1 江苏大学计算机科学与通信工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
2 江苏大学江苏省工业网络安全技术重点实验室,江苏 镇江 212013
为设计新型光学生物传感器,本课题组构造了基于Parity-Time (PT)对称的耦合谐振腔系统,用于实现对人体血糖浓度的测量。通过结构优化,使系统达到PT对称极点状态,然后利用极点状态下透射率对血糖折射率极其敏感的特性,将对血糖浓度的测量转化为对系统透射率的测量,从而达到血糖传感的目的。本文研究了两种传感方式:一是固定特定极点处的频率,测量系统在不同血糖浓度下的透射率;二是在极点附近的频率范围内扫描,测量特定血糖浓度下透射率的峰值。血糖质量浓度为20~182 mg/dL时,第二种方式下传感器的灵敏度均高于第一种方式;当血糖质量浓度高于182 mg/dL时,第一种方式在1466.40 THz频率下的灵敏度要比第二种方式高。可以将本文对血糖浓度的传感方式推广到对其他生物样本的测量上。
传感器 PT对称结构 耦合谐振腔 极点 灵敏度

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
3 e-mail: phytong@zju.edu.cn
We theoretically investigate dark dimer mode excitation and strong coupling with a nanorod dipole. Efficient excitation of a dark mode in a gold (Au) nanorod dimer using an electric dipole can be achieved by an optimal overlap between the dipole moment and dark modal field. By replacing the dipole emitter with an Au nanorod, a plane wave excited dipole mode in the nanorod can be effectively coupled to the dark dimer mode through near-field interaction. At a 10-nm separation of the nanorod and the dimer, plasmonic interaction between dipole-dark modes enters the strong coupling regime with a Rabi-like splitting of 219.2 meV, which is further evidenced by the anticrossing feature and Rabi-like oscillation of electromagnetic energy of the coupled modes. Our results propose an efficient approach to far-field activating dark modes in coupled nanorod dimers and exchanging plasmonic excitations at nanoscale, which may open new opportunities for nanoplasmonic applications such as nanolasers or nanosensors.
Plasmonics Coupled resonators Surface plasmons Photonics Research
2018, 6(9): 09000887
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Washington University, St. Louis, Missouri 63130, USA
2 Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
3 Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA
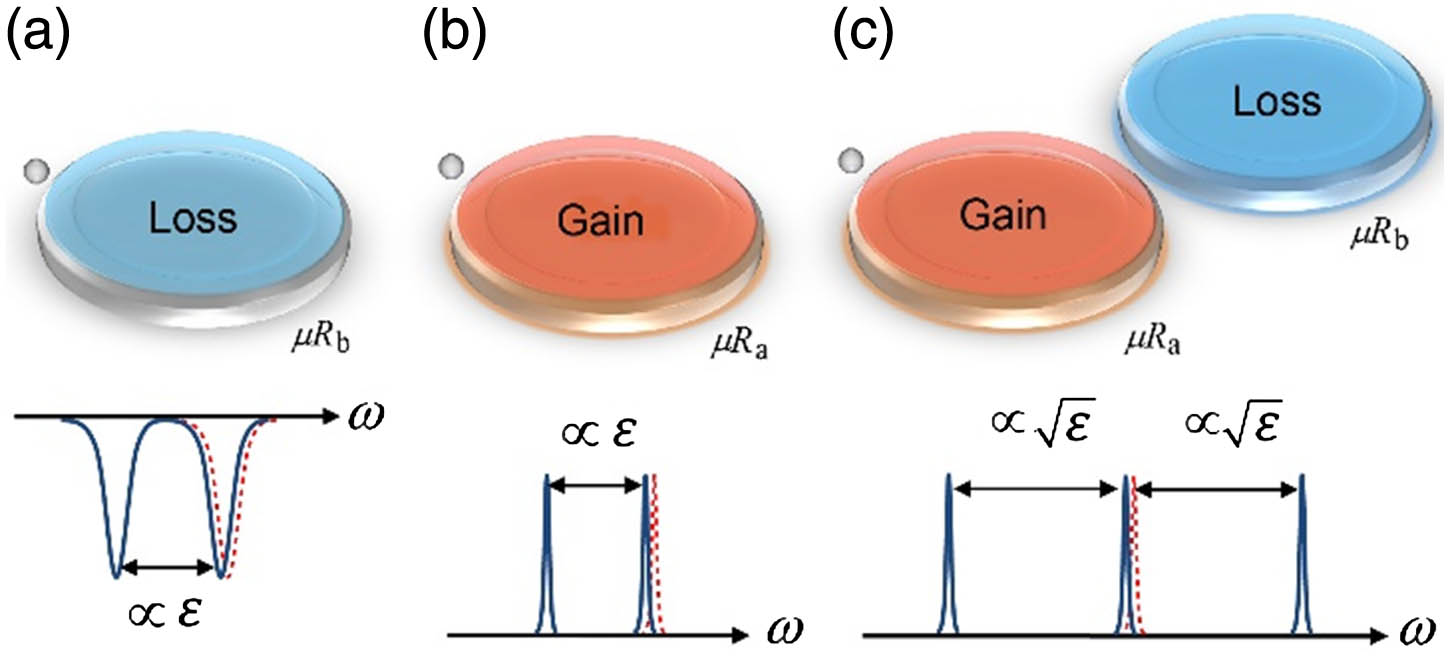
We present a study of single nanoparticle detection using parity-time (PT) symmetric whispering-gallery mode (WGM) resonators. Our theoretical model and numerical simulations show that, with balanced gain and loss, the PT-symmetric WGM nanoparticle sensor, tailored to operate at PT phase transition points (also called exceptional points), exhibits significant enhancement in frequency splitting when compared with a single WGM nanoparticle sensor subject to the same perturbation. The presence of gain in the PT-symmetric system leads to narrower linewidth, which helps to resolve smaller changes in frequency splitting and improve the detection limit of nanoparticle sensing. Furthermore, we also provide a general method for detecting multiple nanoparticles entering the mode volume of a PT-symmetric WGM sensor one by one. Our study shows the feasibility of PT-symmetric WGM resonators for ultrasensitive single nanoparticle and biomolecule sensing.
