
Cheng Xi 1,2,3Peng Wang 1,2,3Xiao Li 1,2,3,†Zejin Liu 1,2,3,†
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha410073, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Pulsed Power Laser Technology, Changsha410073, China
3 Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of High Energy Laser Technology, Changsha410073, China
We report on a new scheme for efficient continuous-wave (CW) mid-infrared generation using difference frequency generation (DFG) inside a periodically poled lithium niobate (PPLN)-based optical parametric oscillator (OPO). The pump sources were two CW fiber lasers fixed at 1018 nm and 1080 nm. One worked as the assisted laser to build parametric oscillation and generate an oscillating signal beam while the other worked at low power (${\leqslant}3~\text{W}$) to induce DFG between it and the signal beam. The PPLN temperature was appropriately adjusted to enable OPO and DFG to synchronously meet phase-matching conditions. Finally, both low-power 1018 nm and 1080 nm pump beams were successfully converted to $3.1~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$ and $3.7~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$ idler beams, respectively. The conversion efficiencies of the 1018 nm and 1080 nm pumped DFG reached 20% and 15%, respectively, while their slope efficiencies reached 19.6% and 15%. All these data were comparable to the OPOs pumped by themselves and never realized before in traditional CW DFG schemes. The results reveal that high-efficiency frequency down-conversion can be achieved with a low-power near-infrared pump source.
difference frequency generation nonlinear wave mixing optical parametric oscillator High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2019, 7(4): 04000e67

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies, CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, C2N Marcoussis, 91460 Marcoussis, France
2 Thales Research and Technology France, 1 avenue Augustin Fresnel, 91120 Palaiseau, France
3 Université Paris Diderot, Sorbone Paris Cité, 75013 Paris, France
We introduce a nanoscale photonic platform based on gallium phosphide. Owing to the favorable material properties, peak power intensity levels of 50 GW/cm2 are safely reached in a suspended membrane. Consequently, the field enhancement is exploited to a far greater extent to achieve efficient and strong light–matter interaction. As an example, parametric interactions are shown to reach a deeply nonlinear regime, revealing cascaded four-wave mixing leading to comb generation and high-order soliton dynamics.
Kerr effect Nonlinear wave mixing Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Integrated optics materials Photonic crystals Microwaves Photonics Research
