1 长春理工大学 光电工程学院, 吉林 长春 130022
2 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 纳米加工平台, 江苏 苏州 215123
3 中国科学技术大学 纳米技术与纳米仿生学院, 安徽 合肥 230026
将表面配体改性的CdSe/ZnS量子点(Quantum dots)和光刻胶混合, 进而采用光刻工艺在InGaN/GaN蓝光Micro-LED上实现了最小尺寸为3 μm的高分辨率、高光效的量子点颜色转换膜层。同时系统研究了不同厚度和混合比例的量子点膜层的吸收/发射光谱及光致发光量子产率(PLQY)。为优化光转换效率, 量子点膜层中加入了TiO2散射粒子以提高蓝光的吸收效率。更进一步地, 经过设计引入分布式布拉格反射镜(DBR), 使得未被吸收的蓝光光子回弹到量子点转换膜层, 这不仅提升了蓝光吸收效率, 也增强了转换色彩的饱和度。同时采用了热激发方式来提升量子点的光致发光量子产率。为得到更高的显示对比度和色彩饱和度, 引入黑色光阻矩阵来削弱临近图形之间的颜色串扰。实验结果表明, 该量子点膜层可以用光刻技术实现高分辨率、高光效的颜色转换图层, 为单片全彩化Micro-LED显示的发展提供了新颖可靠的技术路线。
量子点 分布式布拉格反射镜(DBR) 颜色转换 散射粒子 Micro-LED Micro-LED quantum dot distributed Bragg reflector(DBR) color conversion scattering particles
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute for Electric Light Sources, School of Information Science and Technology, Engineering Research Center of Advanced Lighting Technology, and Academy of Engineering and Technology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario M5S 3H6, Canada
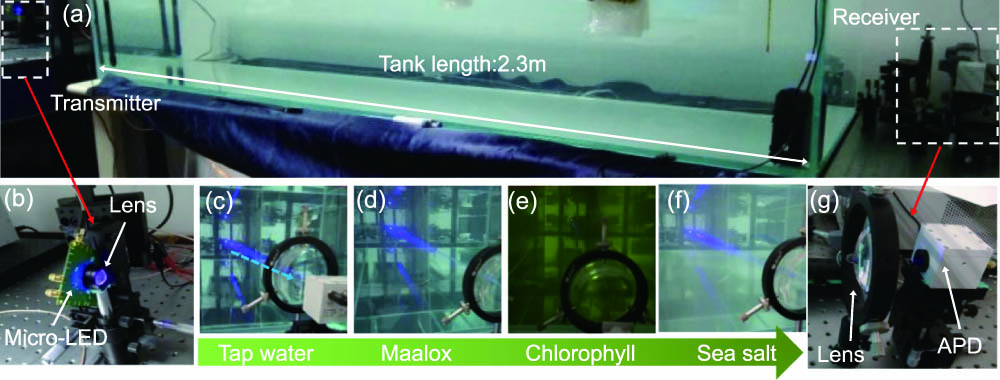
In this work, a blue gallium nitride (GaN) micro-light-emitting-diode (micro-LED)-based underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) system was built, and UWOCs with varied Maalox, chlorophyll, and sea salt concentrations were studied. Data transmission performance of the UWOC and the influence of light attenuation were investigated systematically. Maximum data transmission rates at the distance of 2.3 m were 933, 800, 910, and 790 Mbps for experimental conditions with no impurity, 200.48 mg/m3 Maalox, 12.07 mg/m3 chlorophyll, and 5 kg/m3 sea salt, respectively, much higher than previously reported systems with commercial LEDs. It was found that increasing chlorophyll, Maalox, and sea salt concentrations in water resulted in an increase of light attenuation, which led to the performance degradation of the UWOC. Further analysis suggests two light attenuation mechanisms, e.g., absorption by chlorophyll and scattering by Maalox, are responsible for the decrease of maximum data rates and the increase of bit error rates. Based on the absorption and scattering models, excellent fitting to the experimental attenuation coefficient can be achieved, and light attenuation by absorption and scattering at different wavelengths was also investigated. We believe this work is instructive apply UWOC for practical applications.
220.4830 Systems design 290.5850 Scattering, particles 290.5825 Scattering theory 230.6080 Sources Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100010
1 西北工业大学深圳研究院, 广东 深圳 518057
2 西北工业大学航海学院, 陕西 西安 710072
针对海洋悬浮粒子引起水下激光传输信道的复杂性问题, 采用等效球形粒子米氏散射理论和蒙特卡罗数值模拟方法,研究海洋悬浮粒子对水下光通信链路的影响。分析了悬浮粒子特性及入射光波长与光学系数的关系, 研究了粒子尺寸和复折射率对接收归一化能量、接收光强、信道传输长度、信道时延的影响。理论分析和仿真结果表明:粒子的光学系数会随着粒子尺寸增大而增大, 使相同信道长度的接收归一化能量减小, 接收光强减弱, 信道时延增大;粒子复折射率虚部越小, 接收的归一化能量越强, 接收光强峰值越大, 但复折射率虚部相同而实部不同时, 接收光强峰值的大小取决于反照率, 反照率越大, 接收光强越大。
散射 米氏理论 散射粒子 光子统计

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Jiangxi Engineering Laboratory for Optoelectronics Testing Technology, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
2 National Engineering Laboratory for Nondestructive testing and Optoelectric Sensing Technology and Application, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres with four different particle diameters of 10, 50, 100, and 200 nm suspended in water are investigated theoretical and experimentally in the spectral range of the entire visible range and part of the near-infrared region. The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres suspended in water are described by employing three main parameters: the angular distribution of the scattering intensity I, the scattering extinction coefficient αscat, and the scattering cross section σscat. The results indicate that (i) at a certain wavelength, the angular distribution of the scattering intensity appears as an obviously forward-propagating feature, and the forward-scattering intensity is dominant gradually when the particle diameter increases from 10 to 200 nm, and (ii) the scattering extinction coefficient and cross section can be determined by using the measured transmittance changes of a pure water sample and a given ZnO sample; they all are shown to be dependent on the particle size and incident wavelength. The experimental results of four different scattering samples agree well with the theoretical predictions within the given wavelength range.