Sensors Coupled resonators Resonators Photonics Research
2018, 6(5): 05000A23

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Photonics Research Group, Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica e dell’Informazione, Politecnico di Bari, Via E. Orabona n. 4, 70125 Bari, Italy
2 QOpSyS SRL, Via Matteotti n. 23, 70023 Gioia del Colle, Bari, Italy
Redirecting the flow of light on the basis of the absorption/gain properties of optical systems is of great interest in many research fields, ranging from optical routing to optical cloaking. In this paper we investigate the control of the direction of the light propagation through loss-induced absorption in passive linear coupled optical systems. The considered optical system consists of a mode-splitting resonant cavity formed by coupling a Fabry–Perot (FP) cavity with a ring resonator. The coalescence of the asymmetric resonances, generated through mode-splitting dynamics, is the spectral result of the parity time symmetry breaking at FP resonance wavelengths. For specific values of the FP overall loss, a predominant backward propagation in the FP ring resonator occurs. In fiber optics technology, this device shows an ability to invert the sense of propagation of the light, quantified through the contrast ratio, in the order of 20 dB. This value can be obtained by externally varying the FP loss coefficient for a fixed set of the other physical parameters of the FP ring resonator. Our results can open a new way toward novel high-performance optical modulation and routing schemes.
Resonators Coupled resonators Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000525

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Quantum Manipulation and New Energy Materials, College of Physics and Energy, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, China
2 Fujian Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Semiconductors and Efficient Devices, Xiamen 361005, China
3 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230026, China
We report on the transmission spectra of a sausage-like microresonator (SLM) in aqueous environment, where a fiber taper is used as a light coupler. The transmission spectra show an interesting dependence on the coupling position between the SLM and the fiber taper. When the SLM is moved along the fiber taper, the line shape can evolve periodically among symmetric dips, asymmetric Fano-like resonance line shapes, and symmetric peaks. A coupled-mode theory with feedback is developed to explain the observation. The observation of Fano-like resonance in aqueous environment holds great potential in biochemical sensing.
