1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所精密光学制造与检测中心,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心,北京 100049
首先基于一维双温模型阐明了飞秒激光与RB-SiC表面的相互作用过程,并在此基础上,开展了RB-SiC表面飞秒激光烧蚀规律与抛光工艺研究。结果表明,通过改变脉冲能量、扫描速度、扫描间距等参数,可实现对烧蚀深度和烧蚀表面质量的有效调控。但是通过飞秒激光抛光难以在RB-SiC切割表面上获得较高的表面质量,而对于RB-SiC预抛光表面,通过工艺参数调控,可将其表面粗糙度从36.9 nm抛光至11.56 nm,验证了飞秒激光抛光RB-SiC的可行性。
激光技术 粗糙度 反应烧结碳化硅 飞秒激光抛光 双温模型 中国激光
2023, 50(24): 2402203
1 武汉邮电科学研究院,武汉 430074
2 Molex有限公司,武汉 430074
现如今处于第五代移动通信技术(5G)网络发展建设的重要阶段,前传网建设中带宽需求大、光模块成本高和铺设难度大等问题亟待解决。已知四通道小型可插拔(QSFP)封装具有4个通道,而传统的QSFP28 50 Gbit/s光模块设计方案只使用了其中的两个通道。文章选用比QSFP封装更小的小型可插拔(SFP)封装制成50 Gbit/s光模块,底面积减小了40.5%,体积减小了52.2%,功耗减少了42.1%,传输相同距离光模块成本减少了73.4%。使用4阶脉冲幅度调制(PAM4)技术实现25 Gbit/s光器件传输50 Gbit/s信号,达成了单波长速率翻倍。通过对比测试,常温发射机色散眼图闭合四相(TDECQ)减小了20.5%,灵敏度提高了0.6 dB,且其余各项参数均满足电气与电子工程师协会(IEEE)802.3cd中50 GE以太网的相关要求,能够稳定进行40 km信息传输。
4阶脉冲幅度调制 发射机色散眼图闭合四相 直调激光器 外调激光器 PAM4 TDECQ directly modulated lasers external modulated laser
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所精密光学制造与检测中心, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所薄膜光学实验室, 上海 201800
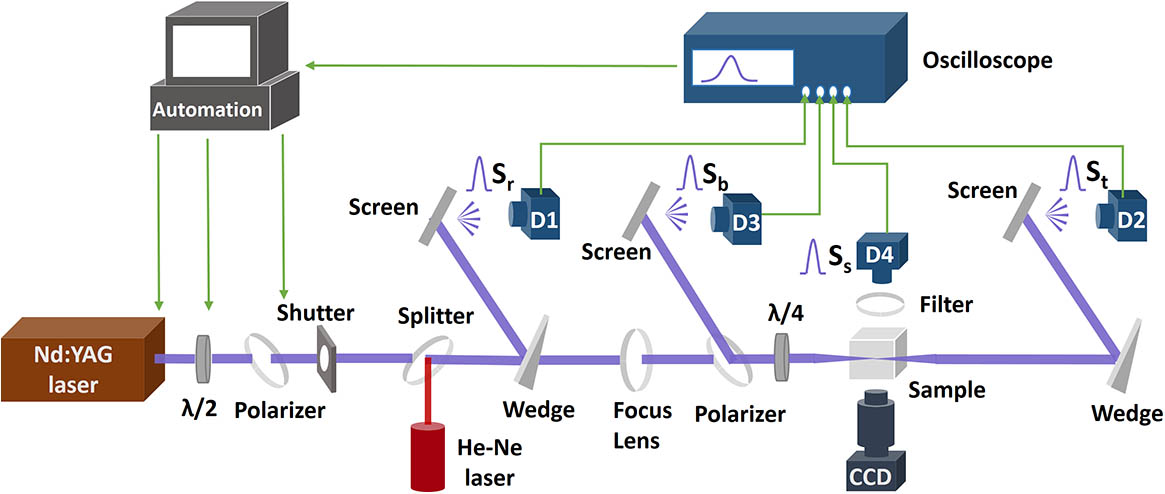
利用时间分辨激光光度计实时测量纳秒脉冲激光诱导熔石英体损伤过程中的透射、反射和散射变化量;通过在同一区域多次动态测量直至损伤产生,获得了多脉冲累积破坏的时间分辨过程。结果表明:在损伤出现前的脉冲辐照过程中,熔石英透过率已明显下降,后向反射率同步上升,甚至可达70%;后向反射率的上升量与透过率的损失量几乎相同;在多脉冲辐照过程中,只要脉冲辐照中出现后向反射,就会产生损伤;受激布里渊散射对多脉冲诱导熔石英体损伤具有促进作用。
激光光学 激光损伤 激光材料 光学性质 熔石英
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Thin Film Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
A time-resolved high-power laser photometer, which measures the real-time variations of transmission, internal reflection, and scattering simultaneously with picosecond time resolution, was developed to investigate the material response sequence during high-power nanosecond laser irradiation in thick fused silica. It was found that the transient transmission decreased sharply, accompanied by an increase in internal reflection at the rising edge of the laser pulse. The transient transmission recovered, while laser damage did not occur, but it did not recover if the scattering increased, indicating the occurrence of laser damage. The reason for the sharp decrease of transmission and the relationship between the transmission drop and laser damage were discussed.
