Author Affiliations
Abstract
1
Department of Electro-Optics and Photonics University of Dayton,
USA
2
Electrical Engineering Department University at Buffalo, SUNY,
USA
Metasurface refers to a type of artificial thin film materials with sub-wavelength features that can generate the desired and/or new optical phenomena. The past decade has witnessed significant advances in the metasurface, ranging from fundamental physics to nanomanufacturing methods and practical applications. Typical research efforts include wave-front engineering and detection [e.g., Yu, Science 334, 333 (2011); Capasso, Nat. Commun. 3, 1278 (2012)], flat optics for focusing and imaging [e.g., Cappaso, Nano Lett. 12, 4932 (2012); Yu, Nat. Mater. 13, 139 (2014)], polarization manipulation [e.g., Zhan, Opt. Lett. 40, 4711 (2015); Sci. Rep. 6, 29626 (2016)], metahologram [e.g., Genevet, Rep. Prog. Phys. 78, 24401 (2015); Tsai, Nano Lett. 14, 225 (2014)], light trapping and localization [e.g., Gan, Adv. Mater. 26, 2737 (2014); Adv. Opt. Mater. 5, 1700223 (2017)], absorption engineering [Gan, Adv. Opt. Mater. 5, 1700166 (2017); Sci. Adv. 3, e1602783 (2017)], and colorimetric display. Being able to manipulate the optical properties of metasurfaces will create new regimes of optical physics and impact a broad range of photonic, energy, and biomedical technologies, including new commercial product research and development. Research and development efforts of these artificial thin film materials in promising areas continue to emerge. To capture the latest developments in this important emerging field of optics, it is our pleasure to introduce the Chinese Optics Letters Special Issue on Advances in Metasurface with contributions from scientists around the world who are active in this field.
Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center for Terahertz Waves and College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Opto-electronics Information and Technical Science, Ministry of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, Oklahoma 74078, USA
Surface waves (SWs) are a special form of electromagnetic waves that travel along the boundary between a metal and a dielectric. The special optical properties of SWs render them very attractive in applications, such as subdiffractional lithography, novel biochemical sensors, and ultrafast integrated circuitries. Herein, we present a review of our recent progress in excitation and manipulation of terahertz SWs due to interference or coupling between a pair of slit resonators in metasurfaces, showing the ability to devise ultrathin and compact plasmonic components.
240.6680 Surface plasmons 160.3918 Metamaterials Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Optical Technologies on Nano-Fabrication and Micro-Engineering, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
As a consequence of Kramers–Kronig relations, the wavelength-dependent behavior of the metasurface is one of the critical limitations in existing metasurface structures, which reduces the design freedom among different wavelengths. Here, we present an approach to construct a high-efficiency multi-wavelength metasurface with independent phase control by coding different wavelengths into orthogonal polarizations. As proof of the concept, two dual-band metasurfaces have been proposed and numerically demonstrated by multiple vortex beam generation in near-field and polarization multiplexing achromatic beam deflection. Furthermore, simulated results show that the proposed metasurface exhibits high transmission efficiency at both wavelengths, which may find widespread applications in subwavelength electromagnetics.
160.3918 Metamaterials 350.4010 Microwaves Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Mechanical Engineering and Texas Materials Institute, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas 78712, USA
We report on mid-infrared superabsorbers based on quasi-periodic moiré metasurfaces in metal-insulator-metal form. By varying the spacer thickness, moiré rotation angle, and filling factor of the superabsorbers, we can tune narrowband or broadband absorption in a systematic way. With their high tunability of near-unity absorption and simple fabrication, in combination with decoupled mode theory for an efficient design, moiré superabsorbers are well-suited for a wide range of applications in sensing, imaging, and communication.
160.3918 Metamaterials 120.4120 Moire' techniques 120.2440 Filters Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, UK
2 Center for Terahertz Waves and College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Indefinite media with mixed signs of dielectric tensor elements possess unbounded equifrequency surfaces that have been utilized for diverse applications such as superimaging, enhanced spontaneous emission, and thermal radiation. One particularly interesting application of indefinite media is an optical cavity supporting anomalous scaling laws. In this Letter, we show that by replacing an indefinite medium with magnetized plasma one can construct a tunable indefinite cavity. The magnetized plasma model is based on realistic semiconductor material properties at terahertz frequencies that show hyperbolic dispersion in a certain frequency regime. The hyperbolic dispersion features are utilized for the design of optical cavities. Dramatically different sizes of cavities can support the same resonance mode at the same frequency. For a cavity of fixed size, the anomalous scaling law between the resonance frequency and mode number is confirmed. The resonance frequency can be strongly modulated by changing the strength of the applied magnetic field. The proposed model provides active controllability of terahertz resonances on the deep subwavelength scale with realistic semiconductor materials.
