北京大学物理学院人工微结构与介观物理国家重点实验室,北京 100871
飞秒强激光与物质相互作用后辐射出的高次谐波,具有单光子能量高、脉冲持续时间短、时空相干性好等特性,可以作为实验室台式化超快真空紫外和软X射线波段光源,同时高次谐波也可用于产生阿秒脉冲。这些先进光源的产生,极大地丰富了人类物质科学的研究手段。结合本课题组的高次谐波研究进展,介绍了气体高次谐波和固体高次谐波的产生原理、优化及应用。
原子与分子物理学 强场物理 高次谐波产生 阿秒脉冲 超快动力学 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(3): 0300001
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强场激光物理国家重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院超强激光科学卓越创新中心, 上海 201800
3 华东师范大学精密光谱科学与技术国家重点实验室, 上海 200062
空气激光是以空气为增益介质产生的相干辐射,具有高准直度、高相干性、高强度以及自由空间传输等优点,为远程探测提供了全新的技术途径。同时,空气激光是强场超快激光与空气中的原子分子相互作用的结果,蕴含了新颖而丰富的强场物理效应。综述了空气激光近年来的主要研究进展。首先介绍了三类空气激光的产生途径及基本特征,然后从氮气离子激光的增益机制以及量子相干性两个层面阐述了空气激光所蕴含的新物理效应,并讨论了空气激光在远程探测中的应用,最后总结了空气激光研究的意义,展望了该方向面临的机遇与挑战。
超快光学 空气激光 强场激光物理 远程探测
利用改进的强场近似方法,结合时间窗函数,分析了氢原子在强场阈上电离过程中的电子波包(EWP)干涉对光电子能谱及二维(2D)动量谱的影响,发现光电子能谱及2D动量谱的一般特征是由周期内干涉和周期间干涉的共同作用引起的,2D动量谱中的扇形结构是由长程库仑势与周期内干涉作用引起的。利用含时薛定谔方程(TDSE)的数值解分析了多周期脉冲电离过程中周期内干涉被抑制的原因,发现当Keldysh参数接近1时,2D动量谱中出现了特殊的条纹结构,研究结果表明长程库仑势对该条纹的形成有重要的影响。
原子与分子物理学 强场物理 阈上电离 电子波包干涉 二维动量谱 光电子能谱 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(8): 080201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 School of Science, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330013, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
We report on an experimental investigation on the dynamic decoherence process of molecular rotational wavepackets during femtosecond laser filamentation based on time-dependent mean wavelength shifts of a weak probe pulse. Details of periodic revival structures of transient alignment can be readily obtained from the measured shifted spectra due to the periodic modulation of the molecular refractive index. Using the method, we measured decoherence lifetimes of molecular rotational wavepackets in N2 and O2 under different experimental conditions. Our results indicate that decoherence lifetimes of molecular rotational wavepackets are primarily determined by the relative population of rotational states in the wave packet and intermolecular collisions, rather than the focusing intensity.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 300.6530 Spectroscopy, ultrafast Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(12): 120201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
2 School of Physical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of IFSA (CICIFSA), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
We systematically investigate the influences of the input infrared spectrum, chirp, and polarization on the emitted intense terahertz spectrum and spatial dispersion in lithium niobate via optical rectification. The terahertz yield and emission spectrum depend on both the chirp and spectrum of the input pump laser pulses. We also observe slight non-uniform spatial dispersion using a knife-edge measurement, which agrees well with the original predictions. The possible mechanism is the nonlinear distortion effect caused by high-energy laser pumping. Our study is very important and useful for developing intense terahertz systems with applications in extreme terahertz sciences and nonlinear phenomena.
Nonlinear optics Ultrafast optics Strong field laser physics Far infrared or terahertz Photonics Research
2018, 6(10): 10000959
利用改进的强场近似方法分析了长程势以及短程势在阈上电离能谱中的贡献, 确定了能谱中低能结构的起因。同时, 为了确定在计算电子与分子离子散射截面时用纯分子代替分子离子是否合理, 计算了不同入射电子能量条件下, 电子和原子离子弹性散射的微分散射截面。理论计算和实验结果表明在入射电子能量较大时, 长程势在激光诱导的电子离子大角度背向散射时的影响可以忽略, 证明了在大角度散射时, 用纯分子来代替分子离子是合理的。
强场激光物理 阈上电离 强场近似方法 长程势 短程势 光电子能谱 激光与光电子学进展
2018, 55(9): 090201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Nuclear Science and Technology, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
2 Key Laboratory of Special Function Materials and Structure Design, Ministry of Education, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