160.4760 Optical properties 140.3330 Laser damage 160.3380 Laser materials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 051601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
To reveal the physical mechanism of laser ablation and establish the prediction model for figuring the surface of fused silica, a multi-physical transient numerical model coupled with heat transfer and fluid flow was developed under pulsed CO2 laser irradiation. The model employed various heat transfer and hydrodynamic boundary and thermomechanical properties for assisting the understanding of the contributions of Marangoni convention, gravitational force, vaporization recoil pressure, and capillary force in the process of laser ablation and better prediction of laser processing. Simulation results indicated that the vaporization recoil pressure dominated the formation of the final ablation profile. The ablation depth increased exponentially with pulse duration and linearly with laser energy after homogenous evaporation. The model was validated by experimental data of pulse CO2 laser ablation of fused silica. To further investigate laser beam figuring, local ablation by varying the overlap rate and laser energy was conducted, achieving down to 4 nm homogenous ablation depth.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 140.3470 Lasers, carbon dioxide 220.5450 Polishing 140.3538 Lasers, pulsed Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 041401
1 中国科学院 上海光学精密机械研究所 中国科学院强激光材料重点实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
针对晶体表面的损伤特性,采用小光斑扫描激光预处理技术预辐照DKDP晶体元件,并采用表面损伤自动探测系统实时分析每个脉冲辐照后晶体表面的损伤情况,比较预处理和未预处理区域的损伤点密度确定表面预处理效果,并进一步模拟分析表面各类缺陷在纳秒强激光辐照下的动态过程,解释激光预处理对精抛表面提升作用的微观机制并分析它对粗抛表面提升不明显的原因。实验结果表明,激光预处理技术对粗抛表面的提升作用并不明显,但是可以大幅度抑制精抛表面的损伤点密度。在本文的实验条件下,晶体表面的抗激光损伤能力可以提升约60%。比较体材料和精抛表面的预处理效果发现: 当体材料的抗破坏能力通过预处理提升后,精抛表面的抗激光损伤能力也会提升,由此可见精抛表面的激光预处理效果与体材料性能相关。
激光损伤 激光预处理 损伤阈值 预处理效果 氘化磷酸二氢钾(DKDP) laser damage laser conditioning damage threshold laser conditioning effects dopted deuterium KDP (DKDP)
光纤通信技术和网络国家重点实验室 武汉邮电科学研究院,湖北 武汉 430074
与传统光网络相比,光分组交换(OPS)网络具有高速、大吞吐量、低时延和能高效地承载IP业务等突出优点。而作为支撑下一代Internet发展的最有希望的骨干光网络,OPS网与传输控制协议/互联网协议(TCP/IP)的兼容性和支持度是一个值得深入研究的课题。文章以光突发交换(OBS)网为模型,对OPS网络中的TCP传输性能进行了研究。
光分组交换 光突发交换 TCP传输性能 OPS OBS TCP transmission performance





