1 华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院,湖北 武汉 430074
2 华中科技大学物理学院,湖北 武汉 430074
3 华中科技大学武汉光电国家研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
4 湖北光谷实验室,湖北 武汉 430074
超短超强激光脉冲驱动的高次谐波是一种极紫外到软X射线波段的光源,具有指向性好、时空相干性高、亮度高等优点。高次谐波不但是在阿秒时间尺度上研究电子动力学的基础,而且其各类技术优点也使之成为一种有效的桌面型极紫外相干光源,在集成电路制造在线检测、材料科学、生物医药等领域中具有广泛应用。然而,受限于传统钛蓝宝石固体飞秒激光的平均功率和高次谐波传播过程中的转换效率,目前高次谐波极紫外光源的平均功率亟待提高。介绍了高重复频率、高平均功率高次谐波极紫外光源的产生方式及其应用。首先介绍了光纤、固体、啁啾光学参量放大器等新型高重复频率、高平均功率飞秒激光驱动源在高次谐波产生方面的研究进展,之后讨论了激光高次谐波在弱电离气体介质中的宏观传播效应和相位匹配条件。在此基础上,介绍了高平均功率高次谐波极紫外光源在成像检测方面的应用。
非线性光学 高次谐波 极紫外光源 飞秒激光器 极紫外成像检测

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics and School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Hubei Key Laboratory of Optical Information and Pattern Recognition, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan 430205, China
We demonstrate a deep-learning neural network (DNN) method for the measurement of molecular alignment by using the molecular-alignment-based cross-correlation polarization-gating frequency resolved optical gating (M-XFROG) technique. Our network has the capacity for direct measurement of molecular alignment from the FROG traces. In a proof-of-principle experiment, we have demonstrated our method in molecules. With our method, the molecular alignment factor (t) of , impulsively excited by a pump pulse, was directly reconstructed. The accuracy and validity of the reconstruction have been verified by comparison with the simulations based on experimental parameters.
molecular alignment deep-learning neural network M-XFROG Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(12): 120021
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics and School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Optics Valley Laboratory, Wuhan 430074, China
We propose and numerically demonstrate a simple and background-free all-optical chiral spectroscopy technique for gas molecules. Our approach is based on high harmonic generation driven by a new type of laser beam that is produced by one linearly polarized single-color beam passing through a lens and a prism. It is shown that chiral and achiral signals are completely separated in frequency, indicating strong background-free and highly sensitive chirality detection. We believe this all-optical method can open new opportunities for ultrafast detection for chiral dynamics in the femtoseond to attosecond time scale.
high harmonic generation strong-field chiral spectroscopy selection rule Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(10): 100004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Infrared Materials and Devices, Research Institute of Advanced Technologies, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
2 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics and School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
3 Laser Physics Center, Research School of Physics, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 2601, Australia
4 Science Program, Texas A&M University at Qatar, Doha 23874, Qatar
The nonlinear Talbot effect is a near-field nonlinear diffraction phenomenon in which the self-imaging of periodic objects is formed by the second harmonics of the incident laser beam. We demonstrate the first, to the best of our knowledge, example of nonlinear Talbot self-healing, i.e., the capability of creating defect-free images from faulty nonlinear optical structures. In particular, we employ the tightly focused femtosecond infrared optical pulses to fabricate nonlinear photonic crystals and show that the defects in the form of the missing points of two-dimensional square and hexagonal periodic structures are restored in the second harmonic images at the first nonlinear Talbot plane. The observed nonlinear Talbot self-healing opens up new possibilities for defect-tolerant optical lithography and printing.
nonlinear Talbot effect nonlinear photonic crystal periodically poled LiNbO3 second harmonic generation self-healing Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(6): 060011

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics and School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Hubei Key Laboratory of Optical Information and Pattern Recognition, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan 430205, China
We investigate the Airy–Talbot effect of an Airy pulse train in time-dependent linear potentials. The parabolic trajectory of self-imaging depends on both the dispersion sign and the linear potential gradient. By imposing linear phase modulations on the pulse train, the Airy–Talbot effects accompanied with positive and negative refractions are realized. For an input composed of stationary Airy pulses, the self-imaging follows straight lines, and the Airy–Talbot distance can be engineered by varying the linear potential gradient. The effect is also achieved in symmetric linear potentials. The study provides opportunities to control the self-imaging of aperiodic optical fields in time dimension.