We investigate the nonadiabatic spectral redshift of high-order harmonic of He driven by two time-delayed orthogonally polarized laser fields. It is found that the nonadiabatic spectral redshift can be observed by properly adjusting the time delay of the two laser fields when the controlling pulse is added in the raising part of the driving pulse in the vertical direction. That is because the controlling pulse in the vertical direction prevents the ionized electrons from returning to the vicinity of parent ions and then reduces the recombination probability. This leads to the high-order harmonic generated mainly in the falling part of the driving pulse. Meanwhile, we also find that the quantity of redshift can be effectively controlled through accommodating the positive time delays. In addition, this scheme can also be used to produce nonadiabatic spectral blueshift.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 320.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 040203
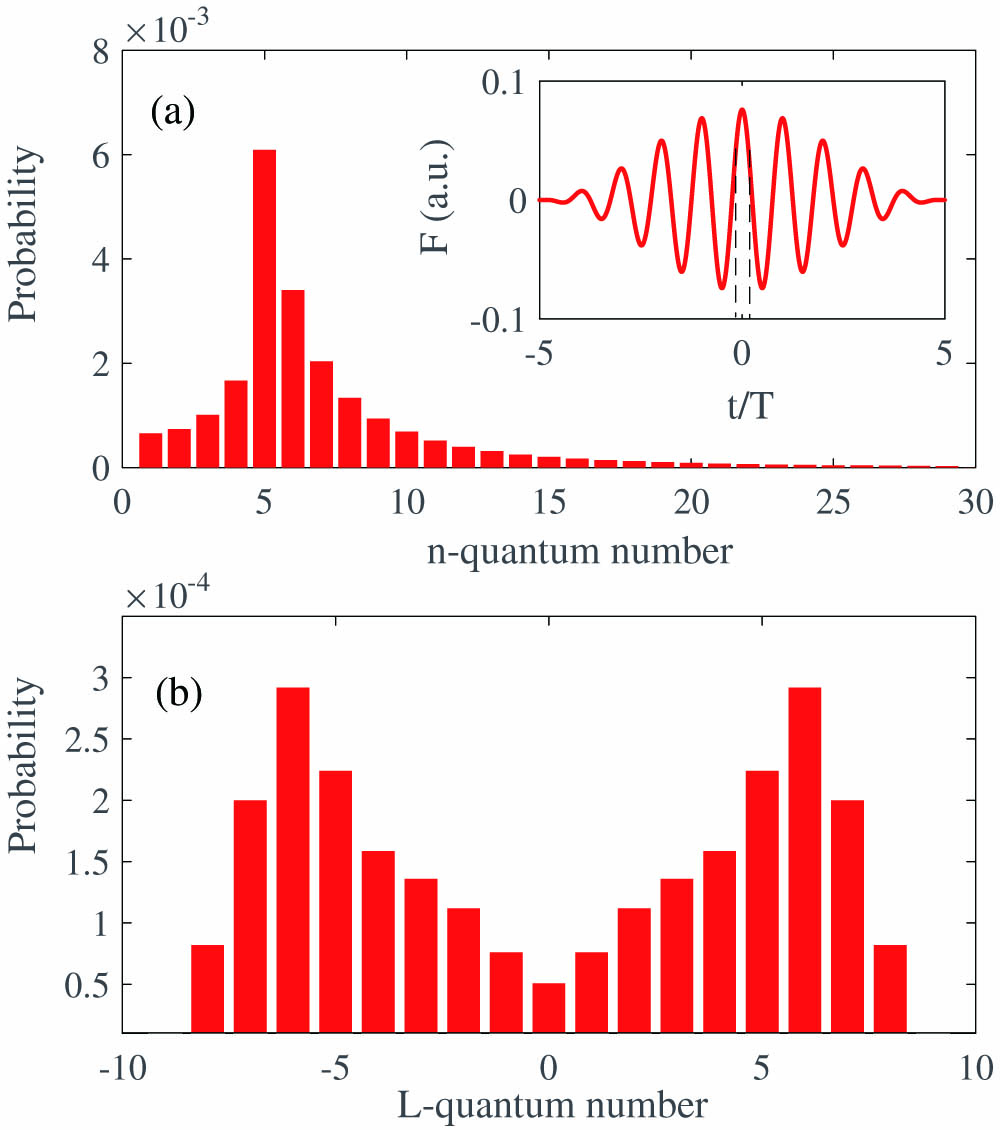
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan 430205, China
Using the classical-trajectory Monte Carlo model, we have theoretically studied the angular momentum distribution of frustrated tunneling ionization (FTI) of atoms in strong laser fields. Our results show that the angular momentum distribution of the FTI events exhibits a double-hump structure. With this classical model, we back traced the tunneling coordinates, i.e., the tunneling time and initial transverse momentum at tunneling ionization. It is shown that for the events tunneling ionized at the rising edge of the electric field, the final angular momentum exhibits a strong dependence on the initial transverse momentum at tunneling. While for the events ionized at the falling edge, there is a relatively harder recollision between the returning electron and the parent ion, leading to the angular momentum losing the correlation with the initial transverse momentum. Our study suggests that the angular momentum of the FTI events could be manipulated by controlling the initial coordinates of the tunneling ionization.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 020.4180 Multiphoton processes 320.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 040202

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of IFSA (CICIFSA), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
4 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
5 School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 200031, China
Beam quality degradation during the transition from a laser wakefield accelerator to the vacuum is one of the reasons that cause the beam transport distortion, which hinders the way to compact free-electron-lasers. Here, we performed transition simulation to initialize the beam parameters for beam optics transport. This initialization was crucial in matching the experimental results and the designed evolution of the beamline. We experimentally characterized properties of high-quality laser-wakefield-accelerated electron beams, such as transverse beam profile, divergence, and directionality after long-distance transport. By installing magnetic quadrupole lenses with tailored strength gradients, we successfully collimated the electron beams with tunable energies from 200 to 600 MeV.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 110.2970 Image detection systems Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 040201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
We theoretically investigate the attosecond pulse generation in an orthogonal multicycle midinfrared two-color laser field. It is demonstrated that multiple continuum-like humps, which consist of about twenty orders of harmonics and an intensity of about one order higher than the adjacent normal harmonics, are generated when longer wavelength driving fields are used. By filtering these humps, intense isolated attosecond pulses (IAPs) are directly generated without any phase compensation. Our proposal provides a simple technique to generate intense IAPs with various central photon energies covering the multi-keV spectral regime by using multicycle midinfrared driving pulses with high pump energy in the experiment.
190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 020.2649 Strong field laser physics 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(7): 071901





