LP11、LP21、LP02、LP31 5-LP模式的稳定传输,有效模场面积分别为113.14、159.70、174.43、104.91、192.74 μm 2,且在传输距离为10 km的情况下,芯间串扰均小于-40 dB,相对纤芯复用因子为62.722。与已报道的多芯少模光纤相比,该光纤具有低串扰和大模场面积的优点,可满足未来大容量、多通道传输系统的需求。
中国激光
2021, 48(19): 1906004
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications (Ministry of Education of China), University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
2 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, 50 Nanyang Avenue, 639798, Singapore
3 Research Center for Optical Fiber Sensing, Zhejiang Laboratory, Hangzhou 310000, China
4 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Microelectronics and Optoelectronics, Koszykowa 75, 00-662 Warsaw, Poland
Fiber optofluidic laser (FOFL) integrates optical fiber microcavity and microfluidic channel and provides many unique advantages for sensing applications. FOFLs not only inherit the advantages of lasers such as high sensitivity, high signal-to-noise ratio, and narrow linewidth, but also hold the unique features of optical fiber, including ease of integration, high repeatability, and low cost. With the development of new fiber structures and fabrication technologies, FOFLs become an important branch of optical fiber sensors, especially for application in biochemical detection. In this paper, the recent progress on FOFL is reviewed. We focuse mainly on the optical fiber resonators, gain medium, and the emerging sensing applications. The prospects for FOFL are also discussed. We believe that the FOFL sensor provides a promising technology for biomedical analysis and environmental monitoring.
Optical fiber sensors optofluidic laser microstructured optical fiber optical microcavity biochemical sensors Photonic Sensors