2018, 6(5): 05000B43
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Technology, University of Jinan, Jinan 250022, China
2 e-mail: sps_xiaw@ujn.edu.cn
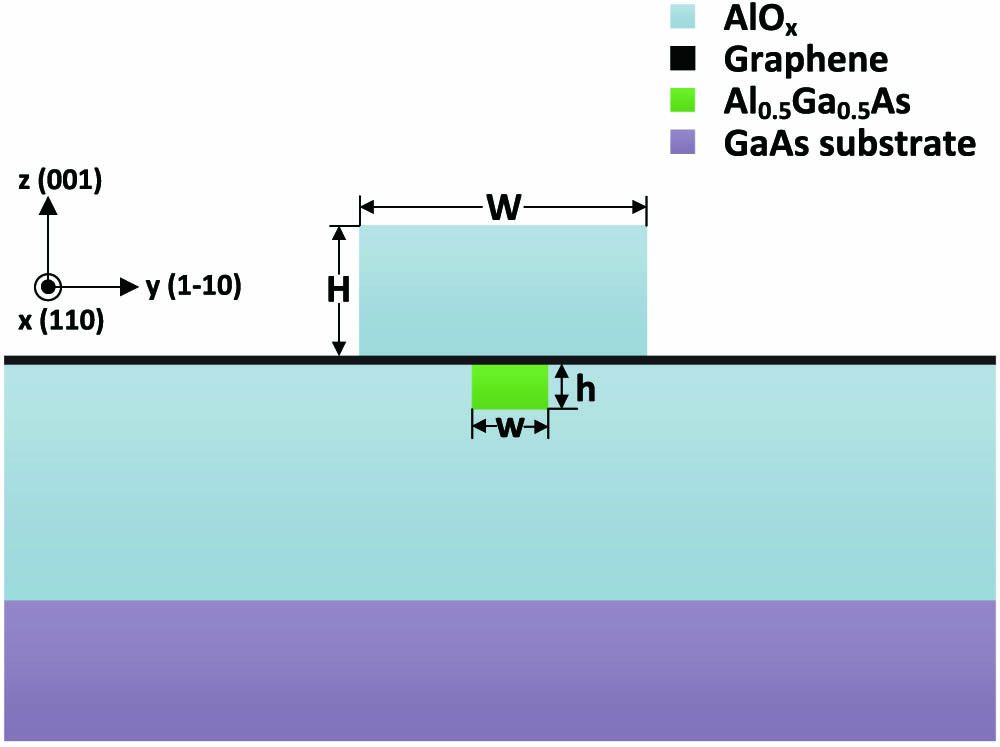
Graphene-based surface plasmon waveguides (SPWs) show high confinement well beyond the diffraction limit at terahertz frequencies. By combining a graphene SPW and nonlinear material, we propose a novel graphene/AlGaAs SPW structure for terahertz wave difference frequency generation (DFG) under near-infrared pumps. The composite waveguide, which supports single-mode operation at terahertz frequencies and guides two pumps by a high-index-contrast AlGaAs/AlOx structure, can confine terahertz waves tightly and realize good mode field overlap of three waves. The phase-matching condition is satisfied via artificial birefringence in an AlGaAs/AlOx waveguide together with the tunability of graphene, and the phase-matching terahertz wave frequency varies from 4 to 7 THz when the Fermi energy level of graphene changes from 0.848 to 2.456 eV. Based on the coupled-mode theory, we investigate the power-normalized conversion efficiency for the tunable terahertz wave DFG process by using the finite difference method under continuous wave pumps, where the tunable bandwidth can reach 2 THz with considerable conversion efficiency. To exploit the high peak powers of pulses, we also discuss optical pulse evolutions for pulse-pumped terahertz wave DFG processes.
Nonlinear wave mixing Surface plasmons Waveguides Semiconductor materials Photonics Research
2018, 6(3): 03000186
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory for Physical Electronics and Devices of the Ministry of Education & Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Information Photonic Technique, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
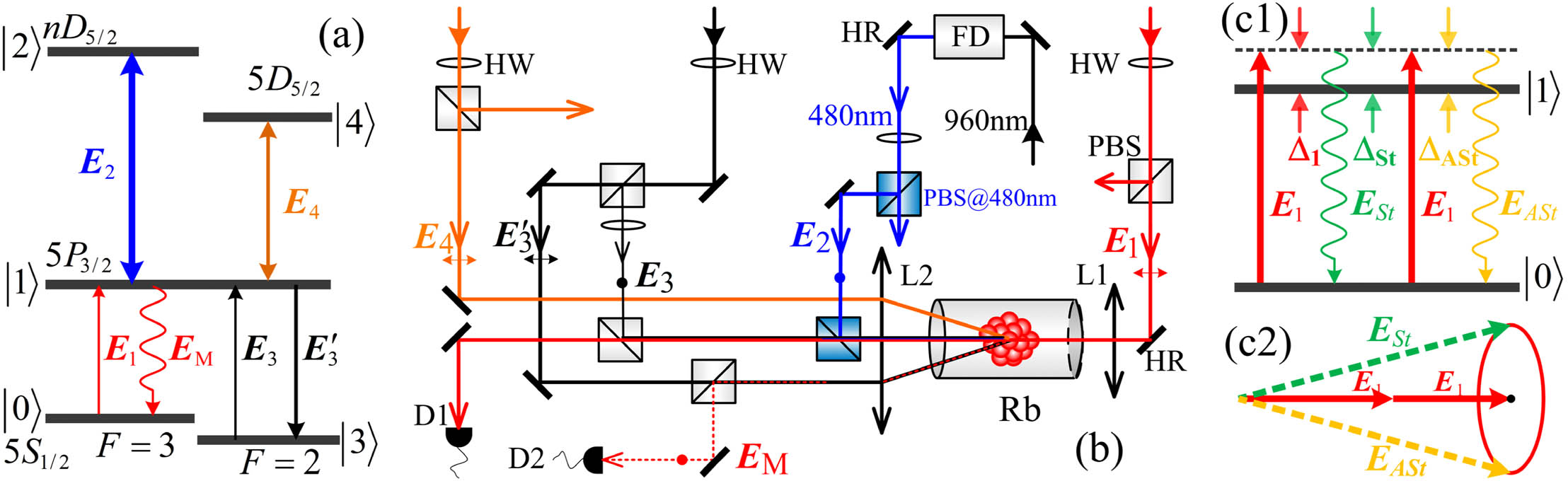
We study the parametric amplification of electromagnetically induced transparency-assisted Rydberg six- and eight-wave mixing signals through a cascaded nonlinear optical process in a hot rubidium atomic ensemble both theoretically and experimentally. The shift of the resonant frequency (induced by the Rydberg–Rydberg interaction) of parametrically amplified six-wave mixing signal is observed. Moreover, the interplays between the dressing effects and Rydberg–Rydberg interactions in parametrically amplified multiwave mixing signals are investigated. The linear amplification of Rydberg multiwave mixing processes with multichannel nature acts against the suppression caused by Rydberg–Rydberg interaction and dressing effect.
