Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
3 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
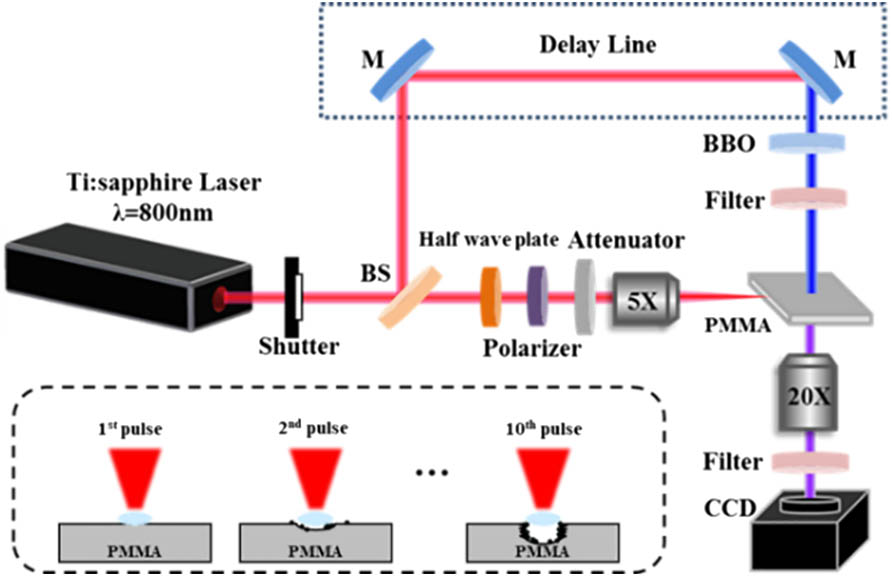
Cylindrical shockwaves inside polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) generated simultaneously with two hemispherical shockwaves induced by a femtosecond Gaussian beam laser were investigated using an ultrafast pump–probe imaging technique. The evolutions of these three shockwaves with probe delay and incident pulse number have been systematically analyzed. The plasma intensity and filament length in the center of cylindrical shockwave both decayed with pulse number. Moreover, the self-focused filament moved downstream towards the output surface with an increased pulse number. The experimental results and mechanism illustrated that energy deposition was suppressed by a degraded nonlinear effect due to a pre-ablated structure in multi-pulse irradiation.
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 320.7120 Ultrafast phenomena 350.5400 Plasmas 350.3390 Laser materials processing Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081405

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Vibration and Noise Control Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
3 School of Optoelectronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
We propose a temperature-insensitive refractive index (RI) fiber sensor based on a Mach–Zehnder interferometer. The sensor with high sensitivity and a robust structure is fabricated by splicing a short photonic crystal fiber (PCF) between two single-mode fibers, where two microcavities are formed at both junctions because of the collapse of the PCF air holes. The microcavity with a larger equatorial dimension can excite higher-order cladding modes, so the sensor presents a high RI sensitivity, which can reach 244.16 nm/RIU in the RI range of 1.333–1.3778. Meanwhile it has a low temperature sensitivity of 0.005 nm/°C in the range of 33°C–360°C.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 020603
1 华中科技大学武汉光电国家实验室, 湖北 武汉 430074
2 美国内布拉斯加林肯大学电子工程系, 林肯 68503, 美国
3 北京理工大学机械与车辆学院, 北京 100081
介绍了碳纳米管(CNTs)/聚合物复合材料分散性、定向排布和组装方面的研究进展, 并利用双光子聚合(TPP)激光直写技术, 实现了多壁碳纳米管(MWNTs)在三维空间的定向排布和分子组装。通过加入硫醇分子, 提升了MWNTs/聚合物复合材料中CNTs的分散性和掺杂浓度, 增强了CNTs/聚合物复合材料在电学、光学、力学方面的性能, 并成功实现了三维CNTs功能器件的制造。研究结果表明, 通过将TPP激光直写技术与热退火工艺相结合, 可以实现对CNTs簇排列方向和位置的精确控制。
激光制造 三维微纳制造 碳纳米管 双光子聚合 飞秒激光直写
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
An optical fiber extrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometer (EFPI) is designed and fabricated for refractive index (RI) sensing. To test the RI of liquid, the following two different methods are adopted: the wavelength tracking method and the Fourier-transform white-light interferometry (FTWLI). The sensitivities of sensors with cavity lengths of 288.1 and 358.5 μm are 702.312 nm/RIU and 396.362 μm/RIU, respectively, by the two methods. Our work provides a new kind of RI sensor with the advantages of high sensitivity, mechanical robustness, and low cross sensitivity to temperature. Also, we provide a new method to deal with gold film with a femtosecond laser.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(2): 020602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano-Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
A simple and repeatable method to fabricate high-aspect-ratio (HAR) and high-quality microgrooves in silica is reported. The method consists of two steps: (1) formation of laser-modified regions by femtosecond Bessel beam irradiation, and (2) removing laser-modified regions through HF etching. Uniform, straight microgrooves can be fabricated and the highest aspect ratio that can be reached is ~52. The phenomenon is attributed to the uniform energy distribution in the long propagation distance, which leads to the long and uniform laser-modified regions and subsequent HF acid etching of laser-modified regions with high selectivity. This method will have potential applications in fabrication of HAR microgrooves in transparent materials.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 230.4000 Microstructure fabrication 320.5540 Pulse shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 041405