Resonators Micro-optical devices Coupled resonators Photonics Research
2017, 5(2): 02000119

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, Shanxi 030006, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices, Institute of Opto-Electronics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
We theoretically propose blue-detuned optical trapping for neutral atoms via strong near-field interfacing in a plasmonic nanohole array. The optical field at resonance forms a nanoscale-trap potential with an FWHM of 200 nm and about ~370 nm away from the nanohole; thus, a stable 3D atom trapping independent of the surface potential is demonstrated. The effective trap depth is more than 1 mK when the optical power of trapping light is only about 0.5 mW, while the atom scattering rate is merely about 3.31 s?1, and the trap lifetime is about 800 s. This compact plasmonic structure provides high uniformity of trap depths and a two-layer array of atom nanotraps, which should have important applications in the manipulation of cold atoms and collective resonance fluorescence.
(240.6680) Surface plasmons (230.4555) Coupled resonators (020.1335) Atom optics (020.7010) Laser trapping. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000436
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Information Engineering, North China University of Technology, Beijing 100144, China
In this paper, optical pulse repetition rate multiplication based on a series-coupled double-ring resonator is proposed. First, the spectral characteristic of the series-coupled double-ring resonator is simulated and the optimum coupling coefficients to achieve a periodic flat-top passband are obtained. Then, high-quality pulse repetition rate multiplication is realized by periodically filtering out spectral lines of the input pulse train. Different multiplication factors N = 2, 3, 4, 5 can be obtained by adjusting the ring radii. In addition, compared with a single-ring resonator, the multiplied output pulse train by a series-coupled double-ring resonator exhibits much better power uniformity.
Integrated optics devices Integrated optics devices Coupled resonators Coupled resonators Wavelength filtering devices Wavelength filtering devices Photonics Research
2016, 4(2): 02000061
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, School of Electronics Engineering and Computer Science, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
We review current silicon photonic devices and their performance in connection with energy consumption. Four critical issues are identified to lower energy consumption in devices and systems: reducing the influence of the thermo-optic effect, increasing the wall-plug efficiency of lasers on silicon, optimizing energy performance of modulators, and enhancing the sensitivity of photodetectors. Major conclusions are (1) Mach–Zehnder interferometer-based devices can achieve athermal performance without any extra energy consumption while microrings do not have an efficient passive athermal solution; (2) while direct bonded III–V-based Si lasers can meet system power requirement for now, hetero-epitaxial grown III–V quantum dot lasers are competitive and may be a better option for the future; (3) resonant modulators, especially coupling modulators, are promising for low-energy consumption operation even when the power to stabilize their operation is included; (4) benefiting from high sensitivity and low cost, Ge/Si avalanche photodiode is the most promising photodetector and can be used to effectively reduce the optical link power budget. These analyses and solutions will contribute to further lowering energy consumption to meet aggressive energy demands in future systems.
Energy transfer Energy transfer Integrated optics devices Integrated optics devices Semiconductor lasers Semiconductor lasers Coupled resonators Coupled resonators Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) Photonics Research
2015, 3(5): 05000B28
湘南学院电子信息与电气工程学院,湖南 郴州 423000
研究了一类L 形和矩形谐振腔侧面耦合MDM结构亚波长表面等离激元滤波器的色散关系和透射谱。研究结果表明等效 折射率的实部和虚部在短波部分变化较大,在800~2000 nm长波部分趋于稳定值,传播距离随着波长的增加和 介质层厚度的增加均增加,当波导宽度在50 nm以上时,SPPs的传播距离在所研究的波长范围内为4~9 μm,可以满足纳米光子器件的尺寸要求。对侧面L型谐振腔和矩形谐振腔耦合的透射谱研究表明在保持腔体总长度不变的 情况下,两种耦合方式所产生的光 谱曲线完全相似,说明禁带的出现只与谐振腔的长度有关系,对集成光子器件的研发具有一定的参考意义。
表面光学 表面等离激元 滤波器 耦合谐振腔 色散关系 透射谱 surface optics surface plasmons filter coupled resonators dispersion relation transmission spectrum
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, School of Electronics Engineering and Computer Science, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Xi’an Flight Automatic Control Research Institute, Aviation Industries of China (AVIC), Xi’an 710065, China
A novel athermal scheme utilizing resonance splitting of a dual-ring structure is proposed. Detailed design and simulation are presented, and a proof of concept structure is optimized to demonstrate an athermal resonator with resonance wavelength variation lower than 5 pm∕K within 30 K temperature range.
Integrated optics devices Wavelength filtering devices Coupled resonators Photonics Research
2014, 2(2): 02000071