Rydberg states Nonlinear wave mixing Nonlinear optics, four-wave mixing Nonlinear optics, parametric processes Photonics Research
2018, 6(7): 07000713

Dexian Yan 1,2Yuye Wang 1,2,3,5,*Degang Xu 1,2,6,*Pengxiang Liu 1,2[ ... ]Jianquan Yao 1,2
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Precision Instrument and Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronics Information Technology, Tianjin University, Ministry of Education, Tianjin 300072, China
3 Institute of Neurosurgery, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing 400038, China
4 Department of Applied Physics, the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
5 e-mail: yuyewang@tju.edu.cn
6 e-mail: xudegang@tju.edu.cn
We have demonstrated a high-average-power, high-repetition-rate optical terahertz (THz) source based on difference frequency generation (DFG) in the GaSe crystal by using a near-degenerate 2 μm intracavity KTP optical parametric oscillator as the pump source. The power of the 2 μm dual-wavelength laser was up to 12.33 W with continuous tuning ranges of 1988.0–2196.2 nm/2278.4–2065.6 nm for two waves. Different GaSe cystal lengths have been experimentally investigated for the DFG THz source in order to optimize the THz output power, which was in good agreement with the theoretical analysis. Based on an 8 mm long GaSe crystal, the THz wave was continuously tuned from 0.21 to 3 THz. The maximum THz average power of 1.66 μW was obtained at repetition rate of 10 kHz under 1.48 THz. The single pulse energy amounted to 166 pJ and the conversion efficiency from 2 μm laser to THz output was 1.68×10 6. The signal-to-noise ratio of the detected THz voltage was 23 dB. The acceptance angle of DFG in the GaSe crystal was measured to be 0.16°.
Infrared and far-infrared lasers Nonlinear wave mixing Nonlinear optics, parametric processes Infrared, far Photonics Research
2017, 5(2): 02000082
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education), Department of Physics and Astronomy, IFSA Collaborative Innovation Centre, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
Back conversion is an intrinsic phenomenon in nonlinear frequency down-conversion processes. However, the physical reason for its occurrence is not well understood. Here, we theoretically reveal that back conversion is the result of a π-phase jump associated with the depletion of one interacting wave. By suppressing the idler phase jump through a deliberate crystal absorption, the back conversion can be inhabited, thus enhancing the conversion efficiency from the pump to the signal. The results presented in this Letter will further the understanding of nonlinear parametric processes and pave the way toward the design of highly efficient down-conversion systems.