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
A surprising phenomenon can be discovered by using femtosecond double-pulse ablation of silicon and germanium in ethanol. The ablation areas present an oscillation increase phenomenon when the pulse delay increases from 200 fs to 1 ps in the fluence range of 0.5–0.6 J/cm2. In contrast, the ablation areas exhibit an oscillation decrease phenomenon as the pulse delay increases when the laser fluence F<0.5 J/cm2, which is consistent with the results of the experiment in air. It is considered that the adjustment of the photon–electron coupling efficiency by pulse train technology plays an important role in the ablation process.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 320.5540 Pulse shaping 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 041402

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
We report a simple, cost-effective and repeatable method for fabricating a large area and uniform substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). The silicon, micromachined by a femtosecond laser, is coated with gold film and then treated through the dewetting process. The morphology shows a higher electric field enhancement due to light trapping. The enhancement factor of the SERS substrate is 9.2×107 with a 5 nm-thick film coated. Moreover, it also exhibits a uniform signal through Raman mapping and chemical stability with the greatest intensity deviation of 6% after a month. The proposed technique provides an opportunity to equip microchips with the SERS capabilities of high sensitivity, chemical stability, and homogeneous signals.
240.6695 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(11): 111401
北京理工大学先进加工技术国防重点学科实验室, 北京 100081
飞秒激光具有超快、超强的特性,在微孔加工中有着独特的优势,尤其是针对高品质、大深径比的微孔加工有着不可替代的作用。介绍了超短脉冲激光微孔加工的优势以及研究意义,综述了近十几年来基于超短脉冲激光的微孔加工研究现状,并讨论了材料、激光脉冲参数、加工方式和加工环境等因素对超短脉冲激光微孔加工的影响。指出了现阶段超短脉冲激光微孔加工的应用前景,并总结了超短脉冲激光微孔加工当前所面临的挑战,以及今后的研究重点。
超快光学 超短脉冲激光 微孔加工 飞秒脉冲 脉冲序列
1 北京理工大学 三院 机械制造及其自动化系, 北京 100081
2 北京理工大学 国际教育合作学院, 北京 100081
3 Laser-Based Manufacturing Laboratory Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Missouri University of Science & Technology (formerly University of Missouri-Rolla) Rolla, MO 65409, USA
飞秒激光烧蚀过程中的微能量传导过程包括两个阶段:1)脉冲激光入射到物质上时电子对激光能量的吸收过程;2)激光脉冲照射后电子所吸收的能量在物质中重新分布导致的材料去除过程,即相变过程。本文讨论了飞秒激光,特别是功率密度在1013 ~ 1014 W/cm2的脉冲与宽禁带物质相互作用中相变过程的理论研究进展,分析了飞秒激光烧蚀过程中的材料去除机理,尤其是热气化和库仑爆炸两种机理。根据对飞秒激光烧蚀中微能量传导过程的讨论,总结了烧蚀阈值功率密度和烧蚀深度计算方面仍有待解决的问题。
热气化 库仑爆炸 阈值功率密度 烧蚀深度
1 北京理工大学 三院 机械制造及其自动化系, 北京 100081
2 北京理工大学 国际教育合作学院, 北京 100081
3 Laser-Based Manufacturing Laboratory Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Missouri University of Science & Technology (formerly University of Missouri-Rolla) Rolla, MO 65409, USA
飞秒激光产生的新现象引导了超快科学新领域的发展,对这些现象中存在的极其复杂的非线性、非平衡过程的理论解释是一个巨大挑战。虽然以飞秒激光为工具已取得大量成功实验结果,但在飞秒激光与物质相互作用方面尚不存在一个完备的理论模型可以全面描述它。本文综述了近期对飞秒激光,特别是功率密度在1013~1014 W/cm2的激光脉冲与宽禁带物质相互作用中光子吸收电离过程的理论研究进展,在该光子-电子相互作用的过程中主要考虑了多光子电离和雪崩电离。
飞秒激光烧蚀 宽禁带物质 光子-电子相互作用 多光子电离 雪崩电离