Airy pulse Talbot and self-imaging effect dispersion linear potential Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(8): 082601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan 430205, China
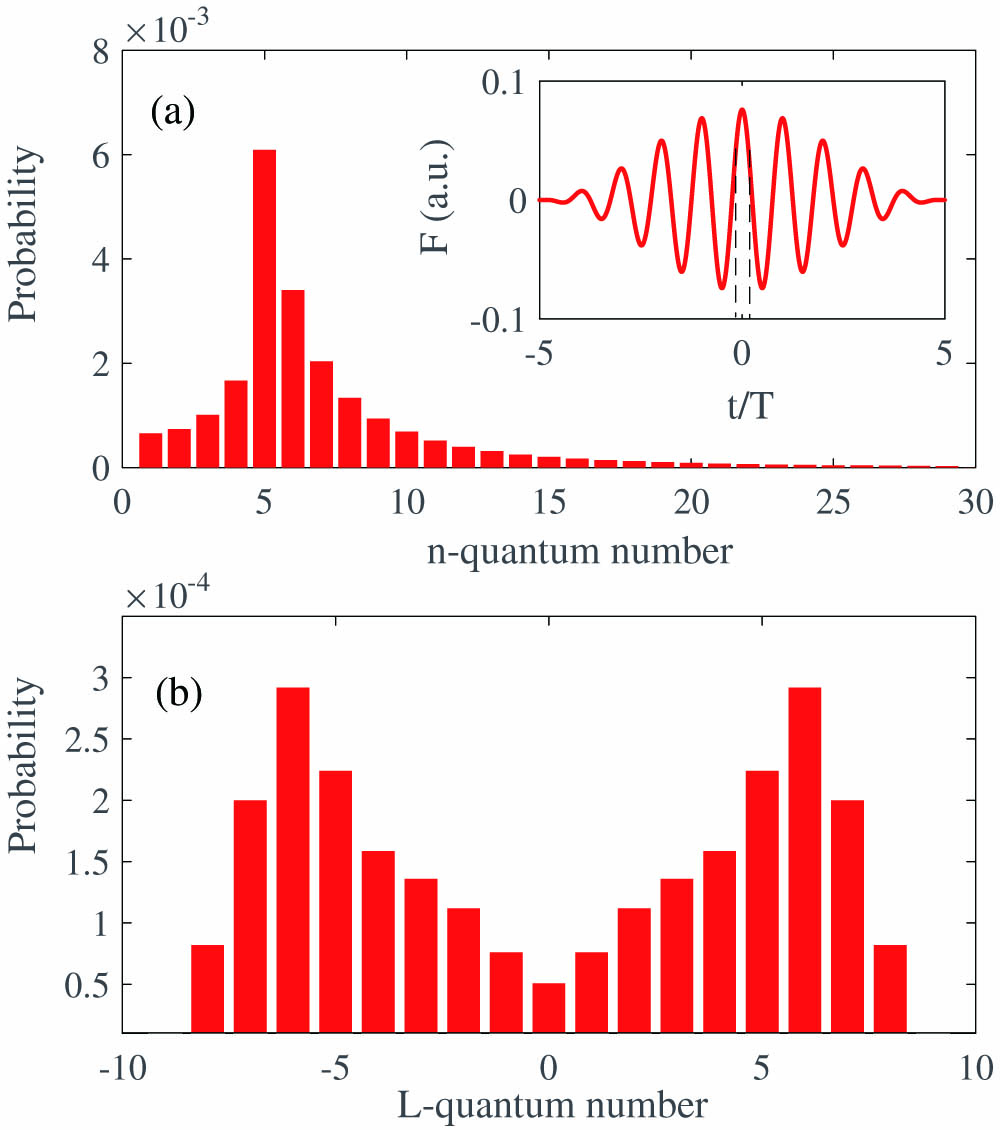
Using the classical-trajectory Monte Carlo model, we have theoretically studied the angular momentum distribution of frustrated tunneling ionization (FTI) of atoms in strong laser fields. Our results show that the angular momentum distribution of the FTI events exhibits a double-hump structure. With this classical model, we back traced the tunneling coordinates, i.e., the tunneling time and initial transverse momentum at tunneling ionization. It is shown that for the events tunneling ionized at the rising edge of the electric field, the final angular momentum exhibits a strong dependence on the initial transverse momentum at tunneling. While for the events ionized at the falling edge, there is a relatively harder recollision between the returning electron and the parent ion, leading to the angular momentum losing the correlation with the initial transverse momentum. Our study suggests that the angular momentum of the FTI events could be manipulated by controlling the initial coordinates of the tunneling ionization.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 020.4180 Multiphoton processes 320.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 040202
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
3 School of Physics and Information Engineering, Jianghan University, Wuhan 430056, China