190.4223 Nonlinear wave mixing 190.4975 Parametric processes 190.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 021901
1 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 中国科学技术大学中国科学院量子信息重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230026
针对惯性约束聚激光装置终端光学系统中使用的大口径超薄晶体的面形畸变,探索了一种低应力新型夹持方法——四周回形全紧固夹持法。从谐波转换模型和晶体准直两方面进行了分析,表明晶体面形畸变将降低三倍频效率和导致准直光斑弥散,并提出了晶体面形总畸变小于5 μm和晶体装夹畸变小于加工畸变的两项控制目标。再根据力学模型,设计了四周回形全紧固夹持法的精密装配结构,并对该结构进行了精密加工控制和有限元分析,以及实验验证。验证结果表明,利用低应力新型夹持方法,晶体装配后的总面形畸变小于5 μm,说明该方法能够满足晶体的面形畸变控制目标。
非线性光学 非线性波混频 惯性约束聚变 大口径超薄晶体 面形畸变 光机装配
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
We report the Hong–Ou–Mandel (HOM) interference, with visibility of 91%, produced from two independent single photons retrieved from collective atomic excitations in two separate cold-atom clouds with high optical depths of 90. The high visibility of the HOM dip is ascribed to the pure single photon in the Fock state that was generated from a dense-cold-atom cloud pumping by a short pulse. The visibility is always the same regardless of the time response of the single-photon detectors. This result experimentally shows that the single photons retrieved are in a separable temporal state with their idler photons.
020.4180 Multiphoton processes 190.4223 Nonlinear wave mixing 020.3320 Laser cooling 270.5565 Quantum communications Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(8): 080201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A compensation method for phase mismatch caused by temperature variation during the frequency conversion process is proposed and the theoretical model is established. The method is based on the principle that phase mismatch can be compensated via the electro-optic effect based on a compensation scheme consisting of two nonlinear crystals and an electro-optic crystal; further, a new dimension adjustment can be achieved by changing the voltage. In a proof-of-principle study, frequency conversion from 1053 nm to 526.5 nm and 351 nm by cascade KH2PO4 (KDP) and KD2PO4 (DKDP) crystals, respectively, is presented as an example. Three-dimensional numerical simulations are conducted to show that the conversion efficiency of frequency doubling and tripling varies with temperature. The results show that the temperature acceptance bandwidth of doubling and tripling can be 2.4 and 3.4 times larger, respectively, than that of the traditional method using a single crystal. We also analyze the stability of the conversion efficiency for 192 beams by our proposed method when the temperature is randomly varied within the range of 24°C–26°C. The standard deviation of the conversion efficiency of frequency doubling and tripling decreases from 1.25% and 6.61% to 0.18% and 0.56%, respectively. In addition, the influence of the reflection loss on the output efficiencies is also analyzed and the results show that it is very small. This indicates that this method may be effective in reducing the temperature sensitivity of conversion efficiency.
Lasers frequency doubled Harmonic generation and mixing Nonlinear wave mixing. Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2016, 14(1): 525

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 Key Laboratory for Laser Plasma (Ministry of Education), IFSA Collaborative Innovation Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Quantum Engineering Research Center, Beijing Institute of Aerospace Control Devices, CASC, Beijing 100094, China
In this Letter, we investigate a method for controlling the intensity of a light by another light in a periodically poled MgO-doped lithium niobate (PPMgLN) crystal with a transverse applied external electric field. The power of the emergent light can be modulated by the power ratio of the incident ordinary and extraordinary beams. The light intensity control is experimentally demonstrated by the Mach–Zehnder interference configuration, and the results are in good agreement with the theoretical predictions.
190.4223 Nonlinear wave mixing 230.6120 Spatial light modulators Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 121902