2021, 11(2): 262
1 香港理工大学电机工程学系, 香港
2 香港理工大学深圳研究院光子研究中心, 广东 深圳 518057
微纳结构光纤光谱学是指以空芯微结构或微纳光纤为样品池,光和物质在纤芯内部或表面进行相互作用的光谱学技术。本文回顾空芯和微纳光纤导光的基本原理,介绍气体、液体样品池构建的理论和方法,综述基于光谱吸收、光热、光声、荧光、拉曼等效应的微纳结构光纤光谱学的最新进展及今后可能的发展方向。微纳结构光纤对光场的束缚能力强、模场能量在空气中的比例高,可实现光和物质在其中的高效、长距离相互作用。微纳结构光纤样品池的采用,可提升传统光谱学系统的性能或构建新型的光谱学系统;应用传输光纤与其他光学元器件进行柔性连接,可促进光谱学仪器和传感器的小型化和实用化。
光谱学 激光光谱 微结构光纤 空芯光纤 光纤传感器 纳米光波导 拉曼光谱学
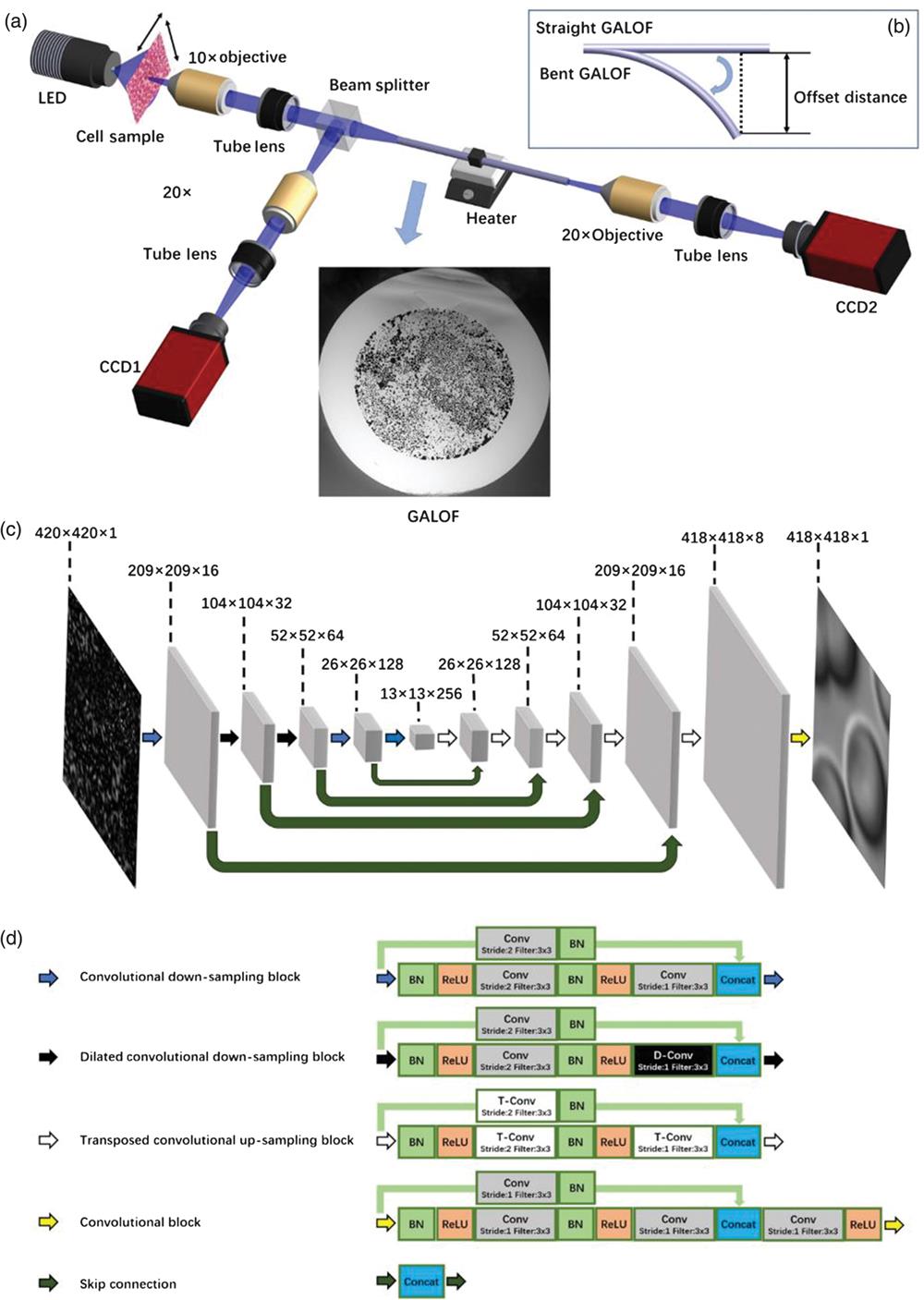
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 University of Central Florida, CREOL, The College of Optics and Photonics, Orlando, Florida, United States
2 Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, State Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Applications, Changchun, China
We demonstrate a deep-learning-based fiber imaging system that can transfer real-time artifact-free cell images through a meter-long Anderson localizing optical fiber. The cell samples are illuminated by an incoherent LED light source. A deep convolutional neural network is applied to the image reconstruction process. The network training uses data generated by a setup with straight fiber at room temperature (~20 ° C) but can be utilized directly for high-fidelity reconstruction of cell images that are transported through fiber with a few degrees bend or fiber with segments heated up to 50°C. In addition, cell images located several millimeters away from the bare fiber end can be transported and recovered successfully without the assistance of distal optics. We provide evidence that the trained neural network is able to transfer its learning to recover images of cells featuring very different morphologies and classes that are never “seen” during the training process.