290.5850 Scattering, particles 290.5820 Scattering measurements 290.5825 Scattering theory Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 012901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Department of Optical Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027, China
2 School of Computer Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, 637553, Singapore
We demonstrate a size sensing technique for nano-particles using optical differential phase measurement by a dual fiber interferometer through phase-generated carrier (PGC) demodulation. Nano-particle diameters are obtained from the differential phase shift as a result of adding an optical scattering perturbation into two-beam interference. Polystyrene nano-particles with diameters from 200 to 900 nm in a microfluidic channel are detected using this technique to acquire real-time particle diameters. Compared with amplitude sensing with over 10 mW of laser irradiance, particle sizing by PGC phase sensing can be achieved at a laser power as low as 1.18 mW. We further analyze major sources of noise in order to improve the limits of detection. This sensing technique may find a broad range of applications from the real-time selection of biological cell samples to rare cell detection in blood samples for early cancer screening.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 290.5850 Scattering, particles Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(12): 120602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
2 Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center on Atmospheric Environment and Equipment Technology, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
3 School of Electronic & Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
4 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Meteorological Observation and Signal Processing, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
In order to improve the inversion precision of aerosol mass concentrations based on the particle group light scattering method, the concept that particles through a laser beam are equivalent to an aggregate is proposed. A fractal model for aerosol mass concentration using the signal amplitude distribution of aggregates is presented, and then the subsection calibration method is given. The experimental results show that the mass concentrations inversed by this model agree well with those measured by the norm-referenced instrument. The average relative errors of the two experiments are 5.6% and 6.0%, respectively, which are less than those obtained by the conventional inversion model.
290.5850 Scattering, particles 120.5820 Scattering measurements 010.1100 Aerosol detection Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(11): 112901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Electronic Engineering, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
A method of chromatic polarization imaging is presented for the online detection of colorless plastic contaminants from ginned cotton in an industrial setting. To understand the experimental results, we consider a realistic microscopic model, including the multiple scattering of anisotropic fibers and the light propagation in anisotropic slabs. A Monte Carlo code, based on the extended Jones matrix, is developed to simulate photon migration with polarization states, and phase information followed. Using simulations and experiments, we analyze the underlying mechanisms and evaluate the performance of this method with different layer thicknesses. Our approaches proposed in this Letter also have the potential to be applied in tissue imaging, remote sensing, and other scenarios.
290.5855 Scattering, polarization 290.7050 Turbid media 290.5850 Scattering, particles Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(9): 092901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu 610068, China
2 Department of Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
The far-zone scattered spectral density of a light wave on the scattering from a collection of particles is investigated, and the relationship between the character of the collection and the distribution of the scattered spectral density is discussed. It is shown that both the number of particles and their locations in the collection play roles in the distribution of the far-zone scattered spectral density. This phenomenon may provide a potential method to reconstruct the structure character of a collection of particles from measurements of the far-zone scattered spectral density.
290.2558 Forward scattering 290.5850 Scattering, particles Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 102901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Information Sensing and Understanding at Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
Research on light scattering from a large chiral sphere shows that the rainbow phenomenon is different from that of an isotropic sphere. A chiral sphere with certain chirality generates three first-order rainbows. In this Letter, we present a geometric optics interpretation for the phenomenon and make a calculation of the rainbow angles. The ray traces inside the sphere are determined by the reflection and refraction laws of light at the achiral–chiral interface and the chiral–achiral interface. The calculated rainbow angles achieve good agreements with those obtained by the analytical solutions. The effects of chirality and the refractive index of the sphere on rainbow angles are analyzed.
160.1585 Chiral media 080.0080 Geometric optics 290.5850 Scattering, particles Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 121602
1 燕山大学电气工程学院, 河北 秦皇岛 066004
2 东北大学秦皇岛分校控制工程学院, 河北 秦皇岛 066004
研究二维ZnO随机散射粒子中2个对称的圆形区域间光波的耦合特性。利用时域有限差分法(FDTD)数值模拟了二维随机散射系统中2个对称圆形区域间的距离D 变化时的光场分布及模式频谱图,并对D 不同时的情况进行对比分析。分析出射激光的强度和中心波长与D的关系,得到D=0.8 μm时为最佳情况。此时,出射激光中心波长为380.57 nm ,强度为4.81×104。通过观察理想情况下散射系统在仿真过程中的光场分布图表明,2个圆形区域之间的电场强度经过耦合得到放大,且随着圆形区域之间距离D 的增大,出射激光的强度增强,光谱线宽度减小,模式数量减少。
激光光学 随机散射粒子 光波耦合 时域有限差分 模式频谱 光学学报
2015, 35(11): 1114001