350.4238 Nanophotonics and photonic crystals 350.5400 Plasmas Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050005

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Metasurfaces and structured light have rapidly advanced over the past few years, from being paradigms to forming functional devices and tailoring special light beams for wide emerging applications. Here, we focus on harnessing metasurfaces for structured light manipulation. We review recent advances in shaping structured light by metasurfaces on different platforms (metal, silica, silicon, and fiber). Structured light manipulation based on plasmonic metasurfaces, reflection-enhanced plasmonic metasurfaces, metasurfaces on fiber facets, dielectric metasurfaces, and sub-wavelength structures on silicon are presented, showing impressive performance. Future trends, challenges, perspectives, and opportunities are also discussed.
160.3918 Metamaterials 050.6624 Subwavelength structures 080.4865 Optical vortices Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronics, Carleton University, 1125 Colonel By Drive, Ottawa, Ontario K1S 5B6, Canada
2 Centre for Research in Photonics, University of Ottawa, 25 Templeton Street, Ottawa, Ontario K1N 6N5, Canada
3 Department of Electrical, Computer and Software Engineering, University of Ontario Institute of Technology, 2000 Simcoe Street North Oshawa, Ontario L1H 7K4, Canada
4 School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Ottawa, 800 King Edward Avenue, Ottawa, Ontario K1N 6N5, Canada
5 Department of Physics, University of Ottawa, 150 Louis Pasteur, Ottawa, Ontario K1N 6N5, Canada
We fabricate Schottky contact photodetectors based on electrically contacted Au nanoantennas on p-Si for the plasmonic detection of sub-bandgap photons in the optical communications wavelength range. Based on a physical model for the internal photoemission of hot carriers, photons coupled onto the Au nanoantennas excite resonant plasmons, which decay into energetic “hot” holes emitted over the Schottky barrier at the Au/p-Si interface, resulting in a photocurrent. In our device, the active Schottky area consists of Au/p-Si contact and is very small, whereas the probing pad for external electrical interconnection is larger but consists of Au/Ti/p-Si contact having a comparatively higher Schottky barrier, thus producing negligible photo and dark currents. We describe fabrication that involves an electron-beam lithography step overlaid with photolithography. This highly compact component is very promising for applications in high-density Si photonics.
240.6680 Surface plasmons Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050007
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Tunable Laser Technology, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Optoelectronic Information System, Shenzhen Graduate School, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
