2018, 16(9) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第16卷 第9期
Previous research shows that few-cycle laser (FCL) pulses with low energy and without a bias field can be used to coherently detect terahertz (THz) pulses. As we know, it is very difficult to stabilize the carrier envelope phase (CEP) of FCL pulses, i.e., there are some random fluctuations for the CEP. Here we theoretically investigate the influence of such instability on the accuracy of THz detection. Our results show that although there is an optimum CEP for THz detection, the fluctuations of the CEP will lead to terrible thorns on the detected THz waveform. In order to solve this problem, we propose an approach using two few-cycle laser pulses with opposite CEPs, i.e., their CEPs are differed by π .
040.2235 Far infrared or terahertz 320.7100 Ultrafast measurements Effects of mask-alignment error on point spread function for multi-level Fresnel diffractive lenses Download:721次
Download:721次
 Download:721次
Download:721次The full aperture complex amplitude transmittance function of a multi-level diffraction lens with mask-alignment errors was derived based on scalar diffraction theory. The point spread function (PSF) was calculated by the Kirchhoff diffraction integral. It is found that the radius of the Airy disk increases with the increase of the error in the direction of misalignment, and the image center shifts along the direction of misalignment. A four-level diffractive lens with a diameter of 80 mm was fabricated, and its PSF and diffraction efficiency of + 1
050.1380 Binary optics 050.1965 Diffractive lenses 110.3000 Image quality assessment An interferometric phase shift fiber Bragg grating sensing system with greatly reduced background phase noise Download:640次
Download:640次
 Download:640次
Download:640次We presented an interferometric phase shift fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensor, which inherited the advantages of FBG sensors, and, at the same time, the greatly reduced full-width-at-half-maximum bandwidth brought longer coherent length, higher sensitivity, and lower phase noise. Experiments show that at least a 7 dB reduction of phase noise can be achieved compared to FBG sensors interrogated by interferometer with the same optical path difference.
060.2310 Fiber optics 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Miniature optical fiber sensors with thin films as sensitive elements could open new fields for optical fiber sensor applications. Thin films work as sensitive elements and a transducer to get response and feedback from environments, in which optical fibers act as a signal carrier. A novel Ag coated intensity modulated optical fiber sensor based on refractive index changes using IR and UV-Vis (UV-visible) light sources is proposed. The sensor with an IR light source has higher sensitivity compared to a UV-Vis source. When the refractive index is enhanced to 1.38, the normalized intensity of IR and UV-Vis light diminishes to 0.2 and 0.8, respectively.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 310.6188 Spectral properties 120.4570 Optical design of instruments Broad bandwidth SOA-based multiwavelength laser incorporating a bidirectional Lyot filter Download:641次
Download:641次
 Download:641次
Download:641次We demonstrate a broad bandwidth multiwavelength laser based on a bidirectional Lyot filter and a semiconductor optical amplifier with a mechanism of intensity-dependent loss as the flatness agent. A wide bandwidth of a multiwavelength spectrum of 32.9 nm within a 5 dB uniformity is obtained under optimized polarization parameters. For this case, the number of generated lasing lines is 329 with a fixed wavelength separation of 0.1 nm. The power stability of this multiwavelength laser is less than 1.35 dB within 200 min time frame. This shows that the bidirectional Lyot filter provides an alternative option for multiwavelength generation in laser systems.
060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3510 Lasers, fiber 060.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers Comparative study on reduced impacts of Brillouin pump depletion and nonlinear amplification in coded DBA-BOTDA Download:704次
Download:704次
 Download:704次
Download:704次The impacts of Brillouin pump depletion and nonlinear amplification in coded long-range Brillouin optical time-domain analysis (BOTDA) based on distributed Brillouin amplification (DBA) were studied. The error of Brillouin frequency shift (BFS) due to Brillouin pump depletion was compared for DBA-BOTDA using non-cyclic and cyclic coding. For non-cyclic coding, significant over- and under-shoots of BFS were found in the range with larger BFS variation, such as hot spot. The impact of Brillouin pump depletion can be reduced considerably by cyclic coding. Furthermore, to compensate the BFS error due to nonlinear amplification, a simple and effective log linearization was proposed and demonstrated.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors The phase modulation characteristics of a reflective liquid crystal (LC) spatial light modulator (SLM) under oblique incidence are studied by using our proposed self-interference method. The experimental setup of the method is very simple and has good robustness to mechanical vibrations. By changing the gray value of the combined grayscale loaded on the LC-SLM, different sheared fringe patterns, generated by the interference between the constant phase-modulated beam and the +1-order diffracted beam of the blazed grating, can be obtained. The amount of phase modulation of the LC-SLM is obtained by subtracting the phase of the two side lobes in the frequency domain. By turning the turntable where the SLM is mounted, the phase modulation characteristics at different incident angles can be measured. The experimental results show that the phase modulation curves do not change significantly with the small angle. When the angle is large (i.e. larger than 10°), the phase modulation curves become different, especially for the high gray levels. With the increase of the incident angle, the phase modulation depth is reduced. The results indicate that the incident angle plays an important role in the performance of the phase modulation of an LC-SLM.