The temporal evolution of Nd:YAG laser-produced Sn plasma in atmospheric pressures from 5 to 104 Pa is investigated. The results show that the extreme ultraviolet radiation exists only at the beginning of the expansion process for 20 ns. The maximum temperature of 18.7 eV and density of 9.6×1017 cm 3 are measured at 73 ns. The effects of air pressure and laser energy on the process of plasma expansion are investigated. The results indicate that the air pressure has an inhibitory effect on kinetic energy, while the electron density and temperature increase with air pressure.
Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(Suppl): S21413
1 华中科技大学 武汉光电国家实验室, 武汉 430074
2 武汉工程大学 理学院, 武汉 430205
采用正交放置的两路CCD,基于图像采集及处理的方法,建立了极紫外光源锡液滴靶发生装置的锡液滴检测系统,可以实时监测锡液滴的运动状态及稳定性。对本实验室频率为34 kHz的锡靶发生器产生的液滴进行了锡液滴监测实验。监测结果显示,锡液滴直径约为137 μm,平均间距为375 μm,稳定性较好,并对水平面上横向稳定性进行了分析。
极紫外光源 激光等离子体 锡液滴靶 稳定性 extreme ultraviolet source laser plasma photosource tin droplet stability 强激光与粒子束
2014, 26(12): 121005
1 华中科技大学光电子科学与工程学院, 武汉光电国家实验室, 湖北 武汉430074
2 武汉工程大学理学院, 湖北 武汉430074
研究了不同条件下脉冲放电CO2激光烧蚀平板锡靶产生的等离子体极紫外辐射特性, 设计并建立了一套掠入射极紫外平焦场光栅光谱仪, 结合X射线CCD探测了光源在6.5~16.8 nm波段的时间积分辐射光谱, 得到了极紫外光谱随激光脉宽, 入射脉冲能量及背景气压的变化规律。 实验结果发现: 入射激光脉冲能量在30~600 mJ变化时, 极紫外辐射光谱的强度随辐照激光脉冲能量的增加而增加, 但并不是线性关系, 具有饱和效应, 且产生极紫外辐射的脉冲能量阈值约为30 mJ, 当激光脉冲能量为425 mJ时具有最高的转换效率, 此时中心波长13.5 nm处2%带宽内的转换效率约为1.2%。 激光脉冲半高全宽在50~120 ns范围内变化时, 极紫外辐射光谱的峰值位置均位于13.5 nm, 光谱形状几乎没有什么变化, 但是脉宽从120 ns变到52 ns后, 由于激光功率密度的提高, 极紫外辐射强度也随之增强了约1.6倍。 极紫外光谱的强度随背景气压的增大而迅速下降, 当腔内空气气压为200 Pa时, 极紫外辐射光子几乎被全部吸收, 而当缓冲氦气气压为7×104 Pa时, 仍能够探测到微弱的极紫外辐射信号, 计算表明100 Pa的空气对13.5 nm极紫外光的吸收系数为3.0 m-1, 而100 Pa的He气的吸收系数为0.96 m-1。
激光等离子体 极紫外辐射 CO2激光 缓冲气体 Laser plasma EUV emission CO2 laser Buffer gas 光谱学与光谱分析
2012, 32(7): 1729