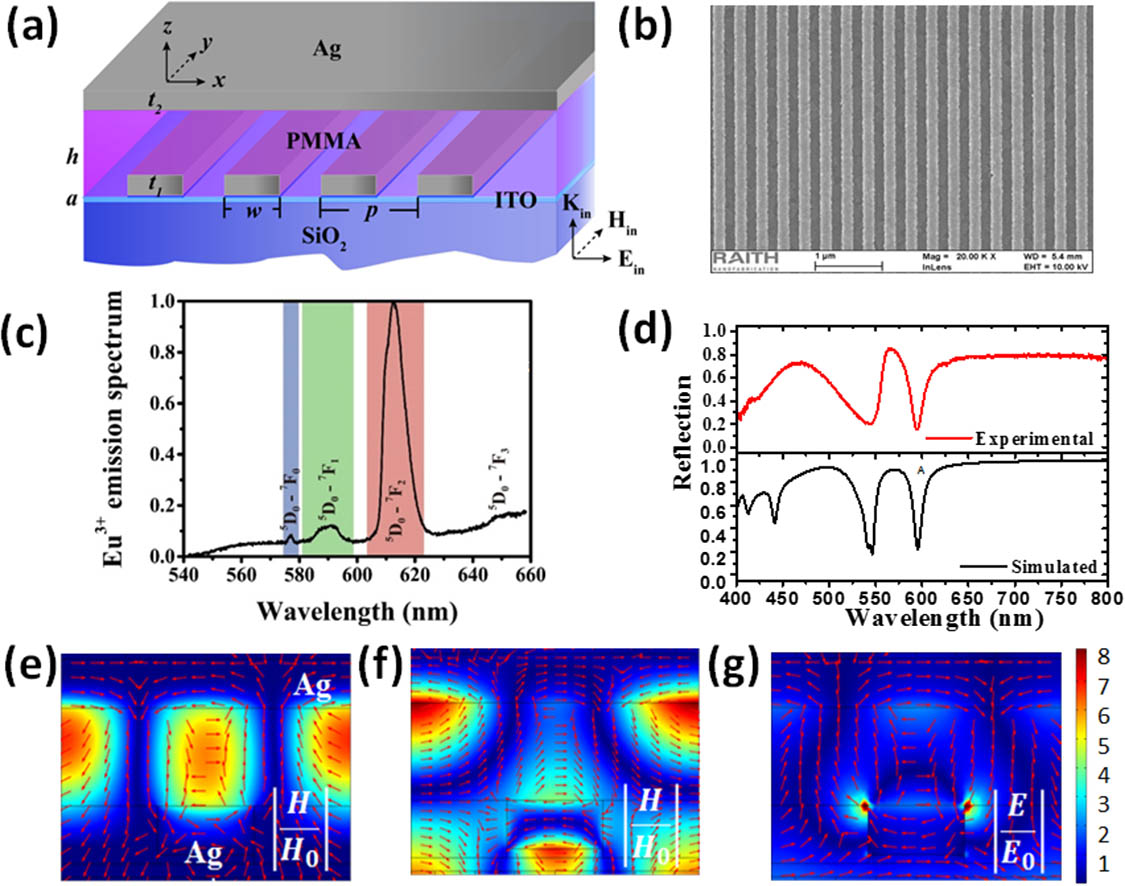
Magnetic dipole (MD) transitions are important for a range of technologies from quantum light sources and displays to lasers and bio-probes. However, the typical MD transitions are much weaker than their electric counterparts and are usually neglected in practical applications. Herein, we experimentally demonstrate that the MD transitions can be significantly enhanced by the well-developed magnetic metamaterials in the visible optical range. The magnetic metamaterials consist of silver nanostrips and a thick silver film, which are separated with an Eu3+:polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) film. By controlling the thickness of the Eu3+:PMMA film, the magnetic resonance has been tuned to match the emission wavelength of MDs. Consequently, the intensity of MD emission has been significantly increased by around 30 times at the magnetic resonance wavelength, whereas the intensity of electric dipole emission is well-preserved. The corresponding numerical calculations reveal that the enhancement is directly generated by the magnetic resonance, which strongly increases the magnetic local density of states around the MD emitter and can efficiently radiate the MD emission into the far field. This is the first demonstration, to the best of our knowledge, that MD transitions can be improved by an additional degree of magnetic freedom, and we believe this research shall pave a new route towards bright magnetic emitters and their potential applications.
160.3918 Metamaterials 160.6990 Transition-metal-doped materials 350.5400 Plasmas 310.6628 Subwavelength structures,nanostructures 300.6550 Spectroscopy, visible Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050008

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Inter-University Semiconductor Research Center, Seoul National University, Gwanak-Gu Gwanakro 1, Seoul 08826, South Korea
2 School of Electronics Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, South Korea
We propose the active metasurface using phase-change material Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST), which has two distinct phases so called amorphous and crystalline phases, for an ultrathin light path switching device. By arranging multiple anisotropic GST nanorods, the gradient metasurface, which has opposite directions of phase gradients at the two distinct phases of GST, is demonstrated theoretically and numerically. As a result, in the case of normal incidence of circularly polarized light at the wavelength of 1650 nm, the cross-polarized light deflects to 55.6° at the amorphous phase and +55.6° at the crystalline phase with the signal-to-noise ratio above 10 dB.