070.6120 Spatial light modulators 120.5060 Phase modulation 120.5050 Phase measurement We propose a novel on-line beam diagnostic method based on single-shot beam splitting phase retrieval. The incident beam to be measured is diffracted into many replicas by a Dammann grating and then propagates through a weakly scattering phase plate with a known structure; the exiting beams propagate along their original direction and form an array of diffraction patterns on the detector plane. By applying the intensity of diffraction patterns into an iterative algorithm and calculating between the grating plane, weakly scattering plane, and detector plane, the complex field of the incident beam can be reconstructed rapidly; the feasibility of this method is verified experimentally with wavelengths of 1053 and 632.8 nm.
100.5070 Phase retrieval 110.1650 Coherence imaging In this Letter, a pair of integrated optoelectronic transceiving chips is proposed. They are constructed by integrating a vertical cavity surface emitting laser unit above a positive-intrinsic-negative photodetector unit. One of the transceiving chips emits light at the wavelength of 848.1 nm with a threshold current of 0.8 mA and a slope efficiency of 0.81 W/A. It receives light between 801 and 814 nm with a quantum efficiency of higher than 70%. On its counterpart, the other one of the transceiving chips emits light at the wavelength of 805.3 nm with a threshold current of 1.1 mA and a slope efficiency of 0.86 W/A. It receives light between 838 and 855 nm with a quantum efficiency of higher than 70%. The proposed pair of integrated optoelectronic transceiving chips can work full-duplex with each other, and they can be applied to single fiber bidirectional optical interconnects.
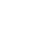
130.3120 Integrated optics devices 130.0250 Optoelectronics 250.7260 Vertical cavity surface emitting lasers We report 20 Gb/s transmission of four-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) signal using a directly modulated tunable distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser. Transmission distance over 20 km was achieved without using optical amplifiers and optical dispersion compensation modules. A wavelength tuning range of 11.5 nm and a 3 dB bandwidth greater than 10 GHz over the entire wavelength tuning range were obtained.
140.5960 Semiconductor lasers 250.5300 Photonic integrated circuits 140.3600 Lasers, tunable Ablation effects and mechanism of sintered silicon carbide ceramics by an ArF excimer laser Download:642次
Download:642次
 Download:642次
Download:642次The ablation of sintered silicon carbide ceramics by an ArF excimer laser was studied. Three zones are generated: the ablation zone that presented molten morphology and was composed by the Si and C phase; the condensation zone formed by vaporized SiC; and the oxidation zone that showed the characteristics of thermal oxidation. The ablation depth and oxidation range increase linearly with fluence and pulses within 0.5–4 J/cm2, but the normalized ablation efficiency is constant (3.60 ± 0.60 μm·mm2/J). The theoretical photochemical ablation depth supplies 25% of the total depth at 1 J/cm2 but decreases to 16% at 4 J/cm2. The ablation is dominated by the photothermal effect and conforms to the thermal evaporation mechanism.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 140.2180 Excimer lasers Mechanisms and absolute quantum yield of upconversion luminescence of fluoride phosphors Download:537次
Download:537次
 Download:537次
Download:537次Mechanisms of upconversion luminescence (UCL) of SrF 2 : Er G 4 11 / 2 → I 4 15 / 2 H 2 9 / 2 → I 4 15 / 2 F 4 5 / 2 → I 4 15 / 2 F 4 7 / 2 → I 4 15 / 2 H 2 11 / 2 → I 4 <
190.7220 Upconversion 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials Flexible and high-efficiency generation of arbitrary vector vortex beams on hybrid-order Poincaré sphere Download:710次
Download:710次
 Download:710次
Download:710次We propose theoretically and verify experimentally a compact optical configuration to directly generate arbitrary vector vortex beams on a hybrid-order Poincaré sphere with good flexibility and high efficiency based on a reflective phase-only liquid crystal spatial light modulator (LC-SLM). The conversion system, consisting of an LC-SLM and a quarter-wave plate, can be considered a flexible dielectric metasurface to simultaneously modulate inhomogeneous polarization and helical phase-front. This approach has some advantages, including a simple experimental setup, good flexibility, and high efficiency. Orthogonally polarized modes alignment and an explicit superposition existing in the conventional method are not necessary in the proposed method, which exhibits potential applications in many advanced domains.
260.5430 Polarization 050.4865 Optical vortices The point-spread function of an optical system determines its optical resolution for both spatial and temporal imaging. For spatial imaging, it is given by a Fourier transform of the pupil function of the system. For temporal imaging based on nonlinear optical processes, such as sum-frequency generation or four-wave mixing, the point-spread function is related to the waveform of the pump wave by a nonlinear transformation. We compare the point-spread functions of three temporal imaging schemes: sum-frequency generation, co-propagating four-wave mixing, and counter-propagating four-wave mixing, and demonstrate that the last scheme provides the best temporal resolution. Our results are valid for both quantum and classical temporal imaging.
270.5585 Quantum information and processing 110.6915 Time imaging Design of double-zone aspheric diffractive intraocular lens with extended depth of focus Download:820次
Download:820次
 Download:820次
Download:820次A double-zone aspheric diffractive intraocular lens (IOL) was designed and manufactured aiming to regain a continuous range of clear vision for pseudophakic presbyopia. After obtaining the IOL structure parameters through optimization based on an aphakic model eye, its imaging performances were analyzed in the model eye. The modulation transfer function at 50 cycles / mm ± 5 °
330.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices 220.2740 Geometric optical design 330.7323 Visual optics, aging changes 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