fiber imaging cell imaging deep learning microstructured optical fiber transverse Anderson localization Advanced Photonics
2019, 1(6): 066001
暨南大学光子技术研究院, 广东省光纤传感与通信技术重点实验室, 广东 广州 510632
提出一种基于大空气孔保偏微结构光纤偏振回旋滤波器(PM-MOF-RF)的光微流折射率传感器。保偏微结构光纤(PM-MOF)沿轴向引入周期性往复扭转结构,可实现光纤中正交偏振模的谐振耦合,通过偏振检测,可得到类似于长周期光栅的透射光谱,从而获得偏振回旋滤波器(PRF)。基于耦合模理论,对该器件的透射光谱进行仿真。在该器件两端与单模光纤(SMF)连接处分别接入一小段C形光纤,可将待测液体导入和导出MOF的空气孔而不影响SMF与MOF的光信号耦合,从而得到一个全光纤的光微流折射率传感器。通过有限元分析方法模拟微流折射率在1.333附近变化时PM-MOF的相模式双折射色散曲线,进而可得不同微流折射率的透射光谱,通过追踪光谱波长漂移,得到7196.4 nm/RIU(RIU为折射率单元)的折射率灵敏度,同时可知当按比例缩小光纤尺寸时,可将其灵敏度提升至16754.0 nm/RIU。
光纤光学 折射率灵敏度 偏振回旋滤波器 微结构光纤 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(17): 170623
华南师范大学广州市特种光纤光子器件与应用重点实验室, 广东 广州 510006
微结构光纤(MOF)在结构和性能上的优越性引起了国内外光纤研究人员的广泛兴趣,成为光电子学领域的前沿热点,并得到了快速发展。MOF根据结构可分为实芯MOF和空芯MOF,根据传输机理可分为全内反射型MOF、光子带隙型MOF和反谐振MOF等多种类型,在激光技术、光传感技术、光通信技术、光电子集成和光纤器件等领域具有重要应用。本文综述了MOF的发展历程,并对MOF的种类、传输机理、结构设计和拉制进行了全面分析和归纳,为未来MOF的研究及应用提供借鉴。
光纤光学 微结构光纤 带隙微结构光纤 空芯反谐振光纤 稀土掺杂微结构光纤 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(17): 170603
廊坊师范学院 电子信息工程学院, 河北 廊坊 065000
为了在理论和实际中研制能够产生高效平坦宽带中红外超连续谱的光纤, 文章提出一种以三硒化二砷(As2Se3)为背景材料的微结构光纤,利用非线性薛定谔方程计算模拟了光纤的结构参数对色散、耗损与非线性特性的影响, 选取优化结构参数实现高非线性色散平坦全正常色散。采用该结构光纤对中超短脉冲的展宽机制进行分析, 研究了光纤长度、泵浦中心波长、峰值功率以及泵浦宽度等参数对超连续谱生成的影响, 并通过此光纤实现平坦中红外超连续谱的输出。搭建了实验平台, 选取优化的光纤长度和泵浦参数检测了飞秒激光脉冲在As2Se3微结构光纤中的传输过程和输出谱, 实验结果表明, 采用该结构光纤能够生成波长展宽为3~6 μm的高效平坦宽带中红外超连续谱, 此连续谱可应用在物质探测、生物化学、食品检测和环境分析等领域。
微结构光纤 超连续谱 中红外波 高非线性 飞秒激光器 microstructured optical fiber supercontinuum mid-infrared wave high-nonlinear femtosecond pulse laser
1 宁波大学高等技术研究院红外材料及器件实验室, 浙江 宁波 315211
2 浙江省光电探测材料及器件重点实验室, 浙江 宁波 315211
硫系玻璃具有超宽的红外光谱透过范围和极高的线性、非线性折射率,因此硫系玻璃光纤成为目前唯一能产生中远红外超连续谱输出的光纤基质材料。综述了传统阶跃型硫系光纤、硫系微结构光纤以及硫系拉锥光纤中红外超连续谱输出的研究进展。
光纤光学 硫系光纤 红外超连续谱 非线性光学 微结构光纤 拉锥光纤 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(9): 090005
1 哈尔滨工程大学 理学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
2 哈尔滨第一机械集团设计研究所,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150056
利用中空悬挂芯光纤研制了一种将荧光猝灭反应区建立在空心光纤内部的光纤集成荧光在线微流传感器。利用CO2激光器在光纤表面刻蚀微孔, 使得试剂可由微孔注入光纤内部并混合形成稳定的微流。在悬挂芯光纤纤芯倏逝场的激发下, 指示剂分子产生荧光, 所产生的荧光被耦合到纤芯内部并在出射端被检测。文中利用光纤内部的荧光猝灭反应实验确定了亚硝酸盐溶液的浓度。结果显示: 微流可在短时间通过光纤, 传感器能以较快的速度检测溶液浓度。另外, 当亚硝酸盐溶液的浓度为0.1~2.6 mmol/L时, 荧光猝灭程度与溶液浓度呈较好的线性关系, 结果证明了该集成式光纤内微流控传感器方案用于微量荧光检测的可行性。
微结构光纤 光纤集成 光纤传感器 荧光传感器 微流传感器 microstructured optical fiber fiber integration optical fiber sensor fluorescence sensor microfluide sensor