160.3918 Metamaterials 220.1080 Active or adoptive optics Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050009

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, Taipei University of Technology, Taipei 10608, China
2 School of Information Science and Engineering, Fujian University of Technology, Fuzhou 350118, China
A 52 m/9 Gb/s four-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM4) plastic optical fiber (POF)-underwater wireless laser transmission (UWLT) convergence with a laser beam reducer is proposed. A 52 m/9 Gb/s PAM4 POF-UWLT convergence is practically demonstrated with the application of a laser beam reducer to reduce the collimated beam diameter. A 50 m graded-index (GI)-POF is employed as an underwater extender to efficiently enhance the coverage of UWLT. The performances of PAM4 POF-UWLT convergence in view of bit error rate (BER) and eye diagrams improve with the decrease of the collimated beam diameter because of the small amount of light absorbed by clear ocean water. Competent BER and eye diagrams (three independent eye diagrams) are achieved over a 50 m GI-POF transmission with a 2 m clear ocean water link.
010.3310 Laser beam transmission 010.7340 Water Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
A simple and robust technique is reported to offset lock a single semiconductor laser to the atom resonance line with a frequency difference easily adjustable from a few tens of megahertz up to tens of gigahertz. The proposed scheme makes use of the frequency modulation spectroscopy by modulating sidebands of a fiber electro-optic modulator output. The short-term performances of a frequency offset locked semiconductor laser are experimentally demonstrated with the Allan variance of around 3.9×10 11 at a 2 s integration time. This method may have many applications, such as in Raman optics for an atom interferometer.
020.1335 Atom optics 140.3425 Laser stabilization 140.3518 Lasers, frequency modulated Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
The fabrication and characterization of p-i-n photodiodes integrated with wide spectrum focusing reflectors using nonperiodic strip and concentric-circular subwavelength gratings are presented. The experimental results show that the gratings can reflect and focus the incident light on the absorber of the photodiode, and thus can simultaneously achieve high speed and high efficiency. For the gratings’ integrated photodiodes, the responsivity is improved over a wide spectral range, and when the absorber was 600 nm and the mesa diameter was 40 μm, a responsivity of 0.46 A/W at a wavelength of 1.55 μm and a 3 dB bandwidth of 21.6 GHz under a reverse bias of 3 V were simultaneously obtained.
130.3120 Integrated optics devices 230.5170 Photodiodes Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 051301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Materials Synthesis and Processing, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
2 Synthetic Single Crystal Research Center, Key Laboratory of Transparent and Opto-Functional Inorganic Materials, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201899, China
3 State Key Laboratory on High Power Semiconductor Lasers, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
4 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, College of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
5 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201899, China
Tm:CaF2 and Tm,Y:CaF2 single crystals were prepared by the temperature gradient technique. The spectral properties of Tm,Y:CaF2 single crystals were investigated and compared with those of Tm:CaF2. It was demonstrated that codoping with Y3+ ions could efficiently improve the spectroscopic properties. Tm,Y:CaF2 crystals have larger absorption cross-sections at the pumping wavelength, larger mid-infrared stimulated emission cross-sections, and much longer fluorescence lifetimes of the upper laser level (Tm3+: H43 level) than Tm:CaF2 crystals. Continuous-wave (CW) lasers around 1.97 μm were demonstrated in 4.0 at. % Tm,4.0 at. % Y:CaF2 single crystals under 792 nm laser diode (LD) pumping. The best laser performance has been demonstrated with a low threshold of 0.368 W, a high slope efficiency of 54.8%, and a maximum output power of 1.013 W.
140.2020 Diode lasers 140.3070 Infrared and far-infrared lasers 140.3380 Laser materials Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 051401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Division of Time and Frequency Metrology, National Institute of Metrology, Beijing 100029, China
2 Department of Precision Instrument, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
A clock laser based on a 30-cm-long ultrahigh finesse optical cavity was developed to improve the frequency stability of the Sr optical lattice clock at the National Institute of Metrology. Using this clock laser to probe the spin-polarized Sr87 atoms, a Rabi transition linewidth of 1.8 Hz was obtained with 500 ms interrogation time. Two independent digital servos are used to alternatively lock the clock laser to the S01 (mF=+9/2)→P03 (mF=+9/2) transition. The Allan deviation shows that the short-term frequency stability is better than 3.2×10 16 and averages down followed by 1.8×10 15/τ.
140.3425 Laser stabilization Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 051402

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
4 National Engineering Laboratory for Modern Materials Surface Engineering Technology, Guangdong Institute of New Materials, Guangzhou 510650, China
Laser-induced modification at 355 nm of deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate (DKDP) crystals following exposure to nanosecond (ns) and sub-ns laser irradiation is investigated in order to probe the absorption mechanism in damage initiation. Laser damage resistance is greatly improved by sub-ns laser conditioning, whereas only a little improvement occurred after ns laser conditioning at the same laser fluence. Moreover, scattering and transmittance variations after the two types of laser conditioning indicate similar reduction of linear absorption. However, by contrast, large differences on nonlinear absorption modification are discovered using Z-scan measurement. This characteristic absorption modification by laser irradiation provides evidence that a nonlinear absorption mechanism plays a key role in damage initiation at 355 nm.
160.4670 Optical materials 190.4180 Multiphoton processes Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 051601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Photonics, Faculty of Science, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
2 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS B3J 2X4, Canada
The optical properties of a three-arm plasmonic nanoantenna with and without broken symmetry were analyzed in detail. For the symmetrical structure, the local electric field can be significantly enhanced and well confined within the feed gap, whilst the extinction spectrum illustrates polarization independence. With broken symmetry, multi-wavelength resonances are observed due to the single dipole resonance and dipole–dipole coupling effect, and wide tunability is also available through minor structural adjustment. Especially when illuminated by a circularly polarized light beam, the extinction and the electric field distribution can be effectively modulated by just varying the incident wavelength.
260.5430 Polarization 290.2200 Extinction Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 052501
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices, Institute of Opto-Electronics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
The intensity difference squeezed state, which means that the fluctuation of the intensity difference between signal and idler beams is less than that of the corresponding shot noise level (SNL), plays an important role in high sensitivity measurement, quantum imaging, and quantum random numbers generation. When an optical parametric oscillator consisting of a type-II phase-matching periodically poled KTiOPO4 crystal operates above the threshold, an intensity difference squeezed state at a telecommunication wavelength can be obtained. The squeezing of 7.7±0.5 dB below the SNL is achieved in an analysis frequency region of 2.4–5.0 MHz.
270.0270 Quantum optics Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 052701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
2 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4 Osaka University, Osaka 565-0871, Japan
In this Letter, we experimentally explore the pulse-contrast degradation caused by surface reflection in optical parameter chirped-pulse amplification. Different pump-to-signal conversion efficiencies and post-pulses with different intensities are obtained by changing the seed-pulse or pump-pulse energy and inserting etalons with different reflection coefficients, respectively. The contrast measurements show that the generated first pre-pulse intensity is proportional to the product of the surface reflection intensity ratio and the square of the pump-to-signal conversion efficiency.
190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 053201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4 School of Life Science and Technology, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
An objective visual performance evaluation with visual evoked potential (VEP) measurements was first integrated into an adaptive optics (AO) system. The optical and neural limits to vision can be bypassed through this system. Visual performance can be measured electrophysiologically with VEP, which reflects the objective function from the retina to the primary visual cortex. The VEP measurements without and with AO correction were preliminarily carried out using this system, demonstrating the great potential of this system in the objective visual performance evaluation. The new system will provide the necessary technique and equipment support for the further study of human visual function.
330.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices 220.1080 Active or adoptive optics 330.4300 Vision system - noninvasive assessment 330.1070 Vision - acuity Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 053301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry of Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 National Demonstration Center for Experimental Physics Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
3 Photonics Research Center, Guilin University of Electronics Technology, Guilin 541004, China
We propose and demonstrate single fiber dual-functionality optical tweezers based on a graded-index multimode fiber. By using the multi-angle fiber grinding and polishing technology, we fabricate the multimode fiber tip to be a special tapered shape, contributing to focus the outgoing beam with a large intensity gradient for the first functionality—three-dimensional contactless trapping of a microparticle. By adjusting the radial direction offset between the lead-in single mode fiber and the graded-index multimode fiber, we perform the second functionality—axial shift of the trapped microparticle with respect to the fiber tip without need of moving the fiber probe itself. It is convenient for practical applications. The theoretical and experimental results about the relationship between the radial offset and the equilibrium positions of the microparticle have the good consistency. Tailoring the trap and axial shift of the microparticle based on the graded-index multimode fiber provides convenient avenues for fiber optical tweezers applied in practical researches.
350.4855 Optical tweezers or optical manipulation Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 053501
 Download:1027次
Download:1027次 Download:852次
Download:852次 Download:688次
Download:688次 Download:819次
Download:819次